Summary: Mitochondria regulate how neural stem cells become neurons during brain development. The findings may help explain how humans developed larger brains during evolution and how mitochondrial defects lead to some neurodevelopmental disorders.
Source: VIB
Mitochondria are small organelles that provide the energy critical for each cell in our body, in particular in the high fuel-consuming brain. In this week’s edition of Science, a Belgian team of researchers led by Pierre Vanderhaeghen (VIB-KU Leuven, ULB) finds that mitochondria also regulate a key event during brain development: how neural stem cells become nerve cells. Mitochondria influence this cell fate switch during a precise period that is twice as long in humans compared to mice. The seminal findings highlight an unexpected function for mitochondria that may help explain how humans developed a bigger brain during evolution, and how mitochondrial defects lead to neurodevelopmental diseases.
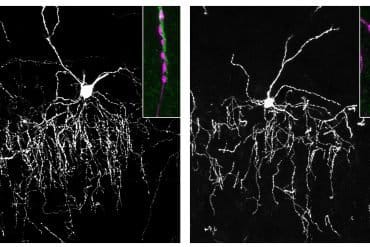
Our brains are made up of billions of incredibly diverse neurons. They first arise in the developing brain when stem cells stop self-renewing and differentiate into a particular type of neuron. This process, called neurogenesis, is precisely regulated to give rise to the enormous complex structure that is our brain. It is thought that small differences in the way neural stem cells generate neurons are at the origin of the dramatic increase in the size and complexity of our brain.
To gain insight in this complex process, prof. Pierre Vanderhaeghen (VIB-KU Leuven, ULB) and his colleagues examined the mitochondria, small organelles that provide energy in every cell in the body, including the developing brain.
“Diseases caused by defects in mitochondria lead to developmental problems in many organs, in particular the brain,” explains Vanderhaeghen, a specialist in stem cell and developmental neurobiology. “We used to think that this was related to the crucial function of mitochondria to provide energy to the cells, but this is only part of the story: recent work in stem cells suggests that mitochondria have a direct influence on organ development. We have tested whether and how this could be the case in the brain.”
Fission and fusion
Together with his team, he explored whether and how mitochondrial remodeling is coupled with neuronal fate commitment during neurogenesis. “Mitochondria are highly dynamic organelles, that can join together (fusion) or split up (fission), and we know these dynamics are associated with fate changes in various types of stem cells,” says Vanderhaeghen.
Ryohei Iwata, a postdoctoral researcher in the Vanderhaeghen lab, developed a new method to watch mitochondria in great detail as the neural stem cells are ‘caught in the act’ to become neurons. “We found that shortly after stem cells divide, the mitochondria in daughter cells destined to self-renew will fuse, while those in daughter cells that become neurons show high levels of fission instead,” says Ryohei Iwata.
But this was not just a coincidence: indeed, the researchers could show that increased mitochondrial fission in fact promotes differentiation to a neuronal fate, while mitochondrial fusion after mitosis redirects daughter cells towards self-renewal.
Time window
So mitochondrial dynamics are important to become a neuron–but there is more.
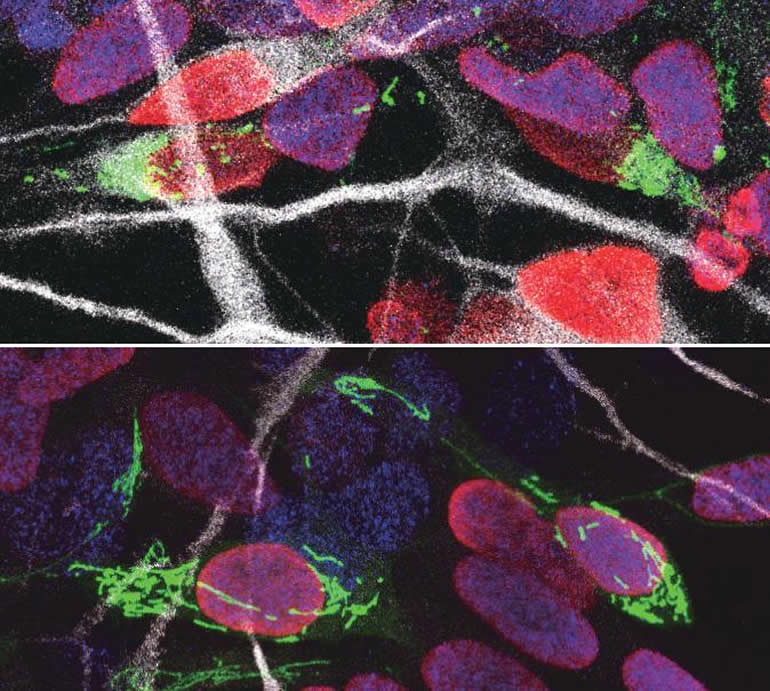
“We found that the influence of mitochondrial dynamics on cell fate choice is limited to a very specific time window, right after cell division,” says Pierre Casimir, a PhD student in Vanderhaeghen’s lab. “Interestingly, the restricted time window is twice as long in humans compared to mice.”
“Previous findings were primarily focused on fate decision of neural stem cells before they divide, but our data reveal that cell fate can be influenced for a much longer period, even after neural stem cell division,” says Vanderhaeghen. This may have interesting implications in the emerging field of cell reprogramming, where scientists try to convert non-neuronal cells directly in neuronal cells for therapeutic purposes for instance.
“Since this period of plasticity is much longer in human cells compared to mouse cells, it is tempting to speculate that it contributes to the increased self-renewal capacity of human progenitor cells, and thus to the uniquely developed brain and cognitive abilities of our species. It is fascinating to think that mitochondria, small organelles that have evolved in cells more than a billion years ago, might have contributed to the recent evolution of the human brain.”
About this neuroscience research article
Source:
VIB
Contacts:
Liesbeth Aerts – VIB
Image Source:
Image credited to VIB – Ryohei Iwata.
Original Research: Closed access
“Mitochondrial dynamics in postmitotic cells regulate neurogenesis” by Ryohei Iwata, et al. Science.
Abstract
Mitochondrial dynamics in postmitotic cells regulate neurogenesis
The conversion of neural stem cells into neurons is associated with the remodeling of organelles, but whether and how this is causally linked to fate change is poorly understood. We examined and manipulated mitochondrial dynamics during mouse and human cortical neurogenesis. We reveal that shortly after cortical stem cells have divided, daughter cells destined to self-renew undergo mitochondrial fusion, whereas those that retain high levels of mitochondria fission become neurons. Increased mitochondria fission promotes neuronal fate, whereas induction of mitochondria fusion after mitosis redirects daughter cells toward self-renewal. This occurs during a restricted time window that is doubled in human cells, in line with their increased self-renewal capacity. Our data reveal a postmitotic period of fate plasticity in which mitochondrial dynamics are linked with cell fate.