Summary: Researchers report bone fractures in those with Down syndrome are unlikely to fully heal.
Source: Texas A&M
New research from the Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine & Biomedical Sciences (VMBS) is the first to provide direct experimental evidence that people with Down syndrome (DS) may not heal from bone fractures.
The recently published study, led by Kirby Sherman, a Ph.D. candidate in the VMBS’ Department of Veterinary Physiology & Pharmacology (VTPP), not only illuminates a previously unknown issue but also highlights a need for doctors to better address the issue of fracture healing in people with DS.
DS, the most common birth defect in the United States, alters human development and leads to a variety of clinical issues, which have included mental impairment, joint laxity, heart defects, sleep apnea, and infertility.
Previous research also had indicated that bone density in people with DS is lower, which increases the likelihood of bone fracture. Scientists previously believed that the healing response to fractures would be different in people with DS, but to discover that fractures in DS would not heal “was incredible,” Sherman said.
“Scientists have been studying fractures for a long time in a lot of different species, and while healing might be slow in some cases, the vast majority of fractures do eventually heal in all species,” Sherman said. “In our research, the fractures didn’t heal at all.
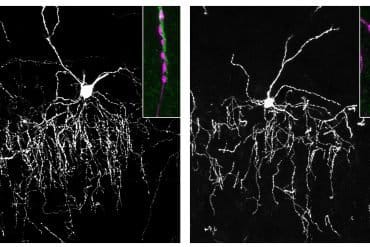
“When bones heal, a soft callous made of cartilage, a sort of glue, will form on the bones and then connect the fractured ends back together; we call this bridging,” said Sherman. “In Down syndrome models, the glue starts to form, but it’s never able to bridge.”
This is alarming, the researchers assert, because a fracture not fully healing can have devastating health impacts, which is compounded for those with DS because of their pronounced bone density loss.
“Based on this, the risk of fractures is a major health concern for the Down syndrome community,” Sherman said.
“A fracture not healing properly, what we call a non-union, can kill people, whether they have Down syndrome or not,” said Dr. Larry Suva, VTPP department head. “If this population really has a higher rate of non-union than the normal population, that’s a big deal.”
According to Suva and Sherman, there are two primary reasons this issue has gone undetected until now; the first is that those with DS are living much longer than they used to.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in 1960, people with DS had a life expectancy of just 10 years. By 2007, as more was learned and applied to offset the endocrine impacts of DS, the life expectancy increased to 47 years.
“We’ve known that bone mass is lower in this population, and the increased life expectancy of this population has allowed researchers to better understand the long-term implications of their lower bone mass,” said Suva. “Today, there are people with DS in their 20s and 30s who have bone mass and bone architecture consistent with someone in their 60s.
They’re active members of the community and they’re playing sports. Obviously, that’s great, but if they’re at increased risk of bone fractures that won’t heal, it’s also a concern.”
The second reason this issue stayed undetected for so long is that specialized care for people with DS has not been a consideration by doctors and hospitals, which means that there wasn’t data readily available to identify this issue.
“There’s not a medical code that identifies people with Down syndrome, so researchers have not had any kind of database they could use to gather statistics that support this kind of research,” said Suva. “Down syndrome support groups and family members don’t want their loved ones or themselves singled out for having a disease. After all, they’re normal people.
“As a result, even with all of the fractures that get recorded every day in the United States, there’s no way to identify which of those patients have Down syndrome and, therefore, no organized way to track their healing,” Suva said.
The next steps in the research will involve trying to find that human data, focusing on the actual mechanisms preventing the healing of the fractures. Since nobody knew this was a problem, nobody was looking for solutions.
In the meantime, with this new awareness of the problem, the researchers hope there will be more widespread adoption of measures to increase bone strength, more careful monitoring when fractures do occur, and that physicians and others will consider the bone health of people with DS.
“We want physicians to say to patients, ‘you’re 17 years old; you can keep playing soccer and being active,’” said Suva. “But we also want them making sure these patients’ diet and vitamin D levels are good, to do all of these things that are suggested for skeletal health. That’s our goal.”
About this neuroscience research news
Author: Lesley Henton
Source: Texas A&M
Contact: Lesley Henton – Texas A&M
Image: The image is in the public domain
Original Research: Closed access.
“Low bone mass and impaired fracture healing in mouse models of Trisomy21 (Down syndrome)” by Larry Suva et al. Bone
Abstract
Low bone mass and impaired fracture healing in mouse models of Trisomy21 (Down syndrome)
Individuals with Down syndrome (DS), the result of trisomy of human chromosome Hsa21 (Ts21), present with an array of skeletal abnormalities typified by altered craniofacial features, short stature and low bone mineral density (BMD).
While bone deficits progress with age in both sexes, low bone mass is more pronounced in DS men than women and osteopenia appears earlier. In the current study, the reproductive hormone status (FSH, LH, testosterone) of 17 DS patients (males, ages range 19–52 years) was measured.
Although testosterone was consistently low, the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis was intact with corresponding rises in FSH and LH. To provide further insight into the heterogeneity of the bone mass in DS, the skeletal phenotypes of three of the most used murine DS models, Ts65Dn (Ts65), TC1, and Dp16(Yey1) (Dp16) were characterized and contrasted.
Evaluation of the bone phenotype of both male and female 3-month-old Dp16 mice demonstrated sexual dimorphism, with low bone mass apparent in males, as it is in Ts65, but not in female Dp16. In contrast, male TC1 mice had no apparent bone phenotype. To determine whether low bone mass in DS impacted fracture healing, fractures of the middle phalanx (P2) digits were generated in both male and female Dp16 mice at 15 weeks of age, an age where the sexually dimorphic low BMD persisted.
Fracture healing was assessed via in vivo microCT over (13 weeks) 93 days post fracture (DPF). At 93 DPF, 0 % of DS male (n = 12) or female (n = 8) fractures healed, compared to 50 % of the male (n = 28) or female (n = 8) WT littermate fractures. MicroCT revealed periosteal unbridged mineralized callus formation across the fracture gap in Dp16 mice, which was confirmed by subsequent histology.
These studies provide the first direct evidence of significantly impaired fracture healing in the setting of DS.