Summary: Researchers from Max Planck Institute have identified a neural connectivity pattern in the medial entorhinal cortex that appears to assist with navigation.
Source: Max Planck Institute.
Scientists discover fundamental connectivity pattern in the brain.
Our brains house extremely complex neuronal circuits, whose detailed structures are still largely unknown. This is especially true for the so-called cerebral cortex of mammals, where among other things vision, thoughts or spatial orientation are being computed. Here the rules by which nerve cells are connected to each other are only partly understood. A team of scientists around Moritz Helmstaedter at the Max Planck Institute for Brain Research in Frankfurt am Main and Helene Schmidt at the Bernstein-Center of Humboldt-University in Berlin have now discovered a surprisingly precise nerve cell connectivity pattern in the part of the cerebral cortex that is responsible for orienting the individual animal or human in space.
The researchers report that synapses in this region of the brain are sorted very precisely along the electrical cables of the nerve cells. The nerve cells establish an unexpectedly precise circuit motive, in which first so-called inhibitory nerve cells are contacted before in the next step the actual (excitatory) activation of the next nerve cell can be executed. This motif of nerve cell “trios” can be considered a core connectivity motif in this type of cortex. Scientists speculate that such a highly precise circuit motive could be used for computing hypotheses about the next step in space.
For a couple of years, novel electron microscopes and improved data analysis methods have enabled scientists to map the neuronal networks in the brain with remarkable accuracy. This rather novel research area called “Connectomics” has its own department at the Max Planck Institute for Brain Research (Frankfurt am Main). Scientists in this department have now used their repertoire of measuring and analysis techniques to study the part of the cerebral cortex in which so-called grid cells provide a very particular representation of the space around the individual animal or human. These grid cells are known to be active when the animal or human is located at highly ordered grid-like locations in a room or a large space. Previously, scientists around Michael Brecht of Humboldt University of Berlin, who is a co-author of this study, had already found a special arrangement of nerve cells in this region of the brain, and had speculated at the time that within these special cell assemblies particular nerve cell circuits could exist.
Synapses exactly positioned
In the current study, the scientists looked at these circuits in more detail and found that, contrary to prior belief, the synapses, i.e. contacts other nerve cells, are exceptionally precisely positioned. Within an extremely dense network of nerve cells (looking like a dense impenetrable forest, see attached figures), the nerve cells are in fact arranged in orderly triplets, in which a nerve cell first activates an inhibitory nerve cell. Transfer of the signal to the next excitatory nerve cell can however be hindered by the veto of the inhibitory nerve cell.
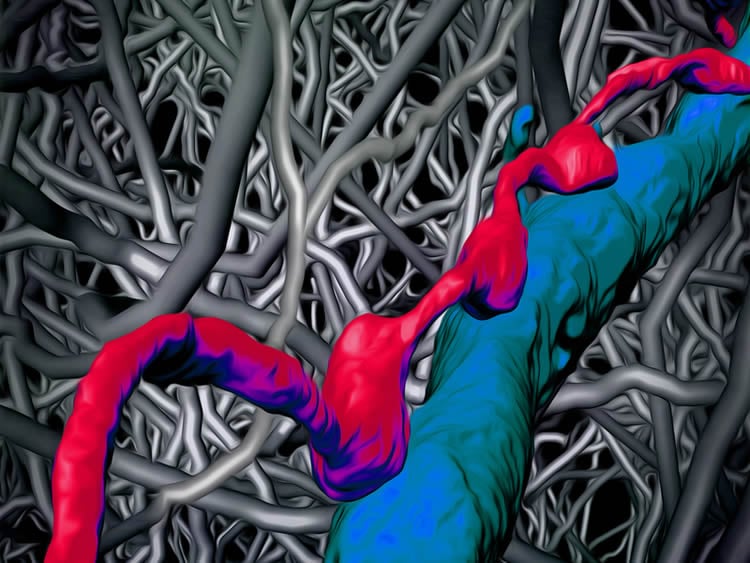

This core circuit, more or less functioning like a cortical transistor, would be able to propagate information in a very selective way, for instance only when additional information about the context and the surrounding of the animal or the human is available. The nerve cells within this transistor apparently use the very precise positioning of contact sites along their electrically conducting nerve cell cables (so-called axons). “While many consider the cerebral cortex as a randomly assembled web of nerve cells and have already turned to simulating this random network, we now discover an extremelyprecise connectivity pattern. In the cerebral cortex, taking a much closer look is clearly worth it”, according to Helmstaedter.
Source: Arjan Vink – Max Planck Institute
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to MPI f. Brain Research.
Original Research: Abstract for “Axonal synapse sorting in medial entorhinal cortex” by Helene Schmidt, Anjali Gour, Jakob Straehle, Kevin M. Boergens, Michael Brecht & Moritz Helmstaedter in Nature. Published online September 20 2017 doi:10.1038/nature24005
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]Max Planck Institute “Highly Precise Wiring in the Cerebral Cortex.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 21 September 2017.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/cerebral-cortex-wiring-7543/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]Max Planck Institute (2017, September 21). Highly Precise Wiring in the Cerebral Cortex. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved September 21, 2017 from https://neurosciencenews.com/cerebral-cortex-wiring-7543/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]Max Planck Institute “Highly Precise Wiring in the Cerebral Cortex.” https://neurosciencenews.com/cerebral-cortex-wiring-7543/ (accessed September 21, 2017).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Axonal synapse sorting in medial entorhinal cortex
Research on neuronal connectivity in the cerebral cortex has focused on the existence and strength of synapses between neurons, and their location on the cell bodies and dendrites of postsynaptic neurons. The synaptic architecture of individual presynaptic axonal trees, however, remains largely unknown. Here we used dense reconstructions from three-dimensional electron microscopy in rats to study the synaptic organization of local presynaptic axons in layer 2 of the medial entorhinal cortex, the site of grid-like spatial representations. We observe path-length-dependent axonal synapse sorting, such that axons of excitatory neurons sequentially target inhibitory neurons followed by excitatory neurons. Connectivity analysis revealed a cellular feedforward inhibition circuit involving wide, myelinated inhibitory axons and dendritic synapse clustering. Simulations show that this high-precision circuit can control the propagation of synchronized activity in the medial entorhinal cortex, which is known for temporally precise discharges.
“Axonal synapse sorting in medial entorhinal cortex” by Helene Schmidt, Anjali Gour, Jakob Straehle, Kevin M. Boergens, Michael Brecht & Moritz Helmstaedter in Nature. Published online September 20 2017 doi:10.1038/nature24005