Summary: According to researchers, people who suffer from migraines have higher sodium concentrations in their cerebrospinal fluid.
Source: RSNA.
Migraine sufferers have significantly higher sodium concentrations in their cerebrospinal fluid than people without the condition, according to the first study to use a technique called sodium MRI to look at migraine patients. The findings were presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Migraine, a type of headache characterized by severe head pain, and sometimes nausea and vomiting, is one of the most common headache disorders, affecting about 18 percent of women and 6 percent of men. Some migraines are accompanied by vision changes or odd sensations in the body known as auras. Diagnosis is challenging, as the characteristics of migraines and the types of attacks vary widely among patients. Consequently, many migraine patients are undiagnosed and untreated. Other patients, in contrast, are treated with medications for migraines even though they suffer from a different type of headache, such as the more common tension variety.
“It would be helpful to have a diagnostic tool supporting or even diagnosing migraine and differentiating migraine from all other types of headaches,” said study author Melissa Meyer, M.D., radiology resident at the Institute of Clinical Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, University Hospital Mannheim and Heidelberg University in Heidelberg, Germany.
Dr. Meyer and colleagues explored a magnetic resonance technique called cerebral sodium MRI as a possible means to help in the diagnosis and understanding of migraines. While MRI most often relies on protons to generate an image, sodium can be visualized as well. Research has shown that sodium plays an important role in brain chemistry.
The researchers recruited 12 women, mean age 34, who had been clinically evaluated for migraine. The women filled out a questionnaire regarding the length, intensity and frequency of their migraine attacks and accompanying auras. The researchers also brought in 12 healthy women of similar ages to serve as a control group. Both groups underwent cerebral sodium MRI. Sodium concentrations of migraine patients and healthy controls were compared and statistically analyzed.
The researchers found no statistical differences between the two groups for sodium concentrations in the gray and white matter, brain stem and cerebellum. However, significant differences emerged when the researchers looked at sodium concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid, the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord, providing a cushion for the brain while also helping to ensure chemical stability for proper brain function.
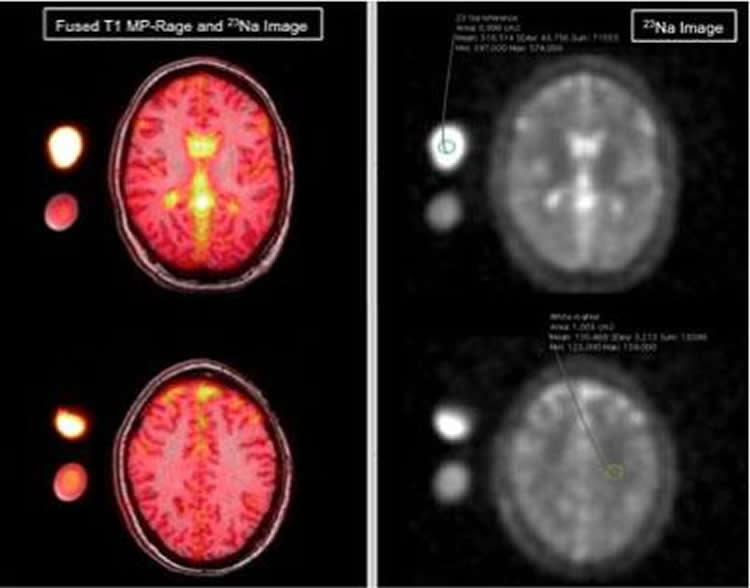
Overall, sodium concentrations were significantly higher in the brain’s cerebrospinal fluid in migraine patients than in the healthy control group.
“These findings might facilitate the challenging diagnosis of a migraine,” Dr. Meyer said.
The researchers hope to learn more about the connection between migraines and sodium in future studies.
“As this was an exploratory study, we plan to examine more patients, preferably during or shortly after a migraine attack, for further validation,” Dr. Meyer said.
Co-authors are Alexander Schmidt, Justus Benrath, Simon Konstandin, Ph.D., Lothar R. Schad, Ph.D., Stefan O. Schoenberg, M.D., Ph.D., and Stefan Haneder, M.D.
Source: Linda Brooks – RSNA
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to RSNA.
Original Research: The study will be presented at RSNA 2017 103rd Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting.
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]RSNA “Migraines Linked to High Sodium Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 28 November 2017.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/sodium-miraine-csf-8043/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]RSNA (2017, November 28). Migraines Linked to High Sodium Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved November 28, 2017 from https://neurosciencenews.com/sodium-miraine-csf-8043/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]RSNA “Migraines Linked to High Sodium Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid.” https://neurosciencenews.com/sodium-miraine-csf-8043/ (accessed November 28, 2017).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]







