Statins found to protect blood vessels from substances that cause inflammation.
A new study conducted at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC) has revealed some of the underlying mechanisms that may increase the risk of heart disease in people with sleep apnea. The study also found that statins — the cholesterol-lowering medications commonly prescribed to combat heart disease — may help reverse this process.
The study was published in the Jan. 6, 2016 online edition of Science Translational Medicine.
More than 18 million adults have obstructive sleep apnea, in which relaxation of muscles in the throat during sleep causes frequent interruptions in breathing. The condition disrupts sleep and causes fluctuations in oxygen levels, which can lead to excessive daytime sleepiness and difficulty concentrating. In addition, sleep apnea triples the risk for developing heart disease, including hypertension, and ischemic stroke.
“It has been well documented that sleep apnea is a powerful and independent risk factor for heart disease, but the underlying reason for this has remained unclear,” said Sanja Jelic, MD, associate professor of medicine at CUMC. “The aim of our study was to understand the mechanisms by which sleep apnea may lead to heart disease in an effort to reduce the risk.”
The study included 128 people who underwent sleep studies at CUMC’s Sleep Disorders Center, including 76 people who were diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea and 52 people who did not meet the criteria for this condition. The researchers analyzed cells that line blood vessel walls (obtained from the participants’ arm veins) to look for differences that may explain the increased risk for heart disease in people with sleep apnea.
The investigators found that people with sleep apnea had higher levels of a protein called CD59, which inhibits the buildup of inflammatory proteins on cell surfaces. Unexpectedly, however, CD59 was found mainly within the cells of those with sleep apnea, instead of on the cell surface. As a result, the cells of the sleep apnea group had larger deposits of inflammatory proteins.
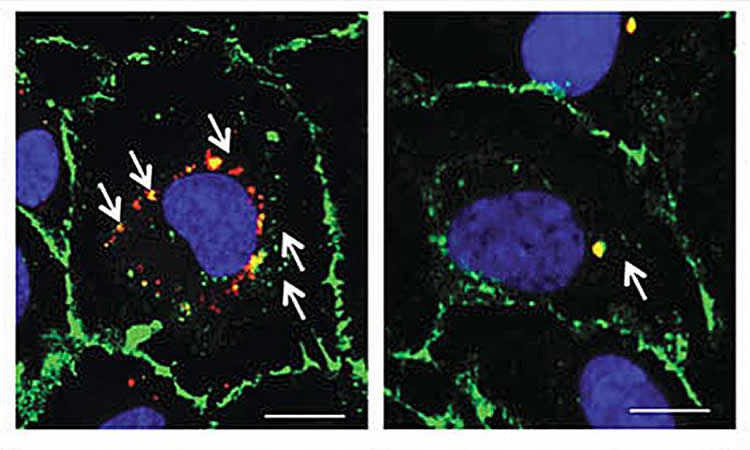
“This unexpected finding suggests that repeatedly interrupting oxygen flow during sleep draws CD59 away from the cell surface, where it is better positioned to do its job in protecting cells from inflammation,” said Dr. Jelic.
The researchers also noticed that CD59 was preserved on the cell surface in a small subset of subjects with sleep apnea who were being treated with statins, similar to those who did not have sleep apnea. Further testing revealed that cholesterol draws CD59 away from the cell surface in a process known as endocytosis.
“We were surprised to discover that these commonly prescribed drugs appeared to reverse the process that leads to vascular injury, and ultimately heart disease, in people with sleep apnea,” said Dr. Jelic. “This striking result provides support for the concept that statins may be considered as a primary prevention strategy for reducing heart disease risk in people with sleep apnea, pending further clinical trials.”
Funding: The study was supported by a grant from the NIH/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (R01HL106041). The researchers declare no financial or other conflicts of interest.
Source: Karin Eskenazi – Columbia University Medical Center
Image Source: The image is credited to Lab of Sanja Jelic/Columbia University Medical Center
Original Research: Abstract for “Increased internalization of complement inhibitor CD59 may contribute to endothelial inflammation in obstructive sleep apnea” by Memet Emin, Gang Wang, Francesco Castagna, Josanna Rodriguez-Lopez, Romina Wahab, Jing Wang, Tessa Adams, Ying Wei and Sanja Jelic in Science Translational Medicine. Published online January 6 2016 doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aad0634
Abstract
Increased internalization of complement inhibitor CD59 may contribute to endothelial inflammation in obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), characterized by intermittent hypoxia (IH) during transient cessation of breathing, triples the risk for cardiovascular diseases. We used a phage display peptide library as an unbiased approach to investigate whether IH, which is specific to OSA, activates endothelial cells (ECs) in a distinctive manner. The target of a differentially bound peptide on ECs collected from OSA patients was identified as CD59, a major complement inhibitor that protects ECs from the membrane attack complex (MAC). A decreased proportion of CD59 is located on the EC surface in OSA patients compared with controls, suggesting reduced protection against complement attack. In vitro, IH promoted endothelial inflammation predominantly via augmented internalization of CD59 and consequent MAC deposition. Increased internalization of endothelial CD59 in IH appeared to be cholesterol-dependent and was reversed by statins in a CD59-dependent manner. These studies suggest that reduced complement inhibition may mediate endothelial inflammation and increase vascular risk in OSA patients.
“Increased internalization of complement inhibitor CD59 may contribute to endothelial inflammation in obstructive sleep apnea” by Memet Emin, Gang Wang, Francesco Castagna, Josanna Rodriguez-Lopez, Romina Wahab, Jing Wang, Tessa Adams, Ying Wei and Sanja Jelic in Science Translational Medicine. Published online January 6 2016 doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aad0634







