Brain imaging shows distinctive aspects of high-inflammation depression.
About one third of people with depression have high levels of inflammation markers in their blood. New research indicates that persistent inflammation affects the brain in ways that are connected with stubborn symptoms of depression, such as anhedonia, the inability to experience pleasure.
The results were published online on Nov. 10 in Molecular Psychiatry.
The findings bolster the case that the high-inflammation form of depression is distinct, and are guiding researchers’ plans to test treatments tailored for it.
Anhedonia is a core symptom of depression that is particularly difficult to treat, says lead author Jennifer Felger, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Emory University School of Medicine and Winship Cancer Institute.
“Some patients taking antidepressants continue to suffer from anhedonia,” Felger says. “Our data suggest that by blocking inflammation or its effects on the brain, we may be able to reverse anhedonia and help depressed individuals who fail to respond to antidepressants.”
In a study of 48 patients with depression, high levels of the inflammatory marker CRP (C-reactive protein) were linked with a “failure to communicate”, seen through brain imaging, between regions of the brain important for motivation and reward.
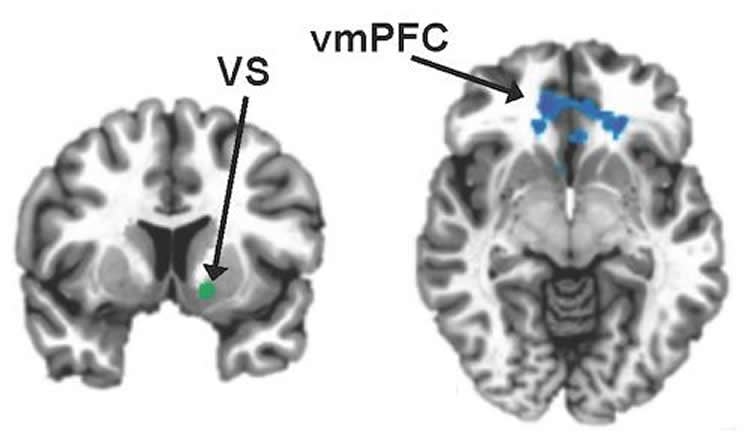
Neuroscientists can infer that two regions of the brain talk to each other by watching whether they light up in magnetic resonance imaging at the same times or in the same patterns, even when someone is not doing anything in particular. They describe this as “functional connectivity.”
In patients with high CRP, Felger and her colleagues observed a lack of connectivity between the ventromedial prefrontal cortex and the ventral striatum. In contrast, patients with low CRP had robust connectivity, they write.
“We were interested in these regions of the brain because of their known importance for response to reward,” she says. “In addition, we had seen reduced activation of these areas in people receiving immuno-stimulatory treatments for hepatitis C virus or cancer, which suggested that they may be sensitive to inflammation.”
High CRP levels were also correlated with patients’ reports of anhedonia: an inability to derive enjoyment from everyday activities, such as food or time with family and friends. Low connectivity between another region of the striatum and the ventromedial prefrontal cortex was linked to a different symptom: slow motor function, as measured by finger tapping speed.
During the brain imaging portion of the study, participants were not taking antidepressants, anti-inflammatory drugs or other medications for at least four weeks, and CRP was measured on repeat visits to make sure its levels were stable. High CRP was also correlated with BMI (body mass index), but the statistical relationship was strong even after correcting for BMI and other variables such as age.
A previous study of people with difficult-to-treat depression found that those with high inflammation (as measured with CRP), but not other participants in the study, improved in response to the anti-inflammatory antibody infliximab.
As a next step, Felger is planning to test whether L-DOPA, a medicine that targets the brain chemical dopamine, can increase connectivity in reward-related brain regions in patients with high-inflammation depression. This upcoming study is being supported by the Dana Foundation.
Felger’s previous research in non-human primates suggests that inflammation leads to reduced dopamine release. L-DOPA is a precursor for dopamine and often given to people with Parkinson’s disease.
“We hope our investigations may lead to new therapies to treat anhedonia in high-inflammation depression,” she says.
Funding: The study was funded by NIH/National Institute of Mental Health, Brain and Behavioral Research Foundation.
Source: Quinn Eastman – Emory University
Image Source: The image is credited to Felger et al, Molecular Psychiatry (2015)
Original Research: Full open access research for “Inflammation is associated with decreased functional connectivity within corticostriatal reward circuitry in depression” by J C Felger, Z Li, E Haroon, B J Woolwine, M Y Jung, X Hu and A H Miller in Molecular Psychiatry. Published online November 10 2015 doi:10.1038/mp.2015.168
Abstract
Inflammation is associated with decreased functional connectivity within corticostriatal reward circuitry in depression
Depression is associated with alterations in corticostriatal reward circuitry. One pathophysiological pathway that may drive these changes is inflammation. Biomarkers of inflammation (for example, cytokines and C-reactive protein (CRP)) are reliably elevated in depressed patients. Moreover, administration of inflammatory stimuli reduces neural activity and dopamine release in reward-related brain regions in association with reduced motivation and anhedonia. Accordingly, we examined whether increased inflammation in depression affects corticostriatal reward circuitry to lead to deficits in motivation and goal-directed motor behavior. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging was conducted on 48 medically stable, unmedicated outpatients with major depression. Whole-brain, voxel-wise functional connectivity was examined as a function of CRP using seeds for subdivisions of the ventral and dorsal striatum associated with motivation and motor control. Increased CRP was associated with decreased connectivity between ventral striatum and ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) (corrected P<0.05), which in turn correlated with increased anhedonia (R=−0.47, P=0.001). Increased CRP similarly predicted decreased dorsal striatal to vmPFC and presupplementary motor area connectivity, which correlated with decreased motor speed (R=0.31 to 0.45, P<0.05) and increased psychomotor slowing (R=−0.35, P=0.015). Of note, mediation analyses revealed that these effects of CRP on connectivity mediated significant relationships between CRP and anhedonia and motor slowing. Finally, connectivity between striatum and vmPFC was associated with increased plasma interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1beta and IL-1 receptor antagonist (R=−0.33 to −0.36, P<0.05). These findings suggest that decreased corticostriatal connectivity may serve as a target for anti-inflammatory or pro-dopaminergic treatment strategies to improve motivational and motor deficits in patients with increased inflammation, including depression. "Inflammation is associated with decreased functional connectivity within corticostriatal reward circuitry in depression" by J C Felger, Z Li, E Haroon, B J Woolwine, M Y Jung, X Hu and A H Miller in Molecular Psychiatry. Published online November 10 2015 doi:10.1038/mp.2015.168







