Summary: Children who sleep less than 9 hours per night have significant differences in brain regions associated with memory, intelligence, and well-being compared to their peers who sleep 9 or more hours per night. Less sleep in children was also associated with increased risks of depression, anxiety, and impulsive behaviors.
Source: University of Maryland
Elementary school-age children who get less than nine hours of sleep per night have significant differences in certain brain regions responsible for memory, intelligence and well-being compared to those who get the recommended nine to 12 hours of sleep per night, according to a new study led by University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers.
Such differences correlated with greater mental health problems, like depression, anxiety, and impulsive behaviors, in those who lacked sleep. Inadequate sleep was also linked to cognitive difficulties with memory, problem solving and decision making.
The findings were published today in the journal Lancet Child & Adolescent Health.
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine recommends that children aged 6 to 12 years of age sleep 9 to 12 hours per night on a regular basis to promote optimal health.
Up until now, no studies have examined the long-lasting impact of insufficient sleep on the neurocognitive development of pre-teens.
To conduct the study, the researchers examined data that were collected from more than 8,300 children aged 9 to 10 years who were enrolled in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study.
They examined MRI images, medical records, and surveys completed by the participants and their parents at the time of enrollment and at a two-year follow-up visit at 11 to 12 years of age. Funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the ABCD study is the largest long-term study of brain development and child health in the US.
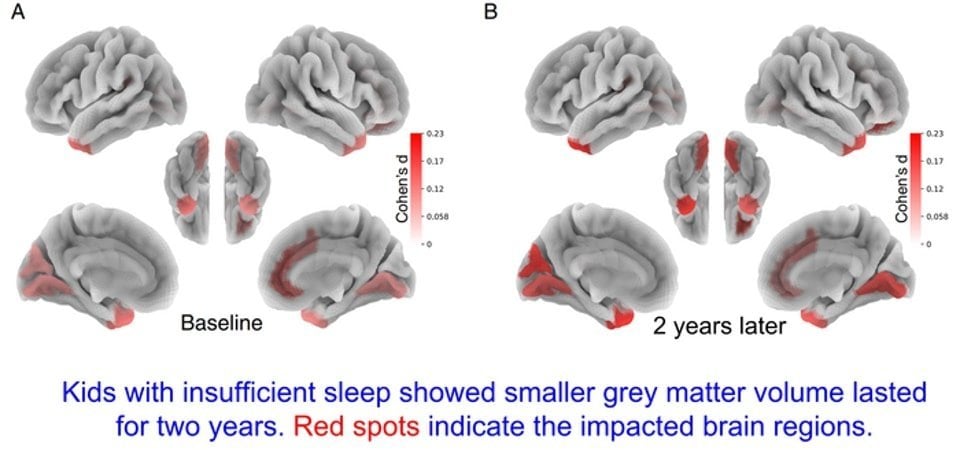
“We found that children who had insufficient sleep, less than nine hours per night, at the beginning of the study had less grey matter or smaller volume in certain areas of the brain responsible for attention, memory and inhibition control compared to those with healthy sleep habits,” said study corresponding author Ze Wang, PhD, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Nuclear Medicine at UMSOM.
“These differences persisted after two years, a concerning finding that suggests long term harm for those who do not get enough sleep.”
This is one of the first findings to demonstrate the potential long-term impact of lack of sleep on neurocognitive development in children. It also provides substantial support for the current sleep recommendations in children, according to Dr. Wang and his colleagues.
In follow-up assessments, the research team found that participants in the sufficient sleep group tended to gradually sleep less over two years, which is normal as children move into their teen years, whereas sleep patterns of participants in the insufficient sleep group did not change much.
The researchers controlled for socioeconomic status, gender, puberty status and other factors that could impact how much a child sleeps and affect brain and cognition.
“We tried to match the two groups as closely as possible to help us more fully understand the long-term impact on too little sleep on the pre-adolescent brain,” Dr. Wang said.
“Additional studies are needed to confirm our finding and to see whether any interventions can improve sleep habits and reverse the neurological deficits.”
