Summary: Researchers reveal a protein essential for memory and cognition looks and acts like a protein from a virus.
Source: University of Utah Health.
A protein involved in cognition and storing long-term memories looks and acts like a protein from viruses. The protein, called Arc, has properties similar to those that viruses use for infecting host cells, and originated from a chance evolutionary event that occurred hundreds of millions of years ago.
The prospect that virus-like proteins could be the basis for a novel form of cell-to-cell communication in the brain could change our understanding of how memories are made, according to Jason Shepherd, Ph.D., a neuroscientist at University of Utah Health and senior author of the study publishing in Cell on Jan. 11.
Shepherd first suspected that something was different about Arc when his colleagues captured an image of the protein showing that Arc was assembling into large structures. With a shape that resembles a capsule from a lunar lander, these structures looked a lot like the retrovirus, HIV.
“At the time, we didn’t know much about the molecular function or evolutionary history of Arc,” says Shepherd who has researched the protein for 15 years. “I had almost lost interest in the protein, to be honest. After seeing the capsids, we knew we were onto something interesting.”
The gap in research was not for want of an interesting subject. Prior work had shown that mice lacking Arc forgot things they had learned a mere 24 hours earlier. Further, their brains lacked plasticity. There is a window of time early in life when the brain is like a sponge, easily soaking up new knowledge and skills. Without Arc, the window never opens.
Scientists had never considered that mechanisms responsible for acquiring knowledge could stem from foreign origins. Now, the work by Shepherd and his team has raised this intriguing possibility.
Everything Old is New Again
Seeing Arc’s unusual propensity to form virus-like structures prompted Shepherd to scrutinize the protein sequence with a new set of eyes. He found that regions of the code were similar to that from viral capsids. An essential tool for viral infection, capsids carry virus’ genetic information and deliver it from cell to cell in its victim.
Given that Arc looks like a viral protein, Shepherd and his colleagues designed a set of experiments to test whether it also acts like one. They first determined that several copies of Arc self-assemble into hollow virus-like capsids and stash its own genetic material, in this case mRNA, inside them. When the scientists added the capsids to mouse brain cells, or neurons, growing in a dish, Arc transferred its genetic cargo into the cells.

After viruses invade host cells, they emerge ready to infect once again. It appears that Arc works in a similar way. The scientists gathered Arc that had been released from mouse neurons and determined that the proteins and their cargo could be taken up by another set of neurons. Unlike for viruses, activating neurons mobilizes Arc, triggering the release of capsids.
“We went into this line of research knowing that Arc was special in many ways, but when we discovered that Arc was able to mediate cell-to-cell transport of RNA, we were floored,” says the study’s lead author, postdoctoral fellow Elissa Pastuzyn, Ph.D. “No other non-viral protein that we know of acts in this way.”
When Lightning Strikes Twice
The story of Arc’s origin is relayed through the genomes of animals throughout evolutionary time. 350-400 million years ago, a chance occurrence struck four-limbed creatures that roamed the earth. An ancestor to retroviruses, called retrotransposons, inserted its genetic material into the animals’ DNA. The event led to the mammalian Arc that we know today.
The significance of such an event is hinted at by the fact that it happened more than once. An accompanying paper in the same issue of Cell shows that a version of Arc found in flies also looks and acts like a viral capsid. Vivian Budnik’s lab at the University of Massachusetts shows that fly Arc transports RNA from neurons to muscles to control movement. Even though mammalian and fly Arc evolved from the same class of retrotransposons, the event in flies occurred about 150 million years later.
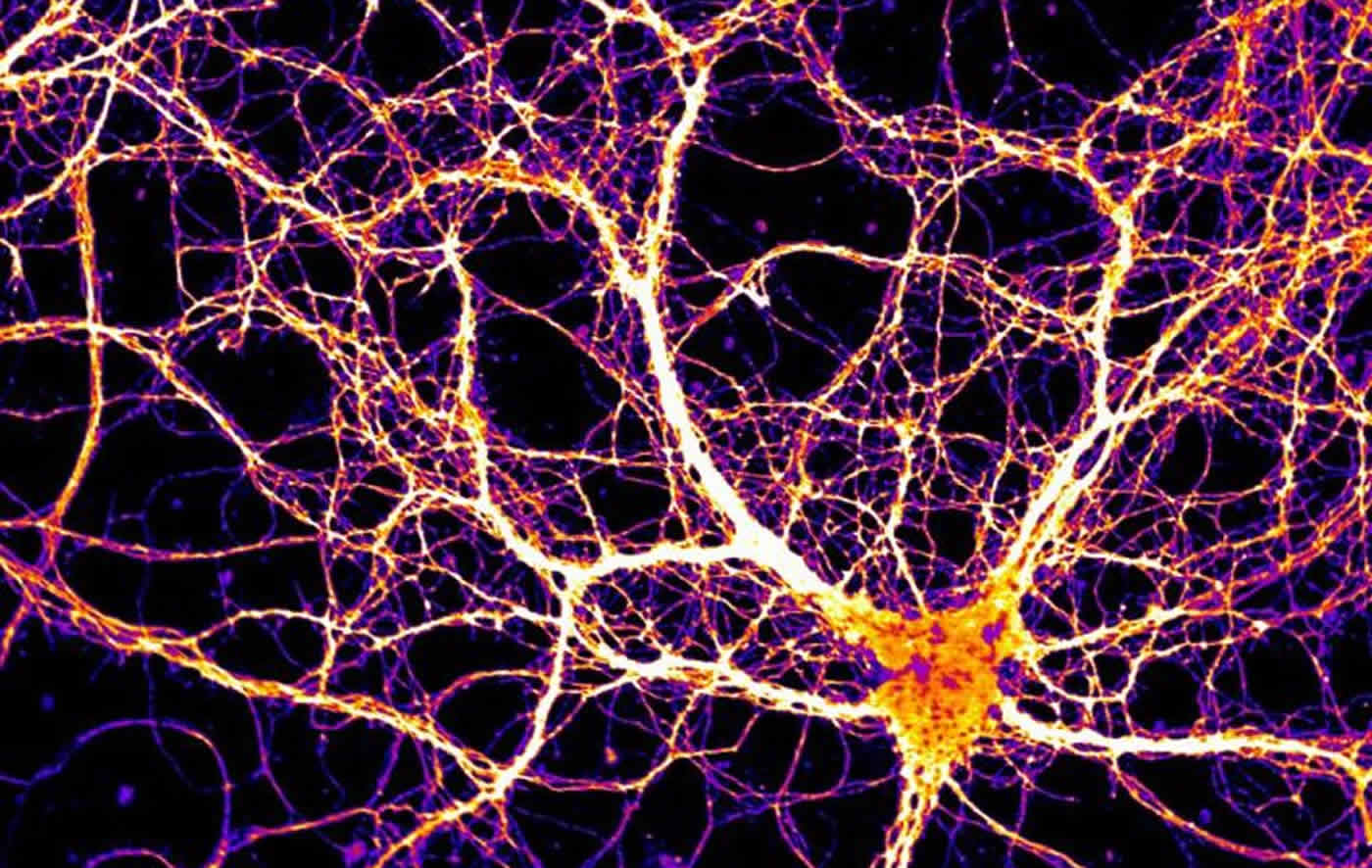
“As an evolutionary biologist this is what is the most exciting to me,” says co-author Cédric Feschotte, Ph.D. a professor at Cornell University. “The fact that it happened at least twice makes us think that it happened even more.”
