Summary: Stool samples taken from Viking latrines allowed researchers to map the genome of the Whipworm parasite. The study maps the parasite’s global spread and relationship with human beings.
Source: University of Copenhagen
Using stool samples from Viking latrines, researchers at the University of Copenhagen have genetically mapped one of the oldest human parasites – the whipworm. The mapping reflects the parasite’s global spread and its interaction with human beings, a delicate relationship that can make us healthier and ill.
Using fossilized eggs in up to 2500-year-old feces from Viking settlements in Denmark and other countries, researchers at the University of Copenhagen’s Department of Plant and Environmental Sciences and the Wellcome Sanger Institute (UK) have made the largest and most in-depth genetic analysis of one of the oldest parasites found in humans – the whipworm.
The study, published in Nature Communications, presents completely new knowledge about the parasite’s development and prehistoric dispersal. This knowledge can be applied in efforts to prevent the parasite’s drug resistance and its future spread.
The study suggests that human and parasite have developed a delicate interaction over thousands of years, whereby the parasite tries to stay “under the radar” not to be repelled, which allows it more time to infect new people. From other studies, it is known that the whipworm stimulates the human immune system and the gut microbiome, to the mutual benefit of both host and parasite.
While whipworm (Trichuris trichiura) is now rare in industrialized countries, and most often only causes minor problems among healthy individuals, the parasite is estimated to affect 500 million people in developing countries.
“In people who are malnourished or have impaired immune systems, whipworm can lead to serious illness. Our mapping of the whipworm and its genetic development makes it easier to design more effective anti-worm drugs that can be used to prevent the spread of this parasite in the world’s poorest regions,” says Professor Christian Kapel of UCPH’s Department of Plant and Environmental Sciences.
Fossilized latrine poop from Copenhagen and Viborg
Eggs, not worms, made it possible for researchers to examine the genetic material of thousands-of-years-old whipworms. Due to extremely durable chitin in egg capsules, their internal DNA has been well preserved while the eggs have been buried in moist soil.
By examining fossilized stool samples which were previously discovered in the latrines of Viking settlements in Viborg and Copenhagen, the researchers isolated the eggs under a microscope, sieved them from the stool and subjected them to refined genetic analyses that the researchers have been perfecting for years in previous studies.
“We have known for a long time that we could detect parasite eggs up to 9000 years old under a microscope. Lucky for us, the eggs are designed to survive in soil for long periods of time. Under optimal conditions, even the parasite’s genetic material can be preserved extremely well. And some of the oldest eggs that we’ve extracted some DNA from are 5000 years old. It has been quite surprising to fully map the genome of 1000-year-old well-preserved whipworm eggs in this new study,” explains Christian Kapel.
The researchers examined archaeological stool samples from several locations. These ancient genetic samples are compared with contemporary samples obtained from people with whipworms from around the world. Doing so has provided researchers with an overview of the worm’s genome and its evolution over ten-thousands of years.
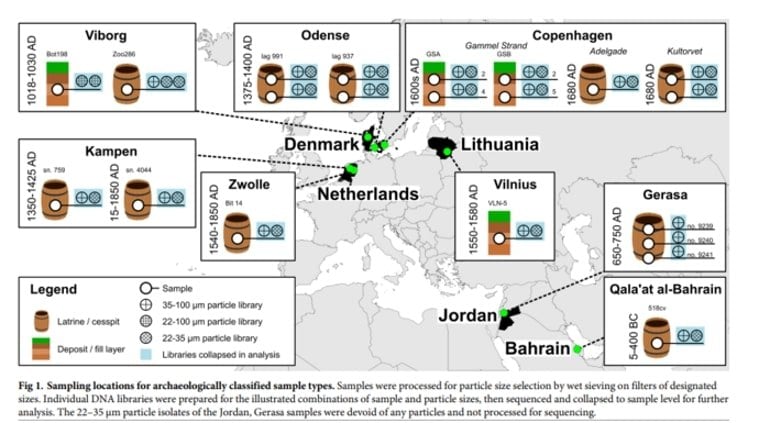
“Unsurprisingly, we can see that the whipworm appears to have spread from Africa to the rest of the world along with humans about 55,000 years ago, following the so-called ‘out of Africa’ hypothesis on human migration,” explains Christian Kapel.
Can live unnoticed in the intestine for months
A whipworm can grow five to seven centimeters in length and live unnoticed in the intestine of a healthy individual for several months. During this time, it lays eggs continuously, which are expelled through feces. In people with weakened immune systems, whipworm can cause a wide range of gastrointestinal diseases, malnutrition and even delay childhood development.
Worms are transmitted via the fecal-oral route, meaning that microscopic parasite eggs in soil can spread to drinking water or food, after which they are ingested through the mouth of a new host.
“The eggs lie in the ground and develop for roughly three months. Once matured, eggs can survive in the wild for even longer, as they wait to be consumed by a new host in whose digestive tract they will then hatch. Their entire life cycle is adapted to survive in soil for as long as possible,” explains Christian Kapel.
As such, the golden years for these worms in our part of the world were when our toilet and kitchen conditions, as well as personal hygiene, were significantly different than today.
“During the Viking Age and well into the Middle Ages, one didn’t have very sanitary conditions or well-separated cooking and toilet facilities. This allowed the whipworm far better opportunities to spread. Today, it is very rare in the industrialized part of world. Unfortunately, favorable conditions for spreading still exist in less developed regions of the world,” says Christian Kapel.
Funding: The study is led by the University of Copenhagen’s Department of Plant and Environmental Sciences, Section for Organism Biology and made in collaboration with the Wellcome Sanger Institute (UK).
About this evolution research news
Author: Michael Jensen
Source: University of Copenhagen
Contact: Michael Jensen – University of Copenhagen
Image: The image is credited to University of Copenhagen
Original Research: Open access.
“Population genomics of ancient and modern Trichuris trichiura” by Christian Kapel et al. Nature Communications
Abstract
Population genomics of ancient and modern Trichuris trichiura
The neglected tropical disease trichuriasis is caused by the whipworm Trichuris trichiura, a soil-transmitted helminth that has infected humans for millennia.
Today, T. trichiura infects as many as 500 million people, predominantly in communities with poor sanitary infrastructure enabling sustained faecal-oral transmission.
Using whole-genome sequencing of geographically distributed worms collected from human and other primate hosts, together with ancient samples preserved in archaeologically-defined latrines and deposits dated up to one thousand years old, we present the first population genomics study of T. trichiura.
We describe the continent-scale genetic structure between whipworms infecting humans and baboons relative to those infecting other primates. Admixture and population demographic analyses support a stepwise distribution of genetic variation that is highest in Uganda, consistent with an African origin and subsequent translocation with human migration.
Finally, genome-wide analyses between human samples and between human and non-human primate samples reveal local regions of genetic differentiation between geographically distinct populations.
These data provide insight into zoonotic reservoirs of human-infective T. trichiura and will support future efforts toward the implementation of genomic epidemiology of this globally important helminth.