Summary: A new review of almost 200 publications suggests the gut microbiota may play a critical role in modulating brain function, social behavior and other symptoms of autism.
Source: USC
A new scoping review of nearly 200 publications covering the relationships between autism spectrum disorder and the brain–gut–microbiome system was published online today in Nutrients.
The review synthesizes the growing body of research suggesting that gut microbiota—the trillions of microorganisms living within the human digestive system—may serve critical roles in modulating brain functions, social behaviors and autistic symptoms.
Two of the review’s co-first authors, Michelle Chernikova and Genesis Flores, were participants in USC’s Diversity, Inclusion, and Access JumpStart program, a structured summer research program for talented undergraduates considering pursuing a Ph.D. degree, at the time of literature review and manuscript preparation.
Joining as co-first author is Emily Kilroy Ph.D. ’18, Postdoc ’22, a postdoctoral scholar in the USC Chan Division of Occupational Science and Occupational Therapy. Jennifer Labus and Emeran Mayer, microbiologists at the University of California, Los Angeles, are co-authors. Senior author is Lisa Aziz-Zadeh, associate professor at the USC Chan Division jointly appointed to the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences’ Brain and Creativity Institute.
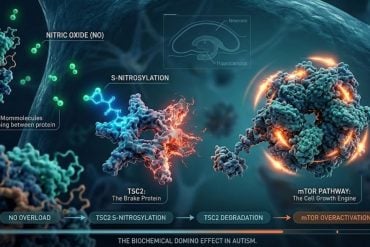
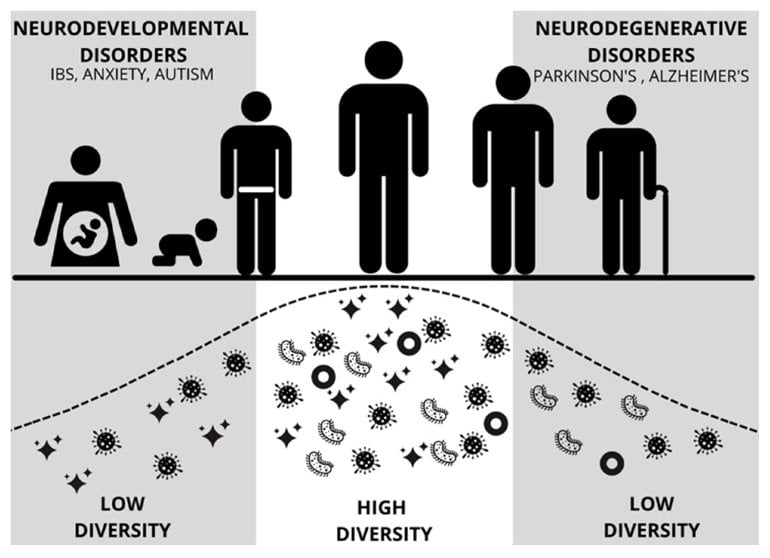
The review synthesizes current understandings about the mechanisms by which gut microbiota, metabolic substances and the brain communicate to influence behaviors, including the different social–communication and restricted or repetitive patterns that characterize autism. Gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea have been reported in 46 to 84 percent of autistic people, giving recent rise to a hypothesis that gut dysregulation may be especially prevalent in autistic populations.
The paper was supported in part by Aziz-Zadeh’s four-year, $506,000 grant from the U.S. Department of Defense’s (DoD) Autism Research Program Idea Development Award.
“To date, most autism studies in humans either look at the brain and behavior, or at the gut microbiome and behavior,” Aziz-Zadeh said. “Our DoD study is one of the largest autism studies to look at all three factors together—brain, gut and behavior. The current paper in Nutrients lays down the theory behind this endeavor, reviewing everything from rodent studies on the topic, potential neurotransmitter pathways that may be involved and potential brain regions that may be modified by this interaction.”
Scientists have yet to determine the exact microbial composition associated with autism, and the authors recommend several future research directions. Those include the need for more standardized sampling, collection and analyses; research studying the prenatal gut microbiome in pregnant mothers; studies comparing the microbiomes of autistic and typically-developing populations; and longitudinal tracking of metabolic states and specific biomarkers through early childhood development.
Two of the review’s co-first authors, Michelle Chernikova and Genesis Flores, were participants in USC’s Diversity, Inclusion, and Access JumpStart program, a structured summer research program for talented undergraduates considering pursuing a Ph.D. degree, at the time of literature review and manuscript preparation.
Joining as co-first author is Emily Kilroy Ph.D. ’18, Postdoc ’22, a postdoctoral scholar in the USC Chan Division of Occupational Science and Occupational Therapy. Jennifer Labus and Emeran Mayer, microbiologists at the University of California, Los Angeles, are co-authors. Senior author is Lisa Aziz-Zadeh, associate professor at the USC Chan Division jointly appointed to the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences’ Brain and Creativity Institute.
The review synthesizes current understandings about the mechanisms by which gut microbiota, metabolic substances and the brain communicate to influence behaviors, including the different social–communication and restricted or repetitive patterns that characterize autism. Gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain, constipation and diarrhea have been reported in 46 to 84 percent of autistic people, giving recent rise to a hypothesis that gut dysregulation may be especially prevalent in autistic populations.
The paper was supported in part by Aziz-Zadeh’s four-year, $506,000 grant from the U.S. Department of Defense’s (DoD) Autism Research Program Idea Development Award.
“To date, most autism studies in humans either look at the brain and behavior, or at the gut microbiome and behavior,” Aziz-Zadeh said. “Our DoD study is one of the largest autism studies to look at all three factors together—brain, gut and behavior. The current paper in Nutrients lays down the theory behind this endeavor, reviewing everything from rodent studies on the topic, potential neurotransmitter pathways that may be involved and potential brain regions that may be modified by this interaction.”
Scientists have yet to determine the exact microbial composition associated with autism, and the authors recommend several future research directions. Those include the need for more standardized sampling, collection and analyses; research studying the prenatal gut microbiome in pregnant mothers; studies comparing the microbiomes of autistic and typically-developing populations; and longitudinal tracking of metabolic states and specific biomarkers through early childhood development.
About this autism research news
Author: Mike McNulty
Source: USC
Contact: Mike McNulty – USC
Image: The image is credited to the researchers
Original Research: Open access.
“The Brain-Gut-Microbiome System: Pathways and Implications for Autism Spectrum Disorder” by Michelle A. Chernikova et al. Nutrients
Abstract
The Brain-Gut-Microbiome System: Pathways and Implications for Autism Spectrum Disorder
Gastrointestinal dysfunction is one of the most prevalent physiological symptoms of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). A growing body of largely preclinical research suggests that dysbiotic gut microbiota may modulate brain function and social behavior, yet little is known about the mechanisms that underlie these relationships and how they may influence the pathogenesis or severity of ASD.
While various genetic and environmental risk factors have been implicated in ASD, this review aims to provide an overview of studies elucidating the mechanisms by which gut microbiota, associated metabolites, and the brain interact to influence behavior and ASD development, in at least a subgroup of individuals with gastrointestinal problems.
\Specifically, we review the brain-gut-microbiome system and discuss findings from current animal and human studies as they relate to social-behavioral and neurological impairments in ASD, microbiota-targeted therapies (i.e., probiotics, fecal microbiota transplantation) in ASD, and how microbiota may influence the brain at molecular, structural, and functional levels, with a particular interest in social and emotion-related brain networks.
A deeper understanding of microbiome-brain-behavior interactions has the potential to inform new therapies aimed at modulating this system and alleviating both behavioral and physiological symptomatology in individuals with ASD.