Summary: A new, non-invasive brain stimulation treatment shows promise in enhancing memories and cognitive function in those with Alzheimer’s disease. Transcranial electromagnetic treatment (TEMT) increases functional connectivity within the cingulate cortex. TEMT is also able to penetrate the brain to break up amyloid-beta and tau deposits, slowing the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
Source: IOS Press
There is finally some encouraging news for the millions of Americans suffering from Alzheimer’s Disease. NeuroEM Therapeutics today announced findings from an open-label clinical trial showing a reversal of cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease patients after just two months of treatment using the company’s wearable head device for in-home treatment.
Results demonstrate that TEMT was safe in all eight participating patients with mild to moderate AD and enhanced cognitive performance in seven of them, as measured by their ADAS-cog score, which is the benchmark for testing AD therapeutics. The study is being published in the new issue of the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
The investigators had previously demonstrated that treating AD mice with electromagnetic waves in the radiofrequency range resulted in protection against memory impairment in young AD mice and reversal of memory impairment in aged AD mice.
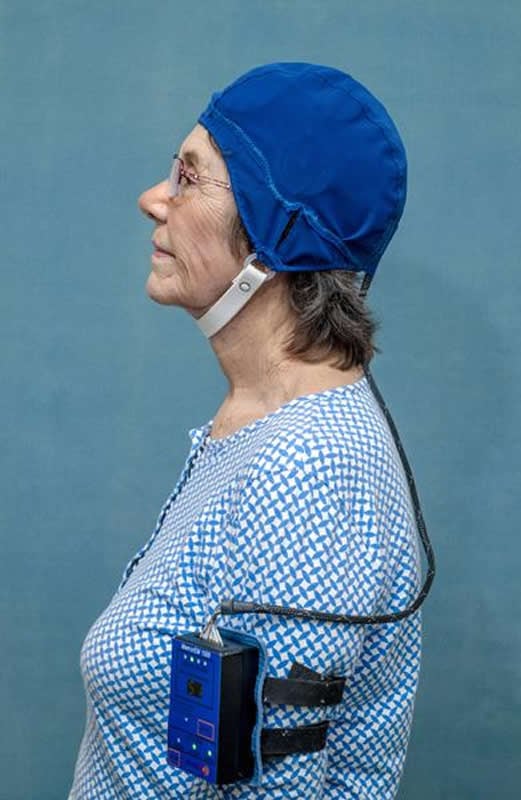
For the present clinical study in humans, the investigators used the same treatment (twice daily for 1-hour) through creation of NeuroEM’s first-in-class MemorEMTM head device. The device has multiple, highly-specialized emitters positioned within a head cap that are activated sequentially, with treatments easily administered in-home by the patient’s caregiver. As well, the device allows for near complete mobility to perform nearly all household activities during treatments.
“Perhaps the best indication that the two months of treatment was having a clinically-important effect on the AD patients in this study is that none of the patients wanted to return their head device to the University of South Florida/Byrd Alzheimer’s Institute after the study was completed”, said Dr.Gary Arendash, CEO of NeuroEM Therapeutics. One patient even exclaimed “I’ve come back.”
The investigators indicated they have strong evidence that TEMT is directly affecting the Alzheimer’s disease process by easily penetrating the brain and brain cells to break up aggregates of two toxic proteins inside brain cells called A-beta and tau.
TEMT’s ability to disaggregate both toxic proteins inside brain cells (neurons) appears to be key to stopping and reversing the cognitive loss of AD. Present AD drugs in clinical trials have great difficulty getting into the brain and then into brain cells. Even if they succeeded in doing so, they do not yet have the capacity to target the small aggregates of A-beta and tau proteins that appear to be causative to AD.
NeuroEM Therapeutics is planning for a pivotal clinical trial to begin recruitment of approximately 150 mild/moderate AD subjects later this year for treatment with the company’s MemorEMTM device. If that trial shows continued safety and cognitive benefits, NeuroEM Therapeutics plans to ask the FDA for approval of the MemorEM device for treatment of AD. The clinical locations for this multi-site trial have not yet been determined.
“Despite significant efforts for nearly 20 years, stopping or reversing memory impairment in people with Alzheimer’s disease has eluded researchers,” said co-author Amanda Smith, M.D., Director of Clinical Research, University of South Florida Health, Byrd Alzheimer’s Institute, the clinical center for the study. “These results provide preliminary evidence that TEMT administration we assessed in this small AD study may have the capacity to enhance cognitive performance in patients with mild to moderate disease.”
After two months of treatment administered at home by their caregivers, none of the eight patients in the study exhibited any deleterious side effects on behavior or physiologic measures, as recorded by caregivers in daily diaries. Moreover, post-treatment brain scans revealed no visible induction of tumors or brain bleedings called microhemorrhages.
Using the benchmark ADAS-cog task to assess a variety of cognitive measures, seven of the eight AD patients collectively responded to treatment with a 4+ point increase in cognitive performance by the end of the 2-month treatment period — the results indicate a very large and clinically-important effect.
