Summary: The behavior of oligodendrocytes plays a critical role in determining whether we tolerate or succumb to stress.
Source: CUNY
Exposure to violence, social conflict, and other stressors increase the risk for psychiatric conditions such as depression and post-traumatic stress disorder. Not everyone who experiences significant stress will develop such a response, however, and the cellular and molecular basis for an individual’s underlying resilience or susceptibility to stressful events has remained poorly understood. Now, a newly published paper in the journal eLife from researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center (ASRC) at The Graduate Center, CUNY suggests that the behavior of oligodendrocytes — the glial cells that produce the myelin sheath that protects nerve fibers — plays a critical role in determining whether we succumb to or tolerate stress.
“Through our study, we were able to identify brain-region-specific differences in the number of mature oligodendrocytes and in the content of myelin between two groups of mice who were categorized based on their resilience or susceptibility to an identical social-defeat stressor,” said the paper’s corresponding author Jia Liu, a research associate professor with the ASRC’s Neuroscience Initiative. “After repeated exposure to an aggressive mouse, some animals, called “susceptible,” avoided any sort of social interaction with their peers, while others remained resilient and continued to be socially engaged.”
In follow-up brain tissue analysis, the research team detected fewer mature oligodendrocytes and irregular myelin coverage in the medial prefrontal cortex — a brain region that plays a critical role in emotional and cognitive processing — in the susceptible mice. In contrast, healthy numbers of oligodendrocytes and myelin were detected in resilient mice.
Methodology
For the study, researchers exposed test mice to an aggressor for five minutes daily over 10 days. Following this period, the mice were placed in the presence of unfamiliar mouse and categorized either as susceptible if they showed signs of social withdrawal or resilient if they still showed interest in socializing with the new mouse — a social behavior that is typically detected in normal mice.
Reseachers next sought to determine if there were myelination differences between susceptible and resilient mice. They looked at two areas of the brain that are known to play a critical role in determining the individual’s response to stress. In one of those areas — the medial prefrontal cortex — they found that the myelinated segments of nerve fiber in susceptible mice were shorter in length and thinner than typical. They did not find this condition in the resilient or control mice groups. They also investigated the state of each mouse group’s glial cells, and discovered that in susceptible mice fewer of these cells had differentiated into myelin-producing oligodendrocytes.
In a final experiment, researchers found that induced damage to the myelin in the medial prefrontal cortex caused altered social behavior in mice, but the behavior returned to normal when new myelin was formed.
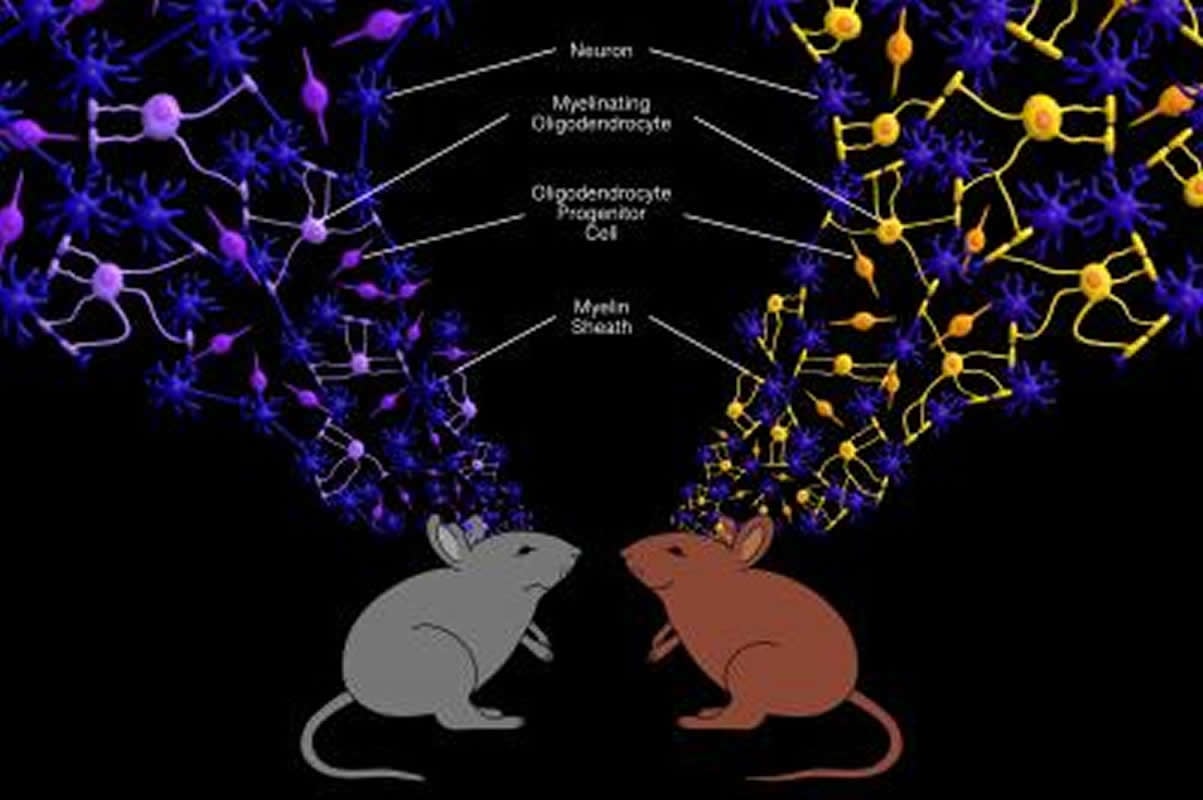
“Dr. Liu’s research has highlighted the importance of stressful social events in changing the epigenetic code of oligodendrocyte progenitors, which may account for the increased susceptibility to developing chronic psychiatric disorders in some individuals,” said Patrizia Casaccia, founding director of the ASRC Neuroscience Initiative. “Her data suggest that oligodendrocyte progenitor differentiation can be affected by emotional and psychological events, and this provides a new concept for preventing and treating depression. Current treatments target neuronal function, but Dr. Liu’s work identifies potential new therapy targets as it suggests glial cell dysfunction could be a cause of stress-related mental disorders.”
Funding: This study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the National Cancer Institute and the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities, and The City University of New York.
Source:
CUNY
Media Contacts:
Shawn Rhea – CUNY
Image Source:
The image is credited to Carter Van Eitreim.
Original Research: Open access
“Region-specific myelin differences define behavioral consequences of chronic social defeat stress in mice”. Valentina Bonnefil, Karen Dietz, Mario Amatruda, Maureen Wentling, Antonio V Aubry, Jeffrey L Dupree, Gary Temple, Hye-Jin Park, Nesha S Burghardt, Patrizia Casaccia, Jia Liu.
eLife. doi:10.7554/eLife.40855
Abstract
Region-specific myelin differences define behavioral consequences of chronic social defeat stress in mice
Exposure to stress increases the risk of developing mood disorders. While a subset of individuals displays vulnerability to stress, others remain resilient, but the molecular basis for these behavioral differences is not well understood. Using a model of chronic social defeat stress, we identified region-specific differences in myelination between mice that displayed social avoidance behavior (‘susceptible’) and those who escaped the deleterious effect to stress (‘resilient’). Myelin protein content in the nucleus accumbens was reduced in all mice exposed to stress, whereas decreased myelin thickness and internodal length were detected only in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) of susceptible mice, with fewer mature oligodendrocytes and decreased heterochromatic histone marks. Focal demyelination in the mPFC was sufficient to decrease social preference, which was restored following new myelin formation. Together these data highlight the functional role of mPFC myelination as critical determinant of the avoidance response to traumatic social experiences.