Summary: A new study reveals lead exposure during childhood can significantly impact mental health and personality traits later in life. Researchers found exposure to leaded gasoline prior to the 1990s was linked to increased psychiatric symptoms experienced by adults.
Source: Duke University.
Lead exposure in childhood appears to have long-lasting negative effects on mental health and personality in adulthood, according to a study of people who grew up in the era of leaded gasoline.
Previous studies have identified a link between lead and intelligence, but this study looked at changes in personality and mental health as a result of exposure to the heavy metal.
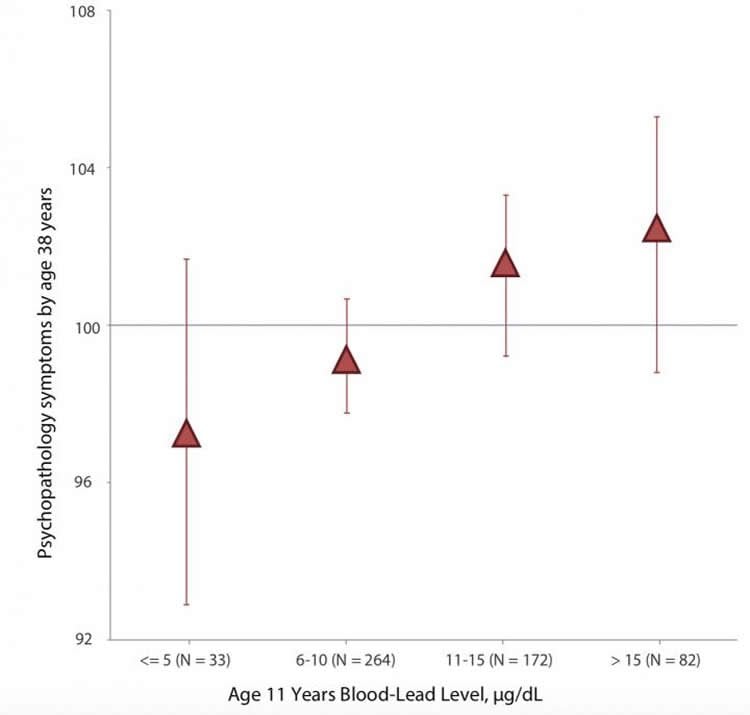
The findings, which will appear Jan. 23 in JAMA Psychiatry, reveal that the higher a person’s blood lead levels at age 11, the more likely they are to show signs of mental illness and difficult personality traits by age 38.
The link between mental health and lead exposure is modest, according to study coauthor Aaron Reuben, a graduate student in clinical psychology at Duke University. But “it’s potentially important because this is a modifiable risk factor that at one point in time everyone was exposed to, and now, certain people in certain cities and countries are still exposed to,” he said.
In a previous study, Reuben and colleagues showed that higher levels of lead in childhood were linked to lower IQ and lower social standing in adulthood.
Both sets of findings suggest that lead’s “effects really can last for quite a long time, in this case three to four decades,” said coauthor Jonathan Schaefer, also a graduate student in clinical psychology at Duke. “Lead exposure decades ago may be harming the mental health of people today who are in their 40s and 50s.”
Because gasoline around the world was treated with high levels of lead from the mid 1960s until the late 1980s, most adults now in their 30s, 40s, and 50s were exposed as children. Lead from automotive exhaust was released into the atmosphere and soils. Today, high lead exposures are rarer, and most often found in children who live in older buildings with lead plumbing and paint.
The subjects of this study are part of a group of more than 1,000 people born in 1972 and 1973 in Dunedin, New Zealand, at a time when gasoline lead levels in New Zealand were among the highest in the world. They have regularly participated in physical and mental health evaluations at the local University of Otago.
Researchers measured blood lead levels — in micrograms per deciliter of blood (ug/dL) — when participants were 11 years old. Today, blood lead levels above 5 ug/dL will trigger additional clinical follow-up of a child. At age 11, 94 percent of participants in the Dunedin Study had blood lead levels above this cutoff.
“These are historical data from an era when lead levels like these were viewed as normal in children and not dangerous, so most of our study participants were never given any treatment for lead toxicity,” said Terrie Moffitt, the senior author of the study and Duke’s Nannerl O. Keohane University Professor of psychology & neuroscience and psychiatry & behavioral sciences.
The Duke research team also assessed participant mental health and personality at various points throughout their lives, most recently at age 38. Diagnostic criteria or symptoms associated with eleven different psychiatric disorders — dependence on alcohol, cannabis, tobacco, or hard drugs; conduct disorder, major depression, generalized anxiety disorder, fears and phobias, obsessive-compulsive disorder, mania, and schizophrenia — were used to calculate a single measure of mental health, called the psychopathology factor, or “p-factor” for short.
The higher an individual’s p-factor score, the greater the number and severity of psychiatric symptoms. Lead’s effects on mental health as measured by the p-factor score are about as strong as those on IQ, explained coauthor Avshalom Caspi, Edward M. Arnett Professor of psychology & neuroscience and psychiatry & behavioral sciences at Duke. “If you’re worried about lead exposure’s impact on IQ, our study suggests you should probably also be worried about mental health,” Caspi said.
The research team also determined that participants exposed to higher levels of lead as children were described as having more difficult adult personalities by family members and friends. Specifically, they found that study members with greater lead exposure were rated as more neurotic, less agreeable, and less conscientious than their less-exposed peers.
