Summary: Scientists have identified three acidic cannabinoids in cannabis that reduces seizure activity in mouse models of Dravet syndrome.
Source: University of Sydney
Research from pharmacologists at the University of Sydney provides new insights into how cannabis extracts may work to treat epilepsy.
The study for the first time reports that three acidic cannabinoids found in cannabis reduced seizures in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome, an intractable form of childhood epilepsy.
The study has been published in the British Journal of Pharmacology.
“From the early nineteenth century cannabis extracts were used in Western medicine to treat seizures but cannabis prohibition got in the way of advancing the science,” said Associate Professor Jonathon Arnold from the Lambert Initiative for Cannabinoid Therapeutics and the Sydney Pharmacy School.
“Now we are able to explore how the compounds in this plant can be adapted for modern therapeutic treatments.”
In 2015, Barry and Joy Lambert made a historic donation to the University of Sydney to advance scientific research on medicinal cannabis and cannabinoid therapeutics. Barry and Joy’s granddaughter Katelyn suffers from Dravet syndrome, which features frequent seizures and causes delays in cognitive and motor development. Conventional therapies often do not provide adequate seizure control and patients have a reduced quality of life.
The Lambert family say they witnessed a dramatic improvement in Katelyn’s health using a cannabis extract and became ardent supporters of cannabis for therapeutic treatment. They also wished to better understand how cannabis works to treat epilepsy and other health conditions.
“After using hemp oil for treatment, we got our daughter back. Instead of fearing constant seizures we had some hope that our daughter could have a life worth living. It was like the noise cleared from her mind and she was able to wake up. Today Katelyn really enjoys her life,” said Michael Lambert, Katelyn’s father.
In 2015 the Lambert Initiative established a preclinical epilepsy research program to help understand how cannabis extracts, a mixture of hundreds of bioactive molecules, have anticonvulsant effects.
Associate Professor Arnold said: “Our research program is systematically testing whether the various constituents of cannabis reduce seizures in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome. We started by testing the compounds individually and found several cannabis constituents with anticonvulsant effects.”
“In this latest paper we describe the anticonvulsant effects of three rarer cannabinoids, all of which are cannabinoid acids.”
Acidic cannabinoids are the cannabinoids that are biosynthesised in the plant and are found in artisanal cannabis extracts used to treat children with epilepsy. One of these cannabinoids, cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), is the “mother of all cannabinoids”, Associate Professor Arnold said, as it is the precursor molecule to the creation of better-known cannabinoids, like cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
“The cannabinoid acids are abundant in cannabis but have received much less scientific attention. We are just beginning to understand their therapeutic potential,” Associate Professor Arnold said.
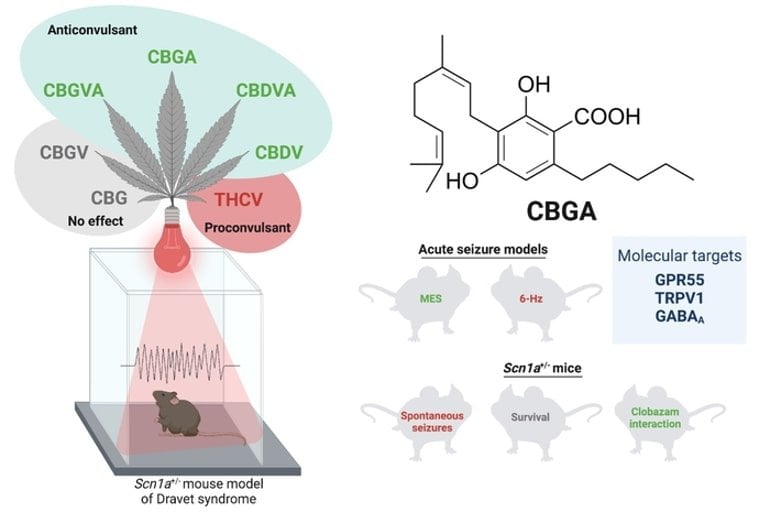
Lead author of the study, Dr Lyndsey Anderson, said: “We found that CBGA was more potent than CBD in reducing seizures triggered by a febrile event in a mouse model of Dravet syndrome. Although higher doses of CBGA also had proconvulsant effects on other seizure types highlighting a limitation of this cannabis constituent. We also found CBGA to affect many epilepsy-relevant drug targets.”
The study involved University of Sydney researchers in the School of Psychology and the Sydney Pharmacy School in collaboration with the laboratory of Dr Jennifer Kearney at Northwestern University (US). Dr Kearney developed the genetic mouse model used in the study and mentored Dr Anderson before she moved to Australia.
The team is continuing their research hoping to develop a better cannabis-based treatment for Dravet syndrome. Many in the community strongly believe there is something uniquely therapeutic about the full spectrum of cannabis components working together.
“We have assessed the cannabinoids one by one and now we are exploring what happens when you put them all back together. There remains a real possibility that all these individual anticonvulsant cannabinoids might work better when combined,” Dr Anderson said.
Barry Lambert said: “We are very proud of the work done by the many researchers at the Lambert Initiative, which is a world-leader in cannabinoid research, and in particular welcome these recent results on ‘the mother of all cannabinoids’.”
Funding: This study was funded by the Lambert Initiative for Cannabinoid Therapeutics and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council.
About this Dravet syndrome and neuropharmacology research news
Author: Marcus Strom
Source: University of Sydney
Contact: Marcus Strom – University of Sydney
Image: The image is credited to Lambert Initiative for Cannabinoid Therapeutics at the University of Sydney
Original Research: Open access.
“Cannabigerolic acid, a major biosynthetic precursor molecule in cannabis, exhibits divergent effects on seizures in mouse models of epilepsy” by Jonathon Arnold et al. British Journal of Pharmacology
Abstract
Cannabigerolic acid, a major biosynthetic precursor molecule in cannabis, exhibits divergent effects on seizures in mouse models of epilepsy
Background and Purpose
Cannabis has been used to treat epilepsy for millennia, with such use validated by regulatory approval of cannabidiol (CBD) for Dravet syndrome. Unregulated artisanal cannabis-based products used to treat children with intractable epilepsies often contain relatively low doses of CBD but are enriched in other phytocannabinoids. This raises the possibility that other cannabis constituents might have anticonvulsant properties.
Experimental Approach
We used the Scn1a+/− mouse model of Dravet syndrome to investigate the cannabis plant for phytocannabinoids with anticonvulsant effects against hyperthermia-induced seizures. The most promising, cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), was further examined against spontaneous seizures and survival in Scn1a+/− mice and in electroshock seizure models. Pharmacological effects of CBGA were surveyed across multiple drug targets.
Key Results
The initial screen identified three phytocannabinoids with novel anticonvulsant properties: CBGA, cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA) and cannabigerovarinic acid (CBGVA). CBGA was most potent and potentiated the anticonvulsant effects of clobazam against hyperthermia-induced and spontaneous seizures, and was anticonvulsant in the MES threshold test. However, CBGA was proconvulsant in the 6-Hz threshold test and a high dose increased spontaneous seizure frequency in Scn1a+/− mice. CBGA was found to interact with numerous epilepsy-relevant targets including GPR55, TRPV1 channels and GABAA receptors.
Conclusion and Implications
These results suggest that CBGA, CBDVA and CBGVA may contribute to the effects of cannabis-based products in childhood epilepsy. Although these phytocannabinoids have anticonvulsant potential and could be lead compounds for drug development programmes, several liabilities would need to be overcome before CBD is superseded by another in this class.






