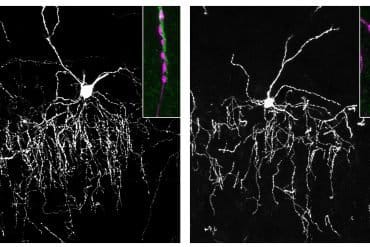
Summary: Genetic mutations, which occur in both the brain and gut, could be a main cause of autism. Using mouse models of ASD, researchers discovered the neuroligin-3 R451C mutation affects neural communication in the brain and causes dysfunction in the gut. The findings strengthen the gut-brain hypothesis of autism.
Source: RMIT University
People with autism often suffer from gut problems, but nobody has known why. Researchers have now discovered the same gene mutations – found both in the brain and the gut – could be the cause.
The discovery confirms a gut-brain nervous system link in autism, opening a new direction in the search for potential treatments that could ease behavioural issues associated with autism by targeting the gut.
Chief Investigator Associate Professor Elisa Hill-Yardin, RMIT University, said scientists trying to understand autism have long been looking in the brain, but the links with the gut nervous system have only been recently explored.
“We know the brain and gut share many of the same neurons and now for the first time we’ve confirmed that they also share autism-related gene mutations,” Hill-Yardin said.
“Up to 90% of people with autism suffer from gut issues, which can have a significant impact on daily life for them and their families.
“Our findings suggest these gastrointestinal problems may stem from the same mutations in genes that are responsible for brain and behavioural issues in autism.
“It’s a whole new way of thinking about it – for clinicians, families and researchers – and it broadens our horizons in the search for treatments to improve the quality of life for people with autism.”
The autism gene and the gut-brain link
The study reveals a gene mutation that affects neuron communication in the brain, which was first identified as a cause of autism, also causes dysfunction in the gut.
The research brings together new results from pre-clinical animal studies with previously unpublished clinical work from a landmark 2003 study led by Swedish researchers and a French geneticist.
The study of two brothers with autism by Professor Christopher Gillberg (University of Gothenburg), Professor Maria Råstam (Lund University) and Professor Thomas Bourgeron (Pasteur Institute) was the first to identify a specific gene mutation as a cause of the neurodevelopmental disorder.
This mutation affects communication by altering the “velcro” between neurons that keeps them in close contact.
While the 2003 study was focused on identifying the genetic basis for autism, Gillberg and Råstam also took detailed clinical notes of the brothers’ significant gastrointestinal problems.
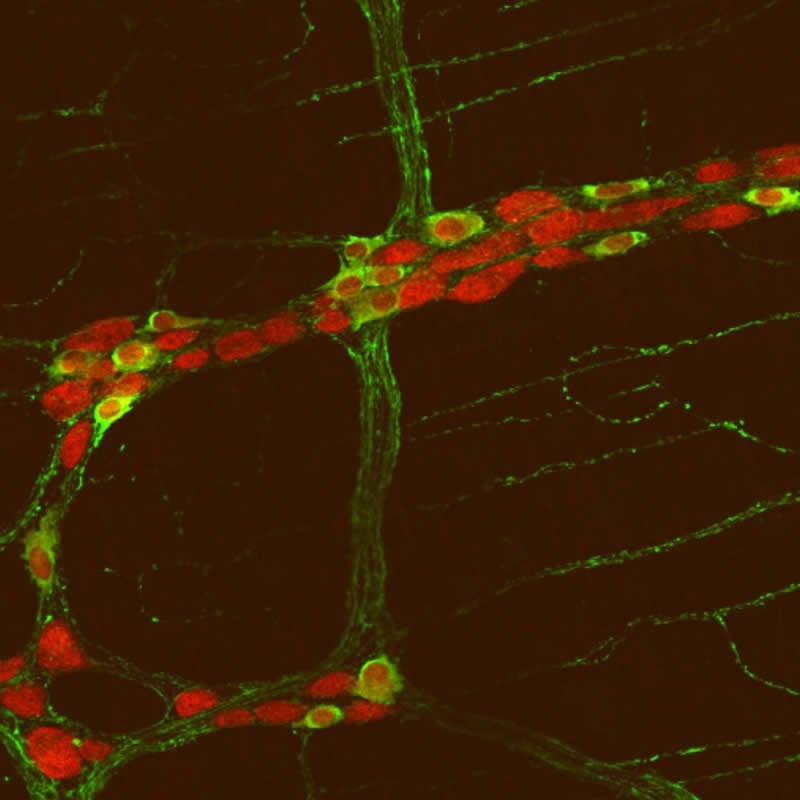
Researchers in the Gut-Brain Axis team at RMIT have built on this clinical work with a series of studies on the function and structure of the gut in mice that have the same “velcro” gene mutation.
