A new MRI study has found distinct injury patterns in the brains of people with concussion-related depression and anxiety, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology. The findings may lead the way to improved treatment and understanding of these common disorders, researchers said.
Post-concussion psychiatric disorders like depression, anxiety and irritability can be extremely disabling for those among the nearly 3.8 million people in the United States who suffer concussions every year. The mechanisms underlying these changes after concussion–also known as mild traumatic brain injury–are not sufficiently understood, and conventional MRI results in most of these patients are normal.
For the new study, researchers from the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPMC) in Pittsburgh used diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), an MRI technique that measures the integrity of white matter–the brain’s signal-transmitting nerve fibers–to see if injuries to the nerves may be the root cause of these post-traumatic depression and anxiety symptoms.
The researchers obtained DTI and neurocognitive testing results for 45 post-concussion patients, including 38 with irritability, 32 with depression and 18 with anxiety, and compared the results with those of 29 post-concussion patients who had no neuropsychiatric symptoms.
“Using other concussion patients as our controls was a big advantage of our study,” said lead author Lea M. Alhilali, M.D., assistant professor of radiology at UPMC. “When you are able to study a similar population with similar risk factors, you get much more reliable results.”
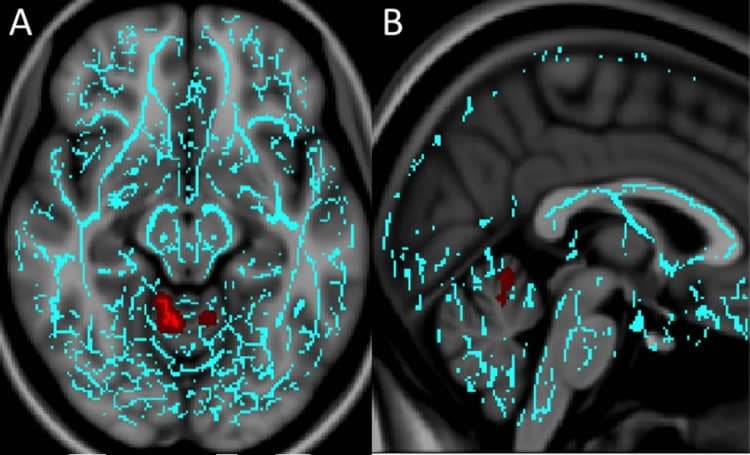
The researchers saw unique white matter injury patterns in the patients who had depression or anxiety. Compared to controls, patients with depression had decreased fractional anisotropy (FA), a measure of the structural integrity of white matter connections, around an area near the deep gray matter of the brain that is strongly associated with the brain’s reward circuit.
“The regions injured in concussion patients with depression were very similar to those of people with non-traumatic major depression disorder,” Dr. Alhilali said. “This suggests there may be similar mechanisms to non-trauma and trauma-dependent depression that may help guide treatment.”
Anxiety patients had diminished FA in a part of the brain called the vermis that helps modulate fear-related behaviors. Since the vermis has not been associated with dysfunction in non-traumatic anxiety disorders, this finding may indicate that different treatment targets are required for patients with anxiety after trauma, the researchers said.
No regions of significantly decreased FA were seen in patients with irritability relative to the control subjects.
“There are two major implications for this study,” Dr. Alhilali said. “First, it gives us insight into how abnormalities in the brain occur after trauma, and second, it shows that treatments for non-trauma patients with neuropsychological symptoms may be applicable to some concussion patients.”

The study also raises the possibility that some people diagnosed with non-traumatic depression may actually have experienced a subclinical traumatic event at some point earlier in their lives that may have contributed to the development of depression, she noted.
In the future, the researchers hope to compare DTI findings in concussion patients with depression to those of people who have non-trauma-related depressive disorders.
Source: Radiological Society of North America
Image Credit: The images are credited to Radiological Society of North America
Original Research: Full open access research for “Evaluation of White Matter Injury Patterns Underlying Neuropsychiatric Symptoms after Mild Traumatic Brain Injury” by Lea M. Alhilali, Joseph A. Delic, Serter Gumus, and Saeed Fakhran in Radiology. Published online June 16 2015 doi:10.1148/radiol.2015142974
Abstract
Evaluation of White Matter Injury Patterns Underlying Neuropsychiatric Symptoms after Mild Traumatic Brain Injury
Purpose
To determine if a central axonal injury underlies neuropsychiatric symptoms after mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) by using tract-based spatial statistics analysis of diffusion-tensor images.
Materials and Methods
The institutional review board approved this study, with waiver of informed consent. Diffusion-tensor imaging and serial neurocognitive testing with the Immediate Post-Concussion Assessment and Cognitive Testing evaluation were performed in 45 patients with mTBI (38 with irritability, 32 with depression, and 18 with anxiety). Control subjects consisted of 29 patients with mTBI without neuropsychiatric symptoms. Fractional anisotropy and diffusivity maps were analyzed by using tract-based spatial statistics with a multivariate general linear model. Diffusion-tensor imaging findings were correlated with symptom severity, neurocognitive test scores, and time to recovery with the Pearson correlation coefficient.
Results
Compared with control subjects, patients with mTBI and depression had decreased fractional anisotropy in the superior longitudinal fasciculus (P = .006), white matter around the nucleus accumbens (P = .03), and anterior limb of the internal capsule (P = .02). Patients with anxiety had diminished fractional anisotropy in the vermis (P = .04). No regions of significantly decreased fractional anisotropy were seen in patients with irritability relative to control subjects. Injury in the region of the nucleus accumbens inversely correlated with recovery time in patients with depression (r = −0.480, P = .005).
Conclusion
Unique white matter injury patterns were seen for two major posttraumatic neuropsychiatric symptoms. Injury to the cerebellar vermis in patients with mTBI and anxiety may indicate underlying dysfunction in primitive fear conditioning circuits in the cerebellum. Involvement of the nucleus accumbens in depression after mTBI may suggest an underlying dysfunctional reward circuit that affects the prognosis in these patients.
“Evaluation of White Matter Injury Patterns Underlying Neuropsychiatric Symptoms after Mild Traumatic Brain Injury” by Lea M. Alhilali, Joseph A. Delic, Serter Gumus, and Saeed Fakhran in Radiology. Published online June 16 2015 doi:10.1148/radiol.2015142974