Summary: Parents who refuse to vaccinate their children against the flu may be exposed to limited, or inaccurate, information that impedes their decision, researchers report.
Source: University of Michigan.
Parents who decline to get their child vaccinated against the flu may be exposed to a limited range of information, a new national poll suggests.
And depending on which sources parents turn to the most, inaccurate information may influence their decision about flu vaccine for their child.
Annual flu vaccination is recommended for all children six months and older, but nearly a third of parents say they are not planning to get their child the vaccine this year, according to the C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health at the University of Michigan. The nationally-representative report is based on responses from 1,977 parents with at least one child ages 1-18.
Four in 10 parents overall say they base their decisions about the flu vaccine on what they read and hear – and those who do are less likely to have their child vaccinated than parents who follow their health care provider’s recommendation.
Among parents who decided to get flu vaccine for their child, the most common source of information that made them want the vaccine was their child’s health care provider, nurses and medical staff. However, 1 in 5 parents polled said their child’s provider did not make any recommendations about the vaccination.
“Child health providers are a critical source of information to explain the rationale for annual flu vaccination and to address parents’ questions about flu vaccine safety and effectiveness,” says poll co-director Sarah Clark. “Without clear guidance from the provider, parents may be left with misinformation, such as the suggestion that flu vaccine causes the flu.”
Parents who were unlikely to get flu vaccine for their child cited family, close friends, and other parents as the most common sources that made them either question the flu vaccine or opt against vaccinating their child.
And it wasn’t just the source of the information. Parents who said they would not get flu vaccine for their child reported seven times as many sources that made them question or not want the vaccine as sources in support of vaccination. The volume of negative information may make it less likely that they will change their minds.
“There appears to be an echo chamber around flu vaccine,” Clark says. “Parents who are not choosing flu vaccination for their child report hearing or reading opinions that question or oppose the vaccine. At the same time, parents who decided their child will get flu vaccine report opinions that largely support vaccination.”
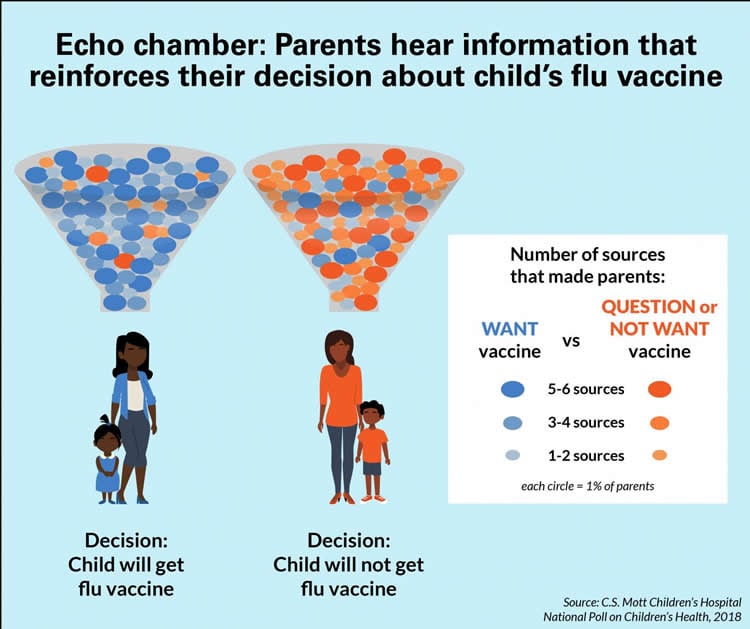
Clark says there are several possible explanations for this echo chamber. Some parents may seek out specific people and information sources who support their overall position on vaccines, so that what they hear and read is largely in line with their established opinions.
Other parents may encounter a broader range of information and opinions, but selectively remember only those that support their decision on whether their child will get flu vaccine.
“It’s important to acknowledge that for some parents, child health providers are not the sole influence, or even the primary influence, on decisions about the flu vaccine,” Clark says. “For these families, we need to explore other mechanisms to convey accurate information and allow parents to hear a more balanced viewpoint.”
Despite the recommendation to get children vaccinated against the flu, the vaccine rate among U.S. children is much lower for flu than for other childhood vaccines. In the last flu season between fall 2017 through spring 2018, a record-setting 180 children died from influenza. Less than 60 percent of the children had received the flu vaccine.
Source: Stephanie Berger – University of Michigan
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health at the University of Michigan.
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]University of Michigan”Does an ‘Echo Chamber’ of Information Impede Flu Vaccinations for Children?.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 19 November 2019.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/vaccine-misinformation-flu-10233/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]University of Michigan(2019, November 19). Does an ‘Echo Chamber’ of Information Impede Flu Vaccinations for Children?. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved November 19, 2019 from https://neurosciencenews.com/vaccine-misinformation-flu-10233/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]University of Michigan”Does an ‘Echo Chamber’ of Information Impede Flu Vaccinations for Children?.” https://neurosciencenews.com/vaccine-misinformation-flu-10233/ (accessed November 19, 2019).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]