Summary: 2016 was a big year for neuroscience research. These are the top 20 most popular neuroscience articles we covered last year.
Source: NeuroscienceNews.
Top 20 Most Popular Neuroscience Articles of the Year
Now that 2017 is officially here, we thought we would take a look at some of our most popular articles of 2016.
We have selected these articles based on stories that received the most views from our readers, as well as the most shares and likes from Reddit, Facebook, Twitter, Google+ and our other social networks.
This list is based on popularity among Neuroscience News audiences and is not based on importance of research directly.
Thanks to all of our readers and social media fans for reading and sharing our news throughout 2016.
In no particular order, here are some of the most popular Neuroscience News articles of 2016.
Happy New Year!

1 – Depression Is Not Just a Mental Illness, It Affects the Whole Organism
Back in March, researchers reported that depression may not be just a psychiatric disorder, but instead a systemic disease.
The research team discovered depression was linked to an increase in oxidative stress and decrease in antioxidant substances. Additionally, after receiving treatment, both levels of malondialdehyde, a biomarker of oxidative stress, and antioxidant substances returned to normal.

2 – Researchers Identify Virus and Two Types of Bacteria as Major Causes of Alzheimer’s
Also from March, researchers from the University of Manchester reported on a major finding that could provide new avenues for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
The international research team linked the development of Alzheimer’s disease to a specific virus and two types of bacteria, providing evidence that the neurodegenerative disease had a dormant microbial component. They also found that the dormant microbes could become active with iron dysregulation. Removing the iron could possibly prevent the cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s.

3 – Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Is Not in Your Head, It’s in Your Gut
One of our most popular stories of the year was published back in late June.
Researchers reported they had identified biomarkers for chronic fatigue syndrome in both inflammatory microbial agents in the blood and gut bacteria.
The findings provide new evidence against the long standing concept that CFS is merely a psychological disorder, by identifying biological biomarkers for the disease.
However, researchers were unable to distinguish whether the alterations in gut bacteria was a result of the disease or a cause of CFS.

4 – Heavy Cannabis Use Associated With Reduced Dopamine Release
One of our more controversial stories was published back in mid-April and centered around the effects of heavy cannabis use on the dopamine system.
Researchers discovered that those who used marijuana heavily expressed lower dopamine release in the striatum, an area of the brain associated with working memory and attention.
This was a ground breaking finding as previous studies had linked similar alterations in dopamine release to heavier drugs, such as cocaine and heroin. However, this paper was the first to link long term cannabis use to reduced dopamine release.

5 – Cognitive Offloading: How the Internet is Increasingly Taking Over Human Memory
Back in August we reported on new findings associated with our reliance on modern technology.
Researchers from UC Santa Cruz and the University of Illinois report that our ever increasing reliance on the internet and our ease of access to new information is affecting our ability to learn and recall facts from memory, as well as impeding our ability to solve problems.
The researchers also found that our ‘cognitive offloading’, our reliance on technology as a memory aid, increased after each time it was used.

6 – Human Behavior Study Identifies Four Basic Personality Types
In October, researchers from the Carlos III University of Madrid released a new paper which claimed that 90 percent of the population can be classified into one of four personality types. The four basic personality types the researchers identified were: trusting, envious, pessimistic and optimistic, with most people falling into the envious personality type (30% of the population).
The researchers believe the findings are not only important for the field of social psychology, but also for the future development of robots to make them more ‘humanized’.

