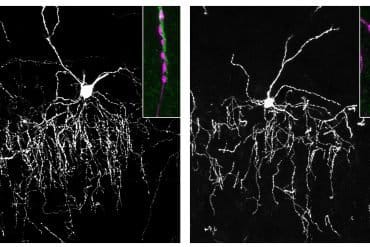
Summary: Vaping e-cigarettes modulates the oral microbiome and increases the abundance of pathobionts. The aerosols in vaping products alter the host response, prompting gum inflammation and making epithelial cells in the mouth susceptible to infection.
Source: NYU
Using e-cigarettes alters the mouth’s microbiome—the community of bacteria and other microorganisms—and makes users more prone to inflammation and infection, finds a new study led by researchers at NYU College of Dentistry.
The study—published in iScience, a Cell Press journal—is the first to demonstrate that vaping changes the oral microbiome and adds to our limited understanding of the safety profile of e-cigarettes.
The mouth is a gateway to the body and harbors many microbial species that colonize our respiratory and digestive tracts. It is well established that smoking traditional cigarettes raises the risk of gum disease and infection by bringing about physiological and structural changes, fostering an environment in which certain infection-causing bacteria flourish and contributing to immune dysfunction.
E-cigarettes—handheld devices in which nicotine is inhaled in a vapor—are thought to be less harmful than cigarettes, but little research (and no long-term data) exist on the safety of e-cigarettes. While vaping has quickly grown in popularity in recent years, a growing number of people are falling ill or dying from vaping-related illnesses.
“Given the popularity of vaping, it is critical that we learn more about the effects of e-cigarette aerosols on the oral microbiome and host inflammatory responses in order to better understand the impact of vaping on human health,” said Xin Li, Ph.D., associate professor of basic science and craniofacial biology at NYU College of Dentistry and the study’s co-senior author.
“The oral microbiome is of interest to us because research shows that changes in its microbial community as a result of environmental and host factors contribute to a range of health issues, including cavities, gum disease, halitosis, and medical conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancers,” said Deepak Saxena, Ph.D., professor of basic science and craniofacial biology at NYU College of Dentistry and the study’s co-senior author.
In this study, Li, Saxena, and their colleagues examined e-cigarette vapor and its influence on the oral microbiome and immune health. They also evaluated how vaping influences infection efficiency of oral pathogens in cell lines using a novel e-cigarette aerosol generating machine and measured pro-inflammatory immune mediators.

Through oral exams and saliva samples, the researchers studied the oral microbiome of 119 human participants from three groups: e-cigarette users, regular cigarette smokers, and those who had never smoked. Gum disease or infection was significantly higher among cigarette smokers (72.5 percent), followed by e-cigarette users (42.5 percent) and non-smokers (28.2 percent).
Using 16S rRNA high throughput sequencing, a technique used to profile microbial communities, the researchers observed different microorganisms in the saliva of e-cigarette users, cigarette smokers, and non-smokers. For instance, e-cigarette users had an abundance of Porphyromonas bacteria, while an increase in Veillonella bacteria was found in both e-cigarette and cigarette users.
“The predominance of these periodontal pathogens in the mouths of e-cigarette users and traditional smokers is a reflection of compromised periodontal health,” said Li.
The researchers also found that the altered microbiome in e-cigarette users influenced the local host immune environment compared to non-smokers and cigarette smokers. IL-6 and IL1β—cytokines involved in inflammatory responses—were highly elevated in e-cigarette users. Cell studies also showed upregulation of IL-6 after exposure to e-cigarette aerosols, resulting in an elevated inflammatory response. Moreover, e-cigarette aerosols made cells prone to bacterial infection, which points to a greater risk for infection in e-cigarette users.
“Our study suggests that vaping electronic cigarettes causes shifts in the oral environment and highly influences the colonization of complex microbial biofilms, which raises the risk for oral inflammation and infection,” said Saxena.
Source:
NYU
Media Contacts:
Rachel Harrison – NYU
Image Source:
The image is in the public domain.
Original Research: Open access
“Electronic Cigarette Aerosol Modulates the Oral Microbiome and Increases Risk of Infection”. Smruti Pushalkar et al.
iScience doi:10.1016/j.isci.2020.100884.
Abstract
Electronic Cigarette Aerosol Modulates the Oral Microbiome and Increases Risk of Infection
Highlights
• E- cigarette vapors contain high nicotine concentration and other toxic compounds
• E-cigarette modulates oral microbiome and increases the abundance of oral pathobionts
• E-cigarette aerosol alters host response and promotes gum inflammation
• E-cigarette aerosol exposure makes epithelial cells susceptible to infection
Summary
The trend of e-cigarette use among teens is ever increasing. Here we show the dysbiotic oral microbial ecology in e-cigarette users influencing the local host immune environment compared with non-smoker controls and cigarette smokers. Using 16S rRNA high-throughput sequencing, we evaluated 119 human participants, 40 in each of the three cohorts, and found significantly altered beta-diversity in e-cigarette users (p = 0.006) when compared with never smokers or tobacco cigarette smokers. The abundance of Porphyromonas and Veillonella (p = 0.008) was higher among vapers. Interleukin (IL)-6 and IL-1β were highly elevated in e-cigarette users when compared with non-users. Epithelial cell-exposed e-cigarette aerosols were more susceptible for infection. In vitro infection model of premalignant Leuk-1 and malignant cell lines exposed to e-cigarette aerosol and challenged by Porphyromonas gingivalis and Fusobacterium nucleatum resulted in elevated inflammatory response. Our findings for the first time demonstrate that e-cigarette users are more prone to infection.