Summary: A new study finds THC reduces amyloid beta proteins in human neurons.
Source: Salk Institute.
Preliminary lab studies at the Salk Institute find THC reduces beta amyloid proteins in human neurons.
Salk Institute scientists have found preliminary evidence that tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and other compounds found in marijuana can promote the cellular removal of amyloid beta, a toxic protein associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
While these exploratory studies were conducted in neurons grown in the laboratory, they may offer insight into the role of inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease and could provide clues to developing novel therapeutics for the disorder.
“Although other studies have offered evidence that cannabinoids might be neuroprotective against the symptoms of Alzheimer’s, we believe our study is the first to demonstrate that cannabinoids affect both inflammation and amyloid beta accumulation in nerve cells,” says Salk Professor David Schubert, the senior author of the paper.
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive brain disorder that leads to memory loss and can seriously impair a person’s ability to carry out daily tasks. It affects more than five million Americans according to the National Institutes of Health, and is a leading cause of death. It is also the most common cause of dementia and its incidence is expected to triple during the next 50 years.
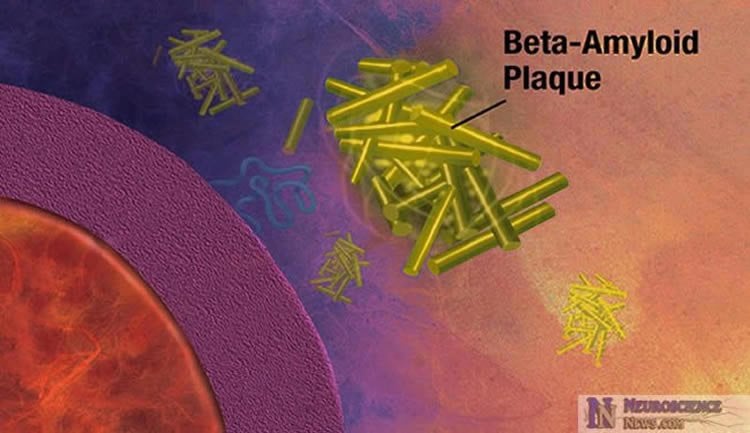
It has long been known that amyloid beta accumulates within the nerve cells of the aging brain well before the appearance of Alzheimer’s disease symptoms and plaques. Amyloid beta is a major component of the plaque deposits that are a hallmark of the disease. But the precise role of amyloid beta and the plaques it forms in the disease process remains unclear.
In a manuscript published in June 2016’s Aging and Mechanisms of Disease, the Salk team studied nerve cells altered to produce high levels of amyloid beta to mimic aspects of Alzheimer’s disease.
The researchers found that high levels of amyloid beta were associated with cellular inflammation and higher rates of neuron death. They demonstrated that exposing the cells to THC reduced amyloid beta protein levels and eliminated the inflammatory response from the nerve cells caused by the protein, thereby allowing the nerve cells to survive.
“Inflammation within the brain is a major component of the damage associated with Alzheimer’s disease, but it has always been assumed that this response was coming from immune-like cells in the brain, not the nerve cells themselves,” says Antonio Currais, a postdoctoral researcher in Schubert’s laboratory and first author of the paper. “When we were able to identify the molecular basis of the inflammatory response to amyloid beta, it became clear that THC-like compounds that the nerve cells make themselves may be involved in protecting the cells from dying.”
Brain cells have switches known as receptors that can be activated by endocannabinoids, a class of lipid molecules made by the body that are used for intercellular signaling in the brain. The psychoactive effects of marijuana are caused by THC, a molecule similar in activity to endocannabinoids that can activate the same receptors. Physical activity results in the production of endocannabinoids and some studies have shown that exercise may slow the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
Schubert emphasized that his team’s findings were conducted in exploratory laboratory models, and that the use of THC-like compounds as a therapy would need to be tested in clinical trials.
In separate but related research, his lab found an Alzheimer’s drug candidate called J147 that also removes amyloid beta from nerve cells and reduces the inflammatory response in both nerve cells and the brain. It was the study of J147 that led the scientists to discover that endocannabinoids are involved in the removal of amyloid beta and the reduction of inflammation.
Other authors on the paper include Oswald Quehenberger and Aaron Armando at the University of California, San Diego; and Pamela Maher and Daniel Daughtery at the Salk Institute.
Funding:The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, The Burns Foundation and The Bundy Foundation.
Source: Salk Institute
Image Source: This NeuroscienceNews.com image is in the public domain.
Original Research: Full open access research for “Amyloid proteotoxicity initiates an inflammatory response blocked by cannabinoids” by Antonio Currais, Oswald Quehenberger, Aaron M Armando, Daniel Daugherty, Pam Maher and David Schubert in Aging and Mechanisms of Disease. Published online June 23 2016 doi:10.1038/npjamd.2016.12
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]Salk Institute. “Cannabinoids May Reduce Alzheimer’s Proteins From Brain Cells.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 29 June 2016.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/thc-amyloid-beta-alzheimers-4598/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]Salk Institute. (2016, June 29). Cannabinoids May Reduce Alzheimer’s Proteins From Brain Cells. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved June 29, 2016 from https://neurosciencenews.com/thc-amyloid-beta-alzheimers-4598/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]Salk Institute. “Cannabinoids May Reduce Alzheimer’s Proteins From Brain Cells.” https://neurosciencenews.com/thc-amyloid-beta-alzheimers-4598/ (accessed June 29, 2016).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Amyloid proteotoxicity initiates an inflammatory response blocked by cannabinoids
The beta amyloid (Aβ) and other aggregating proteins in the brain increase with age and are frequently found within neurons. The mechanistic relationship between intracellular amyloid, aging and neurodegeneration is not, however, well understood. We use a proteotoxicity model based upon the inducible expression of Aβ in a human central nervous system nerve cell line to characterize a distinct form of nerve cell death caused by intracellular Aβ. It is shown that intracellular Aβ initiates a toxic inflammatory response leading to the cell’s demise. Aβ induces the expression of multiple proinflammatory genes and an increase in both arachidonic acid and eicosanoids, including prostaglandins that are neuroprotective and leukotrienes that potentiate death. Cannabinoids such as tetrahydrocannabinol stimulate the removal of intraneuronal Aβ, block the inflammatory response, and are protective. Altogether these data show that there is a complex and likely autocatalytic inflammatory response within nerve cells caused by the accumulation of intracellular Aβ, and that this early form of proteotoxicity can be blocked by the activation of cannabinoid receptors.
“Amyloid proteotoxicity initiates an inflammatory response blocked by cannabinoids” by Antonio Currais, Oswald Quehenberger, Aaron M Armando, Daniel Daugherty, Pam Maher and David Schubert in Aging and Mechanisms of Disease. Published online June 23 2016 doi:10.1038/npjamd.2016.12