Summary: A new study reports leaky capillaries in the brain may be an early sign of Alzheimer’s disease as it can signal cognitive impairment prior to the buildup of proteins associated with the neurodegenerative disease.
Source: USC.
Leaky capillaries in the brain portend early onset of Alzheimer’s disease as they signal cognitive impairment before hallmark toxic proteins amyloid and tau appear, new USC research shows.
The findings, which appear in the Jan. 14 issue of Nature Medicine, could help with earlier diagnosis and suggest new targets for drugs that could slow down or prevent the onset of the disease.
The number of Americans with Alzheimer’s is expected to more than double to about 14 million in 40 years, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. There are currently five Alzheimer’s drugs approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration that temporarily help with memory and thinking problems, but none that treat the underlying cause of the disease or slow its progression. Researchers believe that successful treatment will eventually involve a combination of drugs aimed at multiple targets.
USC’s five-year study, which involved 161 older adults, showed that people with the worst memory problems also had the most leakage in their brain’s blood vessels – regardless of whether abnormal proteins amyloid and tau were present.
“The fact that we’re seeing the blood vessels leaking, independent of tau and independent of amyloid, when people have cognitive impairment on a mild level, suggests it could be a totally separate process or a very early process,” said senior author Berislav Zlokovic, director of the Zilkha Neurogenetic Institute at the Keck School of Medicine of USC. “That was surprising that this blood-brain barrier breakdown is occurring independently.”
In healthy brains, the cells that make up blood vessels fit together so tightly they form a barrier that keeps stray cells, pathogens, metals and other unhealthy substances from reaching brain tissue. Scientists call this the blood-brain barrier. In some aging brains, the seams between cells loosen, and the blood vessels become permeable.
“If the blood-brain barrier is not working properly, then there is the potential for damage,” said co-author Arthur Toga, director of the USC Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute at the Keck School of Medicine. “It suggests the vessels aren’t properly providing the nutrients and blood flow that the neurons need. And you have the possibility of toxic proteins getting in.”
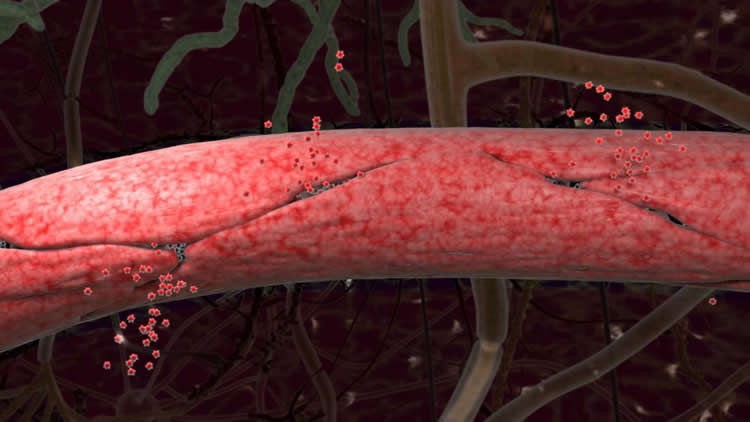
Participants in the study had their memory and thinking ability assessed through a series of tasks and tests, resulting in measures of cognitive function and a “clinical dementia rating score.” Individuals diagnosed with disorders that might account for cognitive impairment were excluded. The researchers used neuroimaging and cerebral spinal fluid analysis to measure the permeability, or leakiness, of capillaries serving the brain’s hippocampus, and found a strong correlation between impairment and leakage.
“The results were really kind of eye-opening,” said first author Daniel Nation, an assistant professor of psychology at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences. “It didn’t matter whether people had amyloid or tau pathology; they still had cognitive impairment.”
The researchers cautioned that their findings represent a snapshot in time. In future studies, they hope to get a better sense of how soon cognitive problems occur after blood vessel damage appears. Zlokovic said it’s unlikely that scientists will soon abandon amyloid and tau as Alzheimer’s biomarkers, “but we should be adding some vascular biomarkers to our toolkit.”
In addition to Zlokovic, Toga and Nation, the study’s authors are Melanie Sweeney and Axel Montagne of USC, who are co-first authors with Nation; Abhay Sagare, Lina D’Orazio, Maricarmen Pachicano, Farshid Sepehrband, Amy Nelson, John Ringman, Lon Schneider, Helena Chui and Meng Law, all of USC; Tammie Benzinger, John Morris and Anne Fagan of the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis; and Michael Harrington and David Buennagel of Huntington Medical Research Institutes in Pasadena.
Funding: The study was supported with grants from the National Institutes of Health (R01AG023084, R01NS090904, R01NS034467, R01AG039452, 1R01NS100459, 5P01AG052350, 5P50AG005142, P01AG052350, RO1AG054434, R21AG055034, R01AG055770, P50AG05681, P01AG03991 and P01AG026276), an Alzheimer’s Association Strategic 509279 Grant, the Cure Alzheimer’s Fund, the Fondation Leducq and the L.K. Whittier Foundation.
Source: Leigh Hopper – USC
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to Arthur Toga Lab/Keck School of Medicine of USC.
Original Research: Abstract for “Blood–brain barrier breakdown is an early biomarker of human cognitive dysfunction” by Daniel A. Nation, Melanie D. Sweeney, Axel Montagne, Abhay P. Sagare, Lina M. D’Orazio, Maricarmen Pachicano, Farshid Sepehrband, Amy R. Nelson, David P. Buennagel, Michael G. Harrington, Tammie L. S. Benzinger, Anne M. Fagan, John M. Ringman, Lon S. Schneider, John C. Morris, Helena C. Chui, Meng Law, Arthur W. Toga & Berislav V. Zlokovic in Nature Medicine. Published January 14 2019.
doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0297-y
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]USC”Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown an Early Driver of Dementia.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 14 January 2019.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/blood-brain-barrier-dementia-10531/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]USC(2019, January 14). Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown an Early Driver of Dementia. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved January 14, 2019 from https://neurosciencenews.com/blood-brain-barrier-dementia-10531/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]USC”Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown an Early Driver of Dementia.” https://neurosciencenews.com/blood-brain-barrier-dementia-10531/ (accessed January 14, 2019).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Blood–brain barrier breakdown is an early biomarker of human cognitive dysfunction
Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment are increasingly recognized as shown by neuropathological, neuroimaging, and cerebrospinal fluid biomarker studies. Moreover, small vessel disease of the brain has been estimated to contribute to approximately 50% of all dementias worldwide, including those caused by Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Vascular changes in AD have been typically attributed to the vasoactive and/or vasculotoxic effects of amyloid-β (Aβ), and more recently tau. Animal studies suggest that Aβ and tau lead to blood vessel abnormalities and blood–brain barrier (BBB) breakdown. Although neurovascular dysfunction and BBB breakdown develop early in AD, how they relate to changes in the AD classical biomarkers Aβ and tau, which also develop before dementia, remains unknown. To address this question, we studied brain capillary damage using a novel cerebrospinal fluid biomarker of BBB-associated capillary mural cell pericyte, soluble platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β8,18, and regional BBB permeability using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Our data show that individuals with early cognitive dysfunction develop brain capillary damage and BBB breakdown in the hippocampus irrespective of Alzheimer’s Aβ and/or tau biomarker changes, suggesting that BBB breakdown is an early biomarker of human cognitive dysfunction independent of Aβ and tau.