Summary: A compound used to treat leukemia shows promise in preventing breast cancer cells from metastasizing in the brain.
Source: Houston Methodist.
Researchers at Houston Methodist used computer modeling to find an existing investigational drug compound for leukemia patients to treat triple negative breast cancer once it spreads to the brain.
The Houston Methodist researchers culled through thousands of existing drugs to see if they could identify a compound that would prevent cancer cells from spreading, or metastasizing. They discovered edelfosine, which has been FDA-approved as an investigational leukemia treatment, and has also been used in clinical research for primary brain tumors.