Shepherd believes this could mean that it is advantageous to have this viral-inspired system in place, and it may represent a novel form of intercellular communication. This hypothesis remains to be tested in mammals. “Knowing what cargo Arc vesicles transport in living animals will be critical to understanding the function of this pathway,” he says.
Remember the unusual viral-like protein that you just learned about? It could be controlling your memory.
Funding: The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health and will be publish as “The Neuronal Gene Arc Encodes a Repurposed Retrotransposon Gag Protein that Mediates Intercellular mRNA Transfer” online in Cell.
In addition to Shepherd, Pastuzyn, and Feschotte, co-authors are Cameron Day, Rachel Kearns, Madeleine Kyrke-Smith, Andrew Taibi, John McCormick, Nathan Yoder, and David Belnap from the University of Utah, and Simon Erlendsson, Dustin Morado, and John Briggs from the MRC Lab of Molecular Biology at the University of Cambridge.
Source: Julie Kiefer – University of Utah Health
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com images are credited to Chris Manfre and Elissa Pastuzyn.
Original Research: Abstract for “The Neuronal Gene Arc Encodes a Repurposed Retrotransposon Gag Protein that Mediates Intercellular RNA Transfer” by Elissa D. Pastuzyn, Cameron E. Day, Rachel B. Kearns, Madeleine Kyrke-Smith, Andrew V. Taibi, John McCormick, Nathan Yoder, David M. Belnap, Simon Erlendsson, Dustin R. Morado, John A.G. Briggs, Cédric Feschotte, and Jason D. Shepherd in Cell. Published online January 11 2018 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.024
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]University of Utah Health “Virus Like Protein is Important for Cognition and Memory.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 11 January 2018.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/arc-memory-cognition-8299/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]University of Utah Health (2018, January 11). Virus Like Protein is Important for Cognition and Memory. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved January 11, 2018 from https://neurosciencenews.com/arc-memory-cognition-8299/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]University of Utah Health “Virus Like Protein is Important for Cognition and Memory.” https://neurosciencenews.com/arc-memory-cognition-8299/ (accessed January 11, 2018).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
The Neuronal Gene Arc Encodes a Repurposed Retrotransposon Gag Protein that Mediates Intercellular RNA Transfer
Highlights
•The neuronal gene Arc encodes a protein that forms virus-like capsids
•Arc protein exhibits similar biochemical properties as retroviral Gag proteins
•Endogenous Arc protein is released from neurons in extracellular vesicles (EVs)
•Arc EVs and capsids can mediate intercellular transfer of Arc mRNA in neurons
Summary
The neuronal gene Arc is essential for long-lasting information storage in the mammalian brain, mediates various forms of synaptic plasticity, and has been implicated in neurodevelopmental disorders. However, little is known about Arc’s molecular function and evolutionary origins. Here, we show that Arc self-assembles into virus-like capsids that encapsulate RNA. Endogenous Arc protein is released from neurons in extracellular vesicles that mediate the transfer of Arc mRNA into new target cells, where it can undergo activity-dependent translation. Purified Arc capsids are endocytosed and are able to transfer Arc mRNA into the cytoplasm of neurons. These results show that Arc exhibits similar molecular properties to retroviral Gag proteins. Evolutionary analysis indicates that Arc is derived from a vertebrate lineage of Ty3/gypsy retrotransposons, which are also ancestors to retroviruses. These findings suggest that Gag retroelements have been repurposed during evolution to mediate intercellular communication in the nervous system.
“The Neuronal Gene Arc Encodes a Repurposed Retrotransposon Gag Protein that Mediates Intercellular RNA Transfer” by Elissa D. Pastuzyn, Cameron E. Day, Rachel B. Kearns, Madeleine Kyrke-Smith, Andrew V. Taibi, John McCormick, Nathan Yoder, David M. Belnap, Simon Erlendsson, Dustin R. Morado, John A.G. Briggs, Cédric Feschotte, and Jason D. Shepherd in Cell. Published online January 11 2018 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.024