7 – Head Impacts Lead to Brain Changes in High School Football Players
In late November, one of our news articles gained national attention after it was featured on a number of other websites. The study focused on brain changes in high school football players following head impacts associated with playing the sport.
Researchers found that, after playing for just one season, football players showed significant changes in both white and gray matter that was associated with head trauma.
The researchers are now hoping to embark on both a larger study and a longitudinal study to evaluate the long term effects of these brain changes.
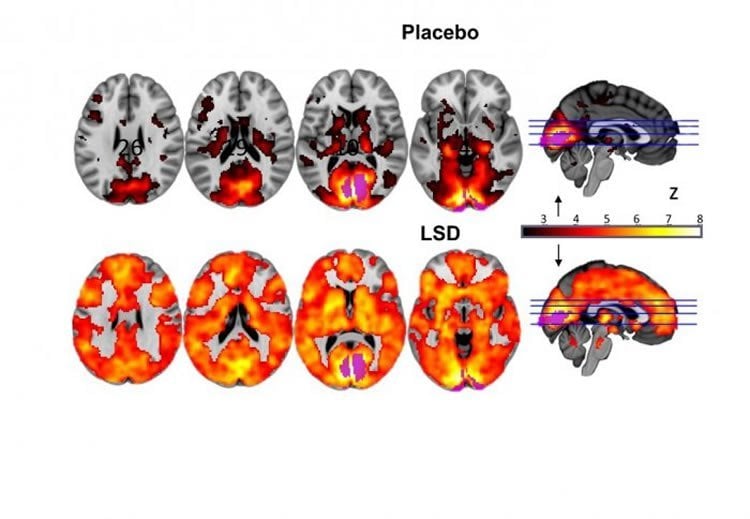
One of the most popular stories both on social media and on our website this year was released back in April.
Researchers from Imperial College London used neuroimaging technology to reveal what happens in the human brain when people experience visual hallucinations after taking LSD.
The findings not only help to identify how LSD can help people overcome psychiatric conditions, such as depression, they also could help to shed new light on current concepts of consciousness, the researchers believe.

9 – Eating Fish While Pregnant Improves Baby’s Brain Development
We have all read reports about how eating fish is good for brain health. One of our earliest top stories was published back in January last year, finding that eating fish is not only important for adult brain health, but also important for fetal brain development.
Researchers from Tohoku University’s School of Medicine advised pregnant women to up their fish consumption as the dietary lipids from fish are essential for normal brain formation in the unborn child.
The study also reveals that fish oils are important for brain function and development as we age.

10 – Dietary Supplement May Prevent and Reverse Damage to Aging Brain
Sticking on the subject of dietary supplements, back in June a new study reported that a complex dietary supplement, which contains over 30 vitamins and minerals, appears to show amazing anti-aging properties.
Additionally, this new supplement may prevent, and even reverse, brain cell loss. This, researchers believe, could have major implications for the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and ALS.
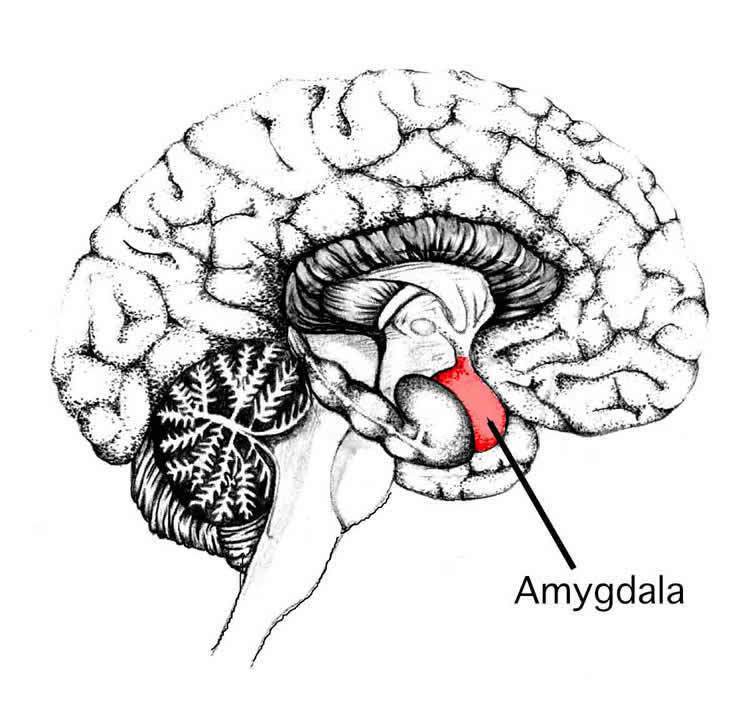
11 – Manipulation of Specific Neurons Helps to Erase Bad Memories and Enhance Good Ones
In early May, we reported on a new study that could have positive implications for treating people with memory related disorders.
Researchers at Stony Brook reported they had discovered a possible method for ‘tuning’ the strength of a memory by manipulating acetylcholine levels with optogenetics. Not only were the researchers able to ‘tune down’ negative memories, they were also able to enhance positive memories.
The findings could be used to develop new treatment options for both neurodegenerative diseases and PTSD.