They team found this mutation affects:
- gut contractions
- the number of neurons in the small intestine
- the speed that food moves through the small intestine
- responses to a critical neurotransmitter important in autism (well known in the brain but not previously identified to play any major role in the gut)
Collaborator Associate Professor Ashley Franks (La Trobe University) also found significant differences in the gut microbes of mice with the mutation and those without it, even though both groups were kept in identical environments.
While this specific “velcro” mutation is rare, it is one of more than 150 autism-related gene mutations that alter neuronal connections, Hill-Yardin said.
“The link we’ve confirmed suggests a broader mechanism, indicating that the mutations that affect connections between neurons could be behind the gut problems in many patients.”
New research horizons on the gut-brain axis
Hill-Yardin, an ARC Future Fellow and Vice-Chancellor’s Senior Research Fellow in the School of Health and Biomedical Sciences at RMIT, said the work identifies a new a target for the development of therapies specifically designed to work on neurotransmitters in the gut.
“We’ve also identified that there’s a need to better understand how existing autism medications that target neurotransmitters in the brain are affecting the gut,” she said.
“Another promising path for future research is investigating how gene mutations in the nervous system relate with microbes in the gut.
“We know these microbes interact with the brain via the gut-brain axis, so could tweaking them improve mood and behaviour?
“While this wouldn’t reverse the gene mutation, we might be able to tone down its effects, and make a real difference in the quality of life for people with autism and their families.”
The research, with collaborators from University of Gothenburg and Lund University (Sweden), Baylor College of Medicine (US), University of Minho (Portugal), La Trobe University, The University of Melbourne, Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health and Monash University (Australia), is published in a forthcoming edition of Autism Research (DOI: 10.1002/AUR.2127).
Funding: The work was supported with funding through an Idea Development Award from the United States Department of Defense (DoD) Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs (CDMRP) Autism Research Program, the Victorian Government through the Operational Infrastructure Scheme, the National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC), and the Royal Melbourne Hospital Neuroscience Foundation.
Source:
RMIT University
Media Contacts:
Gosia Kaszubska – RMIT University
Image Source:
The image is credited to RMIT University.
Original Research: Open access
“Gastrointestinal dysfunction in patients and mice expressing the autism‐associated r451c mutation in neuroligin‐3”. Elisa Hill-Yardin et al.
Autism Research. doi:10.1002/aur.2127
Abstract
Gastrointestinal dysfunction in patients and mice expressing the autism‐associated r451c mutation in neuroligin‐3
Gastrointestinal (GI) problems constitute an important comorbidity in many patients with autism. Multiple mutations in the neuroligin family of synaptic adhesion molecules are implicated in autism, however, whether they are expressed and impact GI function via changes in the enteric nervous system is unknown. We report the GI symptoms of two brothers with autism and an R451C mutation in Nlgn3 encoding the synaptic adhesion protein, neuroligin‐3. We confirm the presence of an array of synaptic genes in the murine GI tract and investigate the impact of impaired synaptic protein expression in mice carrying the human neuroligin‐3 R451C missense mutation (NL3R451C). Assessing in vivo gut dysfunction, we report faster small intestinal transit in NL3R451C compared to wild‐type mice. Using an ex vivo colonic motility assay, we show increased sensitivity to GABAA receptor modulation in NL3R451C mice, a well‐established Central Nervous System (CNS) feature associated with this mutation. We further show increased numbers of small intestine myenteric neurons in NL3R451C mice. Although we observed altered sensitivity to GABAA receptor modulators in the colon, there was no change in colonic neuronal numbers including the number of GABA‐immunoreactive myenteric neurons. We further identified altered fecal microbial communities in NL3R451C mice. These results suggest that the R451C mutation affects the small intestinal and colonic function and alter neuronal numbers in the small intestine as well as impact fecal microbes. Our findings identify a novel GI phenotype associated with the R451C mutation and highlight NL3R451C mice as a useful preclinical model of GI dysfunction in autism.
Lay Summary
People with autism commonly experience gastrointestinal problems, however, the cause is unknown. We report gut symptoms in patients with the autism‐associated R451C mutation encoding the neuroligin‐3 protein. We show that many of the genes implicated in autism are expressed in mouse gut. The neuroligin‐3 R451C mutation alters the enteric nervous system, causes gastrointestinal dysfunction, and disrupts gut microbe populations in mice. Gut dysfunction in autism could be due to mutations that affect neuronal communication.