The progression of Alzheimer’s may slow once symptoms appear and do significant damage , according to a study investigating an inherited form of the disease.
In a paper published in the prestigious journal Science Translational Medicine, Professor Colin Masters from the Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health and University of Melbourne – and colleagues in the UK and US – have found rapid neuronal damage begins 10 to 20 years before symptoms appear.
“As part of this research we have observed other changes in the brain that occur when symptoms begin to appear. There is actually a slowing of the neurodegeneration,” said Professor Masters.
Autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s affects families with a genetic mutation, predisposing them to the crippling disease. These families provide crucial insight into the development of Alzheimer’s because they can be identified years before symptoms develop. The information gleaned from this group will also influence treatment offered to those living with the more common age-related version. Only about one per cent of those with Alzheimer’s have the genetic type of the disease.
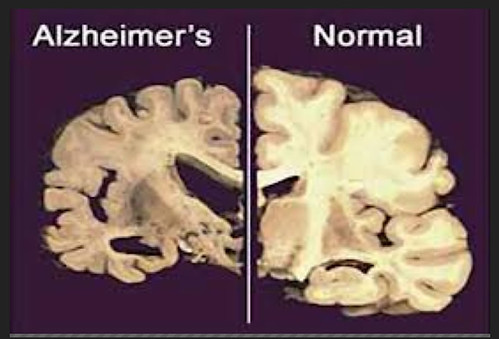
The next part of the study involves a clinical trial. Using a range of imaging techniques (MRI and PET) and analysis of blood and cerebrospinal fluid, individuals from the US, UK and Australia will be observed as they trial new drugs to test their safety, side effects and changes within the brain.
“As part of an international study, family members are invited to be part of a trial in which two experimental drugs are offered many years before symptoms appear,” Prof Masters says. “It’s going to be very interesting to see how clinical intervention affects this group of patients in the decades before symptoms appear.”
Notes about this Alzheimer’s disease research
The Florey is looking to recruit more participants in the Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network (DIAN) study. Those who either know they have a genetic mutation that causes autosomal-dominant Alzheimer’s or who don’t know their genetic status but have a parent or sibling with the mutation are invited to email: [email protected]
Contact: Anne Rahilly – University of Melbourne
Source: University of Melbourne press release
Image Source: The image is adapted from the University of Melbourne press release
Original Research: Abstract for “Longitudinal Change in CSF Biomarkers in Autosomal-Dominant Alzheimer’s Disease” by Anne M. Fagan, Chengjie Xiong, Mateusz S. Jasielec, Randall J. Bateman, Alison M. Goate, Tammie L. S. Benzinger, Bernardino Ghetti, Ralph N. Martins, Colin L. Masters, Richard Mayeux, John M. Ringman, Martin N. Rossor, Stephen Salloway, Peter R. Schofield, Reisa A. Sperling, Daniel Marcus, Nigel J. Cairns, Virginia D. Buckles, Jack H. Ladenson, John C. Morris, David M. Holtzman, and The Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network in Science Translational Medicine. Published online March 5 2014 doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3007901