Summary: Perineuronal nets (PNNs) and the neurons they enmesh can be damaged by poor diets. Excessive consumption of foods high in saturated fats and refined sugars cause inflammation and oxidative stress, resulting in cognitive decline and poor memory.
Source: University of Western Ontario
A poor diet might be damaging more than your waistline – it might be leading to cognitive decline and poor memory, according to Western-led research released this week.
The study, Perineuronal Nets: Plasticity, Protection, and Therapeutic Potential, describes the critical importance of perineuronal nets (PNNs) – structures that enmesh certain neurons in the brain – in protecting the neuron and regulating how often the brain turns experiences into memories.
Amy Reichelt, a BrainsCAN Postdoctoral Fellow, along with Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry neuroscientists Lisa Saksida and Tim Bussey, investigated PNNs to find out what effect they have on the brain and what happens when they’re not working.
“When you’re learning new things, you’re forming memories and making connections (synapses) between neurons in the brain,” said Reichelt, the study’s lead author. “PNNs can either prevent you from learning new things by maintaining existing connections, or they can enable you to form these long-lasting neural pathways in the brain that are vital for behaviour.”
Structurally, PNNs form mesh-like webs around neurons in the brain.
When working properly, PNNs protect neurons and synapses from toxins by forming a physical barrier or a shield around the neuron. PNNs also control the plasticity of these neurons by regulating the stimuli that could influence them.
However, if malfunctioning or nonexistent, neurons without PNNs might be influenced by all experiences, potentially resulting in memories of irrelevant information. This abnormal plasticity has been connected to neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders including anxiety disorders and drug addiction.
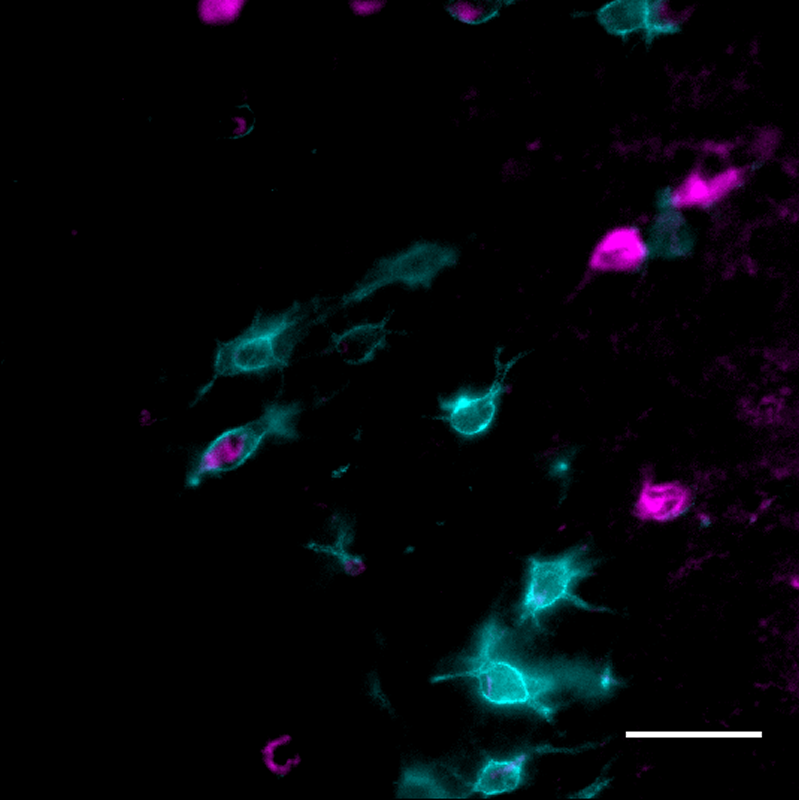
“If you remove PNNs from the area of the brain critical for recognition memory, the memories can last for much longer. This could be a way to overcome the cognitive deficits associated with Alzheimer’s disease,” said Reichelt, who also collaborated with study co-author Dominic Hare from the Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health at the University of Melbourne.
“The caveat is that increasing plasticity in the brain helps form lots of memories, but you’re also exposing your brain to damage because these PNNs protect your neurons.”
Reichelt’s work has shown that PNNs and the neurons they encase can be damaged by poor diets. Excessive consumption of junk foods high in saturated fats and refined sugars can cause toxic inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain resulting in cognitive decline and poor memory.
“If some neurons don’t have the PNNs protecting them they can be vulnerable to toxins,” Reichelt said.
“The inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain caused by junk food diets could be affecting these neurons in particular.”
This shows that diet and lifestyle may have an impact on other elements of the brain like PNNs, and not just the neurons. Reichelt’s research also demonstrates that certain lifestyle factors, including exercise or environmental enrichment, might improve cognition by naturally modifying the PNNs.
“This research gives rise to ideas that potential therapies don’t have to be drugs that affect the firing of neurons in the brain – they could be lifestyle changes that affect the environment the neurons and synapses are contained within,” Reichelt said. “What’s really exciting is that there’s more to the brain than neurons; we’re learning there are many factors that influence how our brain functions.”
Source:
University of Western Ontario
Media Contacts:
Jeff Renaud – University of Western Ontario
Image Source:
The image is credited to Reichelt et al.
Original Research: Closed access
“Perineuronal Nets: Plasticity, Protection, and Therapeutic Potential”. Amy C. Reichelt, Dominic J. Hare, Timothy J. Bussey, and Lisa M. Saksida.
Trends in Neuroscience. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2019.04.003
Abstract
Perineuronal Nets: Plasticity, Protection, and Therapeutic Potential
Perineuronal nets (PNNs) are extracellular matrix structures serving multiple functions, including regulating synaptic plasticity, stabilizing synapses, and protecting neurons from oxidative stress and neurotoxins.
Through their physiological roles, PNNs are also involved in cognition – including encoding, maintaining, and updating memories.
Removal of PNNs can render neurons vulnerable to damage – particularly in neurodegenerative conditions involving increased oxidative stress or neurotoxins.
Removal or digestion of PNNs in animal models increases plasticity, leading to enhanced memory interference from competing information during the encoding process.
Environmental factors, such as physical activity, drugs, and nutrition, can influence brain plasticity, and some of these effects may be mediated by changes in PNN structure.
Defining molecular targets that modify PNN structure may aid development of interventions for individuals experiencing cognitive decline linked to aberrant neural plasticity, such as in dementia.