These findings confirm personality characteristics that have been previously linked to a number of problems, including worse mental and physical health, reduced job satisfaction, and troubled interpersonal relationships.
“For folks who are interested in intervention and prevention, the study suggests that if you’re going to intervene on a group of kids or young adults that have been lead exposed, you may need to think very long-term when it comes to their care,” said Schaefer.
In the future, the Dunedin Study team is interested in whether lead exposure might be linked to the development of later-life diseases such as dementia or cardiovascular disease.
Reuben said the findings are relevant to other developed countries as well. “When we see changes that may be the result of lead exposures in New Zealand it’s very likely that you would have seen those same impacts in America, in Europe, and the other countries that were using leaded gasoline at the same levels at the same time.”
Funding: The New Zealand Health Research Council and the New Zealand Ministry of Business, Innovation, and Employment provided funding to the Dunedin Multidisciplinary Health and Development Research Unit. Support also came from grants T32AG000139 and AG032282 from the National Institute on Aging, T32HD007376 from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, F31ES029358 from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, and MR/P005918/1 from the UK Medical Research Council. The Jacobs Foundation and the Avielle Foundation provided additional funding.
Source: Karl Bates – Duke University
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to JAMA Psychiatry, 2019;76(4):1-9.
Original Research: Open access research for “Association of Childhood Lead Exposure With Adult Personality Traits and Lifelong Mental Health” by Aaron Reuben, MEM; Jonathan D. Schaefer, MA; Terrie E. Moffitt, PhD; Jonathan Broadbent, PhD; Honalee Harrington, BA; Renate M. Houts, PhD; Sandhya Ramrakha, PhD; Richie Poulton, PhD; and Avshalom Caspi, PhD in JAMA Psychiatry. Published January 238 2019.
doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.4192
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]Duke University”Childhood Lead Exposure Linked to Poor Adult Mental Health.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 223 January 2019.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/lead-exposure-mental-health-10622/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]Duke University(2019, January 223). Childhood Lead Exposure Linked to Poor Adult Mental Health. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved January 223, 2019 from https://neurosciencenews.com/lead-exposure-mental-health-10622/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]Duke University”Childhood Lead Exposure Linked to Poor Adult Mental Health.” https://neurosciencenews.com/lead-exposure-mental-health-10622/ (accessed January 223, 2019).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Association of Childhood Lead Exposure With Adult Personality Traits and Lifelong Mental Health
Importance
Millions of adults now entering middle age were exposed to high levels of lead, a developmental neurotoxin, as children. Although childhood lead exposure has been linked to disrupted behavioral development, the long-term consequences for adult mental and behavioral health have not been fully characterized.
Objective
To examine whether childhood lead exposure is associated with greater psychopathology across the life course and difficult adult personality traits.
Design, Setting, and Participants
This prospective cohort study was based on a population-representative birth cohort of individuals born between April 1, 1972, and March 31, 1973, in Dunedin, New Zealand, the Dunedin Multidisciplinary Health and Development Study. Members were followed up in December 2012 when they were 38 years of age. Data analysis was performed from March 14, 2018, to October 24, 2018.
Exposures
Childhood lead exposure ascertained as blood lead levels measured at 11 years of age. Blood lead levels were unrelated to family socioeconomic status.
Main Outcomes and Measures
Primary outcomes were adult mental health disorder symptoms assessed through clinical interview at 18, 21, 26, 32, and 38 years of age and transformed through confirmatory factor analysis into continuous measures of general psychopathology and internalizing, externalizing, and thought disorder symptoms (all standardized to a mean [SD] of 100 [15]) and adult personality assessed through informant report using the Big Five Personality Inventory (assessing neuroticism, extraversion, openness to experience, agreeableness, and conscientiousness) at 26, 32, and 38 years of age (all scores standardized to a mean [SD] of 0 [1]). Hypotheses were formulated after data collection; an analysis plan was posted in advance.
Results
Of 1037 original study members, 579 (55.8%) were tested for lead exposure at 11 years of age (311 [53.7%] male). The mean (SD) blood lead level was 11.08 (4.96) μg/dL. After adjusting for study covariates, each 5-μg/dL increase in childhood blood lead level was associated with a 1.34-point increase (95% CI, 0.11-2.57; P = .03) in general psychopathology, driven by internalizing (b = 1.41; 95% CI, 0.19-2.62; P = .02) and thought disorder (b = 1.30; 95% CI, 0.06-2.54; P = .04) symptoms. Each 5-μg/dL increase in childhood blood lead level was also associated with a 0.10-SD increase in neuroticism (95% CI, 0.02-0.08; P = .02), a 0.09-SD decrease in agreeableness (95% CI, −0.18 to −0.01; P = .03), and a 0.14-SD decrease in conscientiousness (95% CI, −0.25 to −0.03; P = .01). There were no statistically significant associations with informant-rated extraversion (b = −0.09; 95% CI, −0.17 to 0.004; P = .06) and openness to experience (b = −0.07; 95% CI, −0.17 to 0.03; P = .15).
Conclusions and Relevance
In this multidecade, longitudinal study of lead-exposed children, higher childhood blood lead level was associated with greater psychopathology across the life course and difficult adult personality traits. Childhood lead exposure may have long-term consequences for adult mental health and personality.