Since AD patients typically show a 4+ point decline in ADAS-cog performance over a given one year period, the 4+ point improvement provided by TEMT was as if the treated patients had gone back in time to their better cognitive performance of one year earlier.
“We were particularly surprised that this highly significant improvement in the ADAS-cog was maintained even two weeks after treatment was completed”, stated Dr. Arendash.
“The most likely explanation for continued benefit after cessation of treatment is that the Alzheimer’s Disease process itself was being affected.”
Cognitive abilities were improved in other tasks as well, such as the Rey AVLT task, wherein clinically important increases in word recall were present after treatment for 2 months and at two weeks thereafter. Even a 50% reduction in forgetting was observed in this important task.
In addition to cognitive assessment, the study also involved analysis of AD markers in both the blood and the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) before and at the end of the 2-month treatment period. These AD markers were changed in directions expected for TEMT disaggregating the two toxic proteins (A-beta and tau) that appear to be the disease’s root causes.
Also, MRI brain scans in individual AD patients revealed evidence of increased communication between neurons in a brain area critical for cognitive integration called the cingulate cortex/cingulum.

The investigators believe that TEMT may be an entirely new therapeutic intervention against Alzheimer’s disease and that NeuroEM’s bioengineering technology may be succeeding where drug therapy against this devastating disease has thus far failed.
Based on the findings and the enthusiasm for continued treatment that all patients expressed, patients were offered and accepted continued TEMT in a now on-going extension study averaging 17 months between initial study start and extension study finish. More information about both the completed and on-going clinical trials is available at NeuroEM’s website.
More Information About the Study
The open-label study was a single center, single arm trial in eight patients 63 years of age and older with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease (AD) to evaluate the safety and initial efficacy of Transcranial Electromagnetic Treatment (TEMT). Patients were enrolled at the University of South Florida Health/Byrd Alzheimer’s Institute, which also conducted most clinical study assessments. Treatment was administered in the patient’s home by a caregiver (spouse, relative), using the MemorEM device.
Patients received TEMT for one-hour periods twice daily for two months. Although limitations of this study include the small number of subjects, not having a control group, and being of relatively short treatment duration, 120 treatments were administered in-home and the cognitive benefits observed were clinically important/meaningful at the highest levels. Providing additional credibility to the observed cognitive enhancements were the beneficial changes in AD markers in blood and CSF, as well as the enhancement in brain MRI imaging.
Source:
IOS Press
Media Contacts:
Bill Gordon – IOS Press
Image Source:
The image is credited to NeuroEM Therapeutics, Inc.
Original Research: Open access
“A Clinical Trial of Transcranial Electromagnetic Treatment in Alzheimer’s Disease: Cognitive Enhancement and Associated Changes in Cerebrospinal Fluid, Blood, and Brain Imaging”. Gary Arendash, et al.
Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease doi:10.3233/JAD-190367.
Abstract
A Clinical Trial of Transcranial Electromagnetic Treatment in Alzheimer’s Disease: Cognitive Enhancement and Associated Changes in Cerebrospinal Fluid, Blood, and Brain Imaging
Background:
Small aggregates (oligomers) of the toxic proteins amyloid-β (Aβ) and phospho-tau (p-tau) are essential contributors to Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In mouse models for AD or human AD brain extracts, Transcranial Electromagnetic Treatment (TEMT) disaggregates both Aβ and p-tau oligomers, and induces brain mitochondrial enhancement. These apparent “disease-modifying” actions of TEMT both prevent and reverse memory impairment in AD transgenic mice.
Objective:
To evaluate the safety and initial clinical efficacy of TEMT against AD, a comprehensive open-label clinical trial was performed.
Methods:
Eight mild/moderate AD patients were treated with TEMT in-home by their caregivers for 2 months utilizing a unique head device. TEMT was given for two 1-hour periods each day, with subjects primarily evaluated at baseline, end-of-treatment, and 2 weeks following treatment completion.
Results:
No deleterious behavioral effects, discomfort, or physiologic changes resulted from 2 months of TEMT, as well as no evidence of tumor or microhemorrhage induction. TEMT induced clinically important and statistically significant improvements in ADAS-cog, as well as in the Rey AVLT. TEMT also produced increases in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of soluble Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42, cognition-related changes in CSF oligomeric Aβ, a decreased CSF p-tau/Aβ1-42 ratio, and reduced levels of oligomeric Aβ in plasma. Pre- versus post-treatment FDG-PET brain scans revealed stable cerebral glucose utilization, with several subjects exhibiting enhanced glucose utilization. Evaluation of diffusion tensor imaging (fractional anisotropy) scans in individual subjects provided support for TEMT-induced increases in functional connectivity within the cognitively-important cingulate cortex/cingulum.
Conclusion:
TEMT administration to AD subjects appears to be safe, while providing cognitive enhancement, changes to CSF/blood AD markers, and evidence of stable/enhanced brain connectivity.