Summary: Salk researchers report neurons from people on the autism spectrum exhibit different growth patterns and develop at a faster rate.
Source: Salk Institute.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a relatively common developmental disorder of communication and behavior that affects about 1 in 59 children in the US, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Despite its prevalence, it is still unclear what causes the disorder and what are the best ways to treat it.
Researchers at the Salk Institute compared stem cells created from individuals with ASD against stem cells created from those without ASD to uncover, for the first time, measurable differences in the patterns and speed of development in the ASD-derived cells.
The findings, published January 7, 2019, in the journal Nature Neuroscience, could lead to diagnostic methods to detect ASD at an early stage, when preventive interventions could potentially take place.
“Although our work only examined cells in cultures, it may help us understand how early changes in gene expression could lead to altered brain development in individuals with ASD,” says Salk Professor Rusty Gage, the study’s senior author and president of the Institute. “We hope that this work will open up new ways to study neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders.”
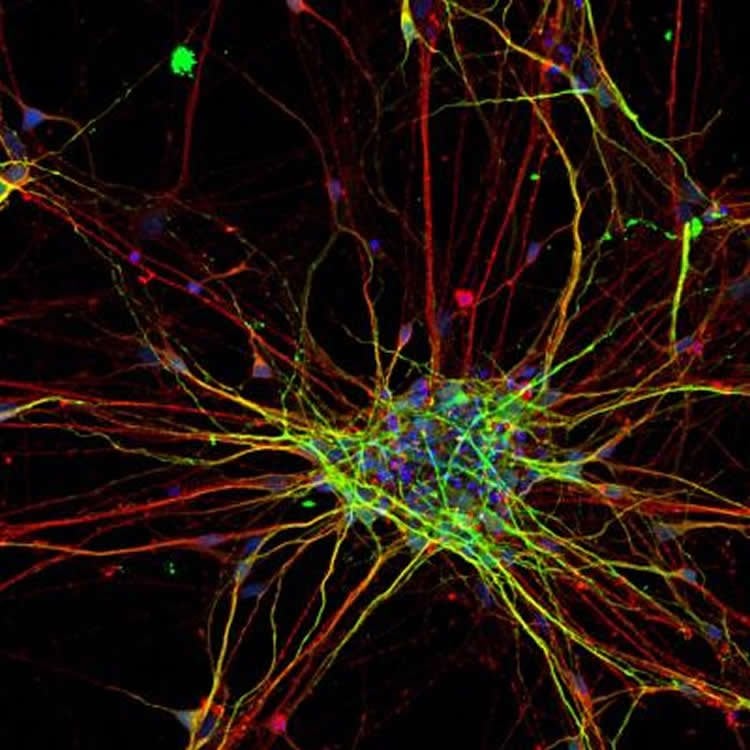
For the study, the researchers took skin cells from eight people with ASD and five people without ASD and turned them into pluripotent stem cells–cells that have the ability to develop into any cell type. They then coaxed the stem cells to develop along the path of becoming neurons by exposing them to certain chemical factors.
By using molecular “snapshots” from different developmental stages in the stem cells, the team was able to track genetic programs that switched on in a certain order as the stem cells developed into neurons. This revealed key differences in the cells derived from people with ASD. For instance, the Salk team observed that the genetic program associated with the neural stem-cell stage turned on earlier in the ASD cells than it did in the cells from those without ASD. This genetic program includes many genes that have been associated with higher chances of ASD. In addition, the neurons that eventually developed from the people with ASD grew faster and had more complex branches than those from the control group.
“It’s currently hypothesized that abnormalities in early brain development lead to autism, but the transition from a normally developing brain to an ASD diagnosis is blurred,” says first author Simon Schafer, a postdoctoral fellow in the Gage lab. “A major challenge in the field has been to determine the critical developmental periods and their associated cellular states. This research could provide a basis for discovering the common pathological traits that emerge during ASD development.”
“This is a very exciting finding, and it encourages us to further refine our methodological framework to help advance our understanding of the early cell biological events that precede the onset of symptoms,” adds Gage, who holds the Vi and John Adler Chair for Research on Age-Related Neurodegenerative Disease. “Studying system dynamics could maximize our chance of capturing relevant mechanistic disease states.”
The researchers say the experiments in this study will lead to more dynamic approaches for studying the mechanisms that are involved in ASD predisposition and progression.
They next plan to focus on the creation of brain organoids, three-dimensional models of brain development in a dish that enable scientists to study the interactions between different types of brain cells.
“The current diagnostic methods are mostly subjective and occur after the emergence of behavioral abnormalities in young children,” Schafer says. “We hope these studies will serve as a framework for developing novel approaches for diagnosis during an early period of child development–long before behavioral symptoms manifest–to have the maximum impact on treatment and intervention.”
Funding: This work was funded by The James S. McDonnell Foundation, G. Harold & Leila Y. Mathers Charitable Foundation, JPB Foundation, the March of Dimes Foundation, National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants MH095741 and MH090258, The Engman Foundation, Annette C. Merle-Smith, The Paul G. Allen Family Foundation, and The Leona M. and Harry B. Helmsley Charitable Trust. It was also supported by NIH grant P30 014195, the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the Chapman Foundation.
Source: Salk Institute
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to Salk Institute.
Original Research: Abstract for “Pathological priming causes developmental gene network heterochronicity in autistic subject-derived neurons” by Simon T. Schafer, Apua C. M. Paquola, Shani Stern, David Gosselin, Manching Ku, Monique Pena, Thomas J. M. Kuret, Marvin Liyanage, Abed AlFatah Mansour, Baptiste N. Jaeger, Maria C. Marchetto, Christopher K. Glass, Jerome Mertens & Fred H. Gage in Nature Neuroscience. Published January 7 2019.
doi:10.1038/s41593-018-0295-x
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]Salk Institute”How the Brain Decides Whether to Hold ’em or Fold ’em.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 7 January 2019.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/asd-development-10454/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]Salk Institute(2019, January 7). How the Brain Decides Whether to Hold ’em or Fold ’em. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved January 7, 2019 from https://neurosciencenews.com/asd-development-10454/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]Salk Institute”How the Brain Decides Whether to Hold ’em or Fold ’em.” https://neurosciencenews.com/asd-development-10454/ (accessed January 7, 2019).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Pathological priming causes developmental gene network heterochronicity in autistic subject-derived neurons
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is thought to emerge during early cortical development. However, the exact developmental stages and associated molecular networks that prime disease propensity are elusive. To profile early neurodevelopmental alterations in ASD with macrocephaly, we monitored subject-derived induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) throughout the recapitulation of cortical development. Our analysis revealed ASD-associated changes in the maturational sequence of early neuron development, involving temporal dysregulation of specific gene networks and morphological growth acceleration. The observed changes tracked back to a pathologically primed stage in neural stem cells (NSCs), reflected by altered chromatin accessibility. Concerted over-representation of network factors in control NSCs was sufficient to trigger ASD-like features, and circumventing the NSC stage by direct conversion of ASD iPSCs into induced neurons abolished ASD-associated phenotypes. Our findings identify heterochronic dynamics of a gene network that, while established earlier in development, contributes to subsequent neurodevelopmental aberrations in ASD.