The American Academy of Pediatrics encourages parents to promote good sleep habits in their children. Their tips include making sufficient sleep a family priority, sticking with a regular sleep routine, encouraging physical activity during the day, limiting screen time and eliminating screens completely an hour before bed.
The study was funded by NIH. Fan Nils Yang, PhD, a post-doctoral fellow in Dr. Wang’s laboratory is a study co-author. Weizhen Xie, PhD, a researcher at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, is also a study co-author. UMSOM faculty members Thomas Ernst, PhD, and Linda Chang, MD, MS, are co-principal investigators of the ABCD study at the Baltimore site but were not involved in the data analysis of this new study.
“This is a crucial study finding that points to the importance of doing long-term studies on the developing child’s brain,” said E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, Executive Vice President for Medical Affairs, UM Baltimore, and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and Dean, University of Maryland School of Medicine.
“Sleep can often be overlooked during busy childhood days filled with homework and extracurricular activities. Now we see how detrimental that can be to a child’s development.”
About this sleep and neurodevelopment research news
Author: Deborah Kotz
Source: University of Maryland
Contact: Deborah Kotz – University of Maryland
Image: The image is credited to University of Maryland
Original Research: Closed access.
“Children Who Lack Sleep May Experience Detrimental Impact on Brain and Cognitive Development That Persists Over Time” by Ze Wang, PhD et al. Lancet Child and Adolescent Health
Abstract
Children Who Lack Sleep May Experience Detrimental Impact on Brain and Cognitive Development That Persists Over Time
Background
Although the American Academy of Sleep Medicine suggests at least 9 h of sleep per day for 6–12-year-olds, children in recent generations often report sleeping less than this amount. Because early adolescence is a crucial period for neurocognitive development, we aimed to investigate how insufficient sleep affects children’s mental health, cognition, brain function, and brain structure over 2 years.
Methods
In this propensity score matched, longitudinal, observational cohort study, we obtained data from a population-based sample of 9–10-year-olds from 21 US study sites in the ongoing Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study.
Participants were categorised as having sufficient sleep or insufficient sleep on the basis of a cutoff of 9 h sleep per day. Using propensity score matching, we matched these two groups of participants on 11 key covariates, including sex, socioeconomic status, and puberty status.
Participants were excluded from our analysis if they did not pass a baseline resting-state functional MRI quality check or had missing data for the covariates involved in propensity score matching. Outcome measures retrieved from the ABCD study were behavioural problems, mental health, cognition, and structural and resting-state functional brain measures, assessed at baseline and at 2-year follow-up.
We examined group differences on these outcomes over those 2 years among all eligible participants. We then did mediation analyses of the neural correlates of behavioural changes induced by insufficient sleep.
Findings
Between Sept 1, 2016, and Oct 15, 2018, 11 878 individuals had baseline data collected for the ABCD study, of whom 8323 were eligible and included in this study (4142 participants in the sufficient sleep group and 4181 in the insufficient sleep group). Follow-up data were collected from July 30, 2018, to Jan 15, 2020.
We identified 3021 matched sufficient sleep–insufficient sleep pairs at baseline and 749 matched pairs at 2-year follow-up, and observed similar differences between the groups in behaviour and neural measures at both timepoints; the effect sizes of between-group differences in behavioural measures at these two timepoints were significantly correlated with each other (r=0·85, 95% CI 0·73–0·92; p<0·0001).
A similar pattern was observed in resting-state functional connectivity (r=0·54, 0·45–0·61; p<0·0001) and in structural measures (eg, in grey matter volume r=0·61, 0·51–0·69; p<0·0001). We found that cortico–basal ganglia functional connections mediate the effects of insufficient sleep on depression, thought problems, and crystallised intelligence, and that structural properties of the anterior temporal lobe mediate the effect of insufficient sleep on crystallised intelligence.
Interpretation
These results provide population-level evidence for the long-lasting effect of insufficient sleep on neurocognitive development in early adolescence. These findings highlight the value of early sleep intervention to improve early adolescents’ long-term developmental outcomes.
Funding
National Institutes of Health.