New study points to a complex, diffuse patchwork of brain pathways.
Ancient Greek philosophers considered the ability to “know thyself” as the pinnacle of humanity. Now, thousands of years later, neuroscientists are trying to decipher precisely how the human brain constructs our sense of self.
Self-awareness is defined as being aware of oneself, including one’s traits, feelings, and behaviors. Neuroscientists have believed that three brain regions are critical for self-awareness: the insular cortex, the anterior cingulate cortex, and the medial prefrontal cortex.
However, a research team led by the University of Iowa has challenged this theory by showing that self-awareness is more a product of a diffuse patchwork of pathways in the brain—including other regions—rather than confined to specific areas.
Meet “Patient R”
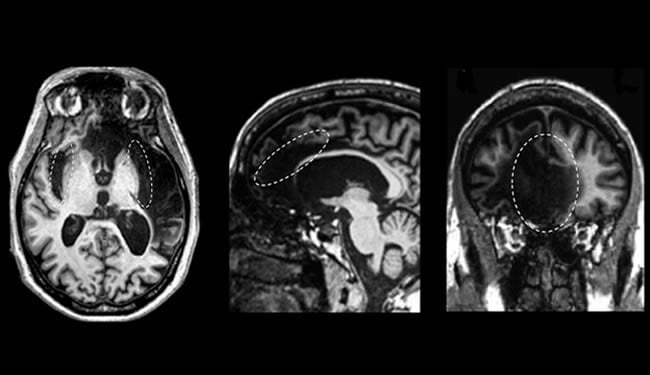
The conclusions came from a rare opportunity to study a person with extensive brain damage to the three regions believed critical for self-awareness. The person, a 57-year-old, college-educated man known as “Patient R,” passed all standard tests of self-awareness. He also displayed repeated self-recognition, both when looking in the mirror and when identifying himself in unaltered photographs taken during all periods of his life.
“What this research clearly shows is that self-awareness corresponds to a brain process that cannot be localized to a single region of the brain,” says David Rudrauf, co-corresponding author of the paper, published online Aug. 22 in the journal PLoS One. “In all likelihood, self-awareness emerges from much more distributed interactions among networks of brain regions.”
The authors believe the brainstem, thalamus, and posteromedial cortices play roles in self-awareness, as has been theorized.
Introspection and agency
The researchers observed that Patient R’s behaviors and communication often reflected depth and self-insight. First author Carissa Philippi, who earned her doctorate in neuroscience at the UI in 2011, conducted a detailed self-awareness interview with Patient R and found he had a deep capacity for introspection, one of humans’ most evolved features of self-awareness.
“During the interview, I asked him how he would describe himself to somebody,” says Philippi, now a postdoctoral research scholar at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. “He said, ‘I am just a normal person with a bad memory.’”
Patient R also demonstrated self-agency, meaning the ability to perceive that an action is the consequence of one’s own intention. When rating himself on personality measures collected over the course of a year, Patient R showed a stable ability to think about and perceive himself. However, his brain damage also affected his temporal lobes, causing severe amnesia that has disrupted his ability to update new memories into his “autobiographical self.” Beyond this disruption, all other features of R’s self-awareness remained fundamentally intact.
“Most people who meet R for the first time have no idea that anything is wrong with him,” notes Rudrauf, a former assistant professor of neurology at the UI and now a research scientist at the INSERM Laboratory of Functional Imaging in France. “They see a normal-looking middle-aged man who walks, talks, listens, and acts no differently than the average person.
“According to previous research, this man should be a zombie,” he adds. “But as we have shown, he is certainly not one. Once you’ve had the chance to meet him, you immediately recognize that he is self-aware.”
Unique pool of patients
Patient R is a member of the UI’s world-renowned Iowa Neurological Patient Registry, which was established in 1982 and has more than 500 active members with various forms of damage to one or more regions in the brain.
The researchers had begun questioning the insular cortex’s role in self-awareness in a 2009 study that showed that Patient R was able to feel his own heartbeat, a process termed “interoceptive awareness.”
The UI researchers estimate that Patient R has ten percent of tissue remaining in his insula and one percent of tissue remaining in his anterior cingulate cortex. Some had seized upon the presence of tissue to question whether those regions were in fact being used for self-awareness. But neuroimaging results presented in the current study reveal that Patient R’s remaining tissue is highly abnormal and largely disconnected from the rest of the brain.
“Here, we have a patient who is missing all the areas in the brain that are typically thought to be needed for self-awareness yet he remains self-aware,” says co-corresponding author Justin Feinstein, who earned his doctorate at the UI in February. “Clearly, neuroscience is only beginning to understand how the human brain can generate a phenomenon as complex as self-awareness.”
Notes about this neuroscience research
The research team included Daniel Tranel, UI professor of neurology and psychology and director of the Neuroscience Graduate Program; Gregory Landini, UI professor of philosophy; Antonio Damasio, professor of neuroscience at the University of Southern California; Sahib Khalsa, co-chief resident of psychiatry at the University of California Los Angeles; and Kenneth Williford, associate professor of philosophy and humanities at the University of Texas at Arlington.
This study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS, P01 NS19632), National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA, R01 DA022549), and the Mathers Foundation, and by funds from the University of Iowa, College of Medicine. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Written by John Riehl
Contacts: Justin Feinstein, Neurology – University of Iowa
David Rudrauf, Neurology – University of Iowa
John Riehl, Graduate College – University of Iowa
Source: University of Iowa press release
Image Source: Brain image adapted from University of Iowa press release image credited to the UI Department of Neurology.
Original Research: Open access research paper for “Preserved Self-Awareness following Extensive Bilateral Brain Damage to the Insula, Anterior Cingulate, and Medial Prefrontal Cortices” by Carissa L. Philippi, Justin S. Feinstein, Sahib S. Khalsa, Antonio Damasio, Daniel Tranel, Gregory Landini, Kenneth Williford, David Rudrauf in PLoS ONE 22 August 2012 7(8): e38413. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0038413