12 – Single Species of Gut Bacteria Can Reverse Autism Related Social Behavior: Mouse Study
In June, researchers reported that a strain of Lactobacillus reuteri found in human breast milk has the potential to reverse problematic social behaviors in mouse models of Autism.
The researchers suggested that the absence of this specific species of bacteria could be a cause of the social deficits associated with ASD.
They also reported that introducing the bacteria back into the gut could, potentially, help to reverse some social and behavioral problems in people on the Autism spectrum.

13 – Rhythm of Breathing Affects Memory and Fear
Perhaps our top story of the year was published in early December and comes from a team of researchers from Northwestern University.
Researchers have been able to link breathing rhythm to emotional judgement and enhanced memory recall.
There is a ‘dramatic difference’ in neural activity in both the hippocampus and amygdala depending on whether you are inhaling or exhaling, the researchers report. This can affect how you perceive stimuli and your ability to recall memories.

During 2016, we seemed to report fairly often on the neurobiological effects of LSD. Back in August, a new study was released that looked at the effect LSD had on language processing and skills.
Researchers reported that, when people under the influence of LSD were asked to name specific objects, their reaction times did not change, but they were more likely to mistakenly call objects by different names. For example, when presented with an image of a car, people who had taken LSD would instead name the stimuli as a ‘bus’ or other vehicle.
Based on their findings, the researchers believe that LSD could allow ‘quicker access to far away concepts stored in the brain’ (Neiloufar Family) and could help in the treatment of psychiatric illnesses.

15 – Broca and Wernicke Are Dead – It’s Time to Rewrite the Neurobiology of Language
One of the most influential news stories of the year was released in early November and could have implications for the way researchers consider the neurological basis of language function.
A new paper published by the BPS argued that the ‘Classic Model’ of language function in the brain is obsolete and the continued use could be hampering progress when it comes to researching language production. The researchers call for a new approach that considers how much of language function is overlaid on the cognitive system.
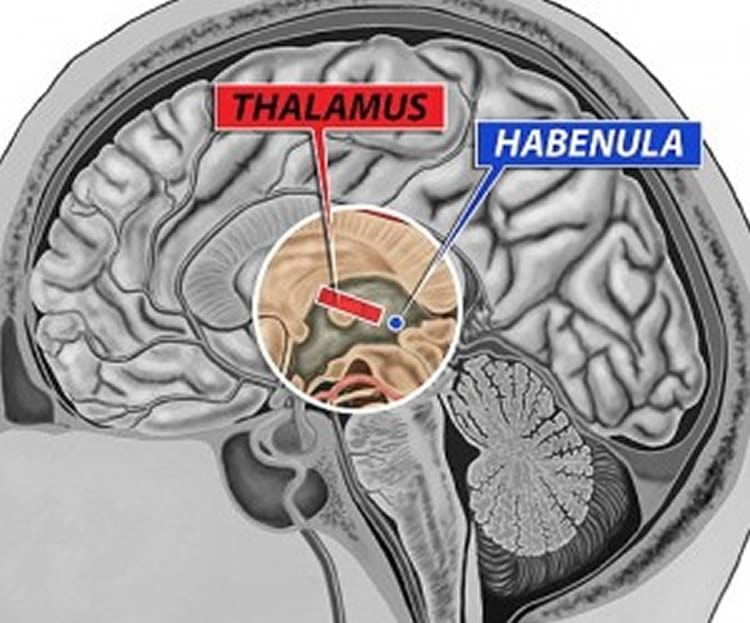
16 – Brain Structure That Tracks Negative Events Backfires in Depression
Back in May, we reported on a significant new finding which relates to the neurobiology of depression.
Researchers from University College London discovered people with depression had hyperactive habenula function. Surprisingly, when faced with an adverse event, habenula activity decreased in depressed people. The findings suggest that this brain area functions in a much different way in people with this psychiatric condition.
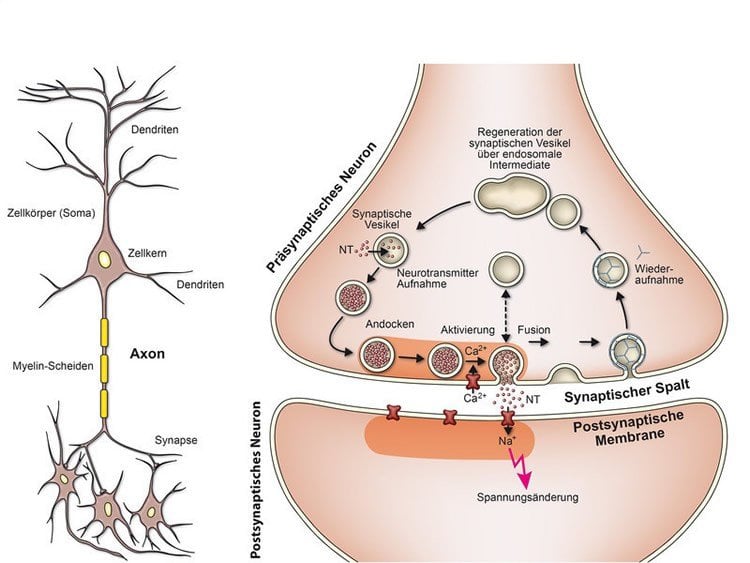
17 – How Neurons Talk to Each Other
While not so much of a breaking news story, one of our most popular articles of the year provided a comprehensive breakdown of the process of neurotransmission. The article received a great deal of attention via our social network accounts and became quite a hit with educational communities and groups online.

