Summary: Brain imprints on cranial bones from humans and great apes refute the long-standing belief that the human pattern of brain asymmetry is unique. Researchers noted similar patterns of asymmetry in our great ape ancestors. However, there was more variability in this pattern in humans. Findings suggest lateralized and uniquely human cognitive abilities, such as language, evolved by adapting an ancestral brain asymmetry pattern.
Source: Max Planck Institute
The left and right side of the brain are involved in different tasks. This functional lateralization and associated brain asymmetry are well documented in humans, but little is known about brain asymmetry in our closest living relatives, the great apes. Using endocasts (imprints of the brain on cranial bones), scientists now challenge the long-held notion that the human pattern of brain asymmetry is unique. They found the same asymmetry pattern in chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans. However, humans were the most variable in this pattern. This suggests that lateralized, uniquely human cognitive abilities, such as language, evolved by adapting a presumably ancestral asymmetry pattern.
The left and right side of our brain are specialized for some cognitive abilities. For example, in humans, language is processed predominantly in the left hemisphere, and the right hand is controlled by the motor cortex in the left hemisphere. The functional lateralization is reflected by morphological asymmetry of the brain. Left and right hemisphere differ subtly in brain anatomy, the distribution of nerve cells, their connectivity and neurochemistry. Asymmetries of outer brain shape are even visible on endocasts. Most humans have a combination of a more projecting left occipital lobe (located in the back of the brain) with a more projecting right frontal lobe. Brain asymmetry is commonly interpreted as crucial for human brain function and cognition because it reflects functional lateralization. However, comparative studies among primates are rare and it is not known which aspects of brain asymmetry are really uniquely human. Based on previously available data, scientists assumed that many aspects of brain asymmetry evolved only recently, after the split between the human lineage from the lineage of our closest living relatives, the chimpanzees.
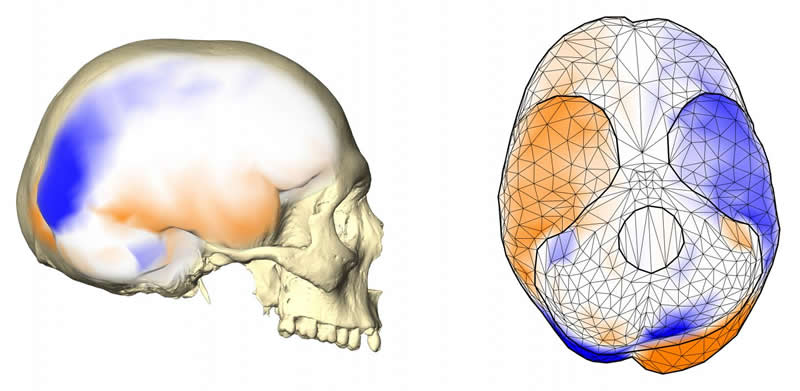
In a new paper researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and the University of Vienna measured the magnitude and pattern of shape asymmetry of endocasts from humans and apes. “Great ape brains are rarely available for study, but we have developed methods to extract brain asymmetry data from skulls, which are easier to access. This made our study possible in the first place”, says lead author Simon Neubauer.
The team found that the magnitude of asymmetry was about the same in humans and most great apes. Only chimpanzees were, on average, less asymmetric than humans, gorillas, and orangutans. They also investigated the pattern of asymmetry and could demonstrate that not only humans, but also chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans showed the asymmetry pattern previously described as typically human: the left occipital lobe, the right frontal lobe, as well as the right temporal pole and the right cerebellar lobe projecting more relatively to their contralateral parts. “What surprised us even more,” says Philipp Mitteroecker, a co-author of the study, “was that humans were least consistent in this asymmetry with a lot of individual variation around the most common pattern.” The authors interpret this as a sign of increased functional and developmental modularization of the human brain. For example, the differential projections of the occipital lobe and the cerebellum are less correlated in humans than in great apes. This finding is interesting because the cerebellum in humans underwent dramatic evolutionary changes and it seems that thereby its asymmetry was affected as well.
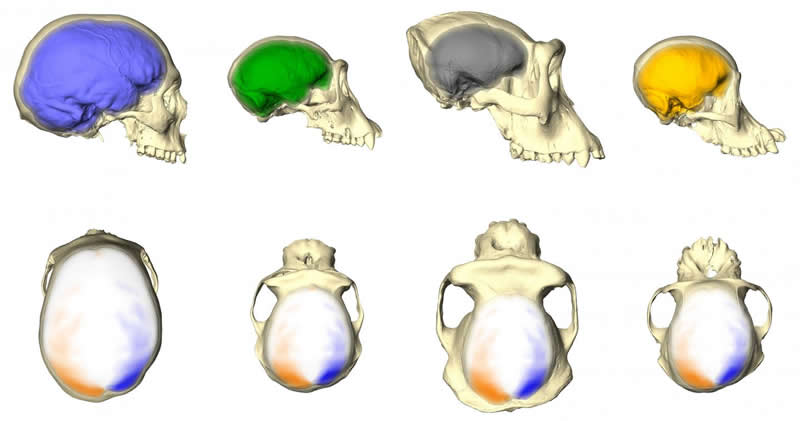
The finding of a shared asymmetry pattern but greater variability in humans is intriguing for the interpretation of human brain evolution. An endocast of one of our fossil ancestors that shows this asymmetry can no longer be interpreted as evidence for human-specific functional brain lateralization without other (archaeological) data. Philipp Gunz, a co-author of the study, explains: “This shared asymmetry pattern of the brain evolved already before the origin of the human lineage. Humans seem to have built upon this morphological pattern to establish functional brain lateralization related to typical human behaviors.”
Source:
Max Planck Institute
Media Contacts:
Dr. Simon Neubauer – Max Planck Institute
Image Source:
The images are credited to Simon Neubauer, CC BY-NC-ND 4.0.
Original Research: Open access
“Evolution of brain lateralization: A shared hominid pattern of endocranial asymmetry is much more variable in humans than in great apes”. Simon Neubauer, Philipp Gunz, Nadia A. Scott, Jean-Jacques Hublin and Philipp Mitteroecker.
Science Advances doi:10.1126/sciadv.aax9935.
Abstract
Evolution of brain lateralization: A shared hominid pattern of endocranial asymmetry is much more variable in humans than in great apes
Brain lateralization is commonly interpreted as crucial for human brain function and cognition. However, as comparative studies among primates are rare, it is not known which aspects of lateralization are really uniquely human. Here, we quantify both pattern and magnitude of brain shape asymmetry based on endocranial imprints of the braincase in humans, chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans. Like previous studies, we found that humans were more asymmetric than chimpanzees, however so were gorillas and orangutans, highlighting the need to broaden the comparative framework for interpretation. We found that the average spatial asymmetry pattern, previously considered to be uniquely human, was shared among humans and apes. In humans, however, it was less directed, and different local asymmetries were less correlated. We, thus, found human asymmetry to be much more variable compared with that of apes. These findings likely reflect increased functional and developmental modularization of the human brain.






