Summary: Researchers report a healthy diet, regular exercise and a normal BMI can help protect against the build up of proteins associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Source: UCLA.
A study by researchers at UCLA’s Semel Institute for Neuroscience and Human Behavior has found that a healthy diet, regular physical activity and a normal body mass index can reduce the incidence of protein build-ups that are associated with the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
In the study, 44 adults ranging in age from 40 to 85 (mean age: 62.6) with mild memory changes but no dementia underwent an experimental type of PET scan to measure the level of plaque and tangles in the brain. Researchers also collected information on participants’ body mass index, levels of physical activity, diet and other lifestyle factors. Plaque, deposits of a toxic protein called beta-amyloid in the spaces between nerve cells in the brain; and tangles, knotted threads of the tau protein found within brain cells, are considered the key indicators of Alzheimer’s.
The study found that each one of several lifestyle factors — a healthy body mass index, physical activity and a Mediterranean diet — were linked to lower levels of plaques and tangles on the brain scans. (The Mediterranean diet is rich in fruits, vegetables, legumes, cereals and fish and low in meat and dairy, and characterized by a high ratio of monounsaturated to saturated fats, and mild to moderate alcohol consumption.)
“The fact that we could detect this influence of lifestyle at a molecular level before the beginning of serious memory problems surprised us,” said Dr. David Merrill, the lead author of the study, which appears in the September issue of the American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
Earlier studies have linked a healthy lifestyle to delays in the onset of Alzheimer’s. However, the new study is the first to demonstrate how lifestyle factors directly influence abnormal proteins in people with subtle memory loss who have not yet been diagnosed with dementia, Merrill said. Healthy lifestyle factors also have been shown to be related to reduced shrinking of the brain and lower rates of atrophy in people with Alzheimer’s.
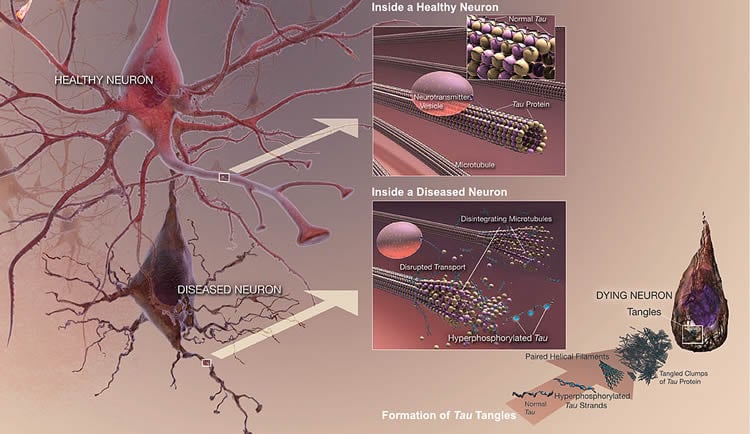
Older age is the No. 1 non-modifiable risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease, which affects an estimated 5.2 million people in the United States and results in more than $200 billion in health care costs annually.
“The study reinforces the importance of living a healthy life to prevent Alzheimer’s, even before the development of clinically significant dementia,” Merrill said. “This work lends key insight not only into the ability of patients to prevent Alzheimer’s disease, but also physicians’ ability to detect and image these changes.”
The next step in the research will be to combine imaging with intervention studies of diet, exercise and other modifiable lifestyle factors, such as stress and cognitive health, Merrill said.
Merrill sees patients with cognitive problems, particularly memory loss, at the UCLA Psychiatry Cognitive Health Clinic and Research Program.
Funding: The research was funded by National Institutes of Health (MH077650, AT003480, P01-AG024831, AG13308, P50 AG 16570, MH/AG58156, AG10123 and M01-RR00865), the Department of Energy (DE-FC03-87-ER60615), the Larry L. Hillblom Foundation, the Fran and Ray Stark Foundation Fund for Alzheimer’s Disease Research, the Ahmanson Foundation, the Lovelace Foundation, the National Science Foundation, UCLA’s Claude D. Pepper Older Americans Independence Center funded by the National Institute on Aging (5P30AG028748), the American Federation of Aging Research, the John A. Hartford Foundation and the Centers of Excellence National Program, and the NIH/National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences UCLA CTSI (UL1TR000124).
Source: Roxanne Moster – UCLA
Image Source: This NeuroscienceNews.com image is in the public domain. Credit: NIH/NIA.
Original Research: The study will appear in American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry.
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]UCLA. “Exercise and Diet Can Reduce Build Up of Protein Linked to Alzheimer’s.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 16 August 2016.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/tau-alzheimers-exercise-diet-4856/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]UCLA. (2016, August 16). Exercise and Diet Can Reduce Build Up of Protein Linked to Alzheimer’s. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved August 16, 2016 from https://neurosciencenews.com/tau-alzheimers-exercise-diet-4856/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]UCLA. “Exercise and Diet Can Reduce Build Up of Protein Linked to Alzheimer’s.” https://neurosciencenews.com/tau-alzheimers-exercise-diet-4856/ (accessed August 16, 2016).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Balanced translocation linked to psychiatric disorder, glutamate, and cortical structure/function
Rare genetic variants of large effect can help elucidate the pathophysiology of brain disorders. Here we expand the clinical and genetic analyses of a family with a (1;11)(q42;q14.3) translocation multiply affected by major psychiatric illness and test the effect of the translocation on the structure and function of prefrontal, and temporal brain regions. The translocation showed significant linkage (LOD score 6.1) with a clinical phenotype that included schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, and recurrent major depressive disorder. Translocation carriers showed reduced cortical thickness in the left temporal lobe, which correlated with general psychopathology and positive psychotic symptom severity. They showed reduced gyrification in prefrontal cortex, which correlated with general psychopathology severity. Translocation carriers also showed significantly increased activation in the caudate nucleus on increasing verbal working memory load, as well as statistically significant reductions in the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex glutamate concentrations. These findings confirm that the t(1;11) translocation is associated with a significantly increased risk of major psychiatric disorder and suggest a general vulnerability to psychopathology through altered cortical structure and function, and decreased glutamate levels.
“Balanced translocation linked to psychiatric disorder, glutamate, and cortical structure/function” by Pippa A Thomson, Barbara Duff, Douglas H R Blackwood, Liana Romaniuk, Andrew Watson, Heather C Whalley, Xiang Li, Maria R Dauvermann, T William J Moorhead, Catherine Bois, Niamh M Ryan, Holly Redpath, Lynsey Hall, Stewart W Morris, Edwin J R van Beek, Neil Roberts, David J Porteous, David St. Clair, Brandon Whitcher, John Dunlop, Nicholas J Brandon, Zoë A Hughes, Jeremy Hall, Andrew McIntosh and Stephen M Lawrie in Schizophrenia. Published online August 10 2016 doi:10.1038/npjschz.2016.24