18 – Our Brains Have a Basic Algorithm That Enables Our Intelligence
Back in November, we reported on a groundbreaking piece of research that demonstrated our complex brain computations and intelligence are reliant upon a fairly basic algorithm. However, the researcher noted exceptions to the math rule in areas such as the reward system.

19 – Religious Beliefs Activate Neural Reward Circuits in Same Way As Sex and Drugs
One of our favorite stories of the year was published back in late November and came to us from researchers at the University Of Utah School Of Medicine.
A new neurotheology study looked at the neural networks that are involved in feelings of spirituality.
Through neuroimaging technology, researchers identified activation in the nucleus accumbens, an area of the brain associated with reward, when powerful spiritual feelings are encountered. Interestingly, similar brain activation occurs when people are exposed to pleasurable stimuli such as sex, drugs, music and gambling.
20 – How the Hippocampus Influences Future Thinking
To conclude our review of the top NeuroscienceNews stories to hit our pages in 2016, we’ll take you back to a fairly recent article.
Published in early December, researchers from Boston University Medical Center reported a new role for the hippocampus. While the hippocampus is well known for its role in memory, researchers discovered that this area of the brain may also be critical for imagination and future planning.
We hope that you enjoyed this brief breakdown of our most popular stories of 2016. We look forward to bringing you more ground breaking neuroscience research news throughout 2017.
Source: Victoria Driscoll – Neuroscience News
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to NeuroscienceNews.
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]NeuroscienceNews.com “Top 20 Neuroscience News Stories of 2016.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, January 4 2017.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/top-2016-neuroscience-news-stories-5842/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]NeuroscienceNews.com (2017, January 4). Top 20 Neuroscience News Stories of 2016. NeuroscienceNew. Retrieved January 4, 2017 from https://neurosciencenews.com/top-2016-neuroscience-news-stories-5842/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]NeuroscienceNews.com “Top 20 Neuroscience News Stories of 2016.” https://neurosciencenews.com/top-2016-neuroscience-news-stories-5842/ (accessed January 4, 2017).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]