LA BioMed researcher says study identified new potential site for medications to target.
In a promising finding for epileptic patients suffering from persistent seizures known as status epilepticus, researchers reported today that new medication could help halt these devastating seizures. To do so, it would have to work directly to antagonize NMDA receptors, the predominant molecular device for controlling synaptic activity and memory function in the brain.
“Despite the development of new medications to prevent seizures, status epilepticus remains a life-threatening condition that can cause extensive brain damage in the patients that survive these persistent seizures,” said David E. Naylor, MD, PhD, a lead researcher at the Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center (LA BioMed) and corresponding author of the new study. “Our research holds promise for the development of new therapies to treat this devastating condition because we have found a potential new target for medical intervention that should bolster the current standard therapies to treat the acute seizures. It may also prevent the long-term adverse effects of persistent seizure activity on the brain.”
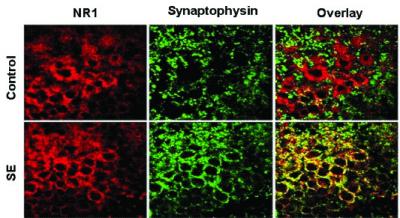
“The increased presence of the NMDA receptors on the cell surface during these seizures may explain the successful use of NMDA antagonists – medication that inhibits the activity of the NMDA receptors in the brain – in the latter stages of a seizure, long after other medications have stopped working,” said Dr. Naylor. “We concluded that medications that suppress the activity of the NMDA receptors, in conjunction with other medications, may be successful in stopping persistent seizures. Further research is, of course, needed.”
Notes about this epilepsy research article
In addition to Dr. Naylor, the researchers who participated in the study were Drs. Hantao Liu at the Veterans Administration Greater Los Angeles County Healthcare System’s Department of Neurology and Jerome Niquet and Claude G. Wasterlain of the David Geffen School of Medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles Department of Neurology. The research was funded by LA BioMed and a Veterans Administration Career Development Award.
Contact: Laura Mecoy – LA BioMed
Source: Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center (LA BioMed)
Image Source: NMDA receptors image credited to Dr. David E. Naylor, LA Biomed. This image accompanies the research article and has no usage restrictions.
Original Research: Abstract and highlights of “Rapid surface accumulation of NMDA receptors increases glutamatergic excitation during status epilepticus” by David E. Naylor, Hantao Liu, Jerome Niquet and Claude G. Wasterlain in Neurobiology of Disease. Posted online January 8, 2013 doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.12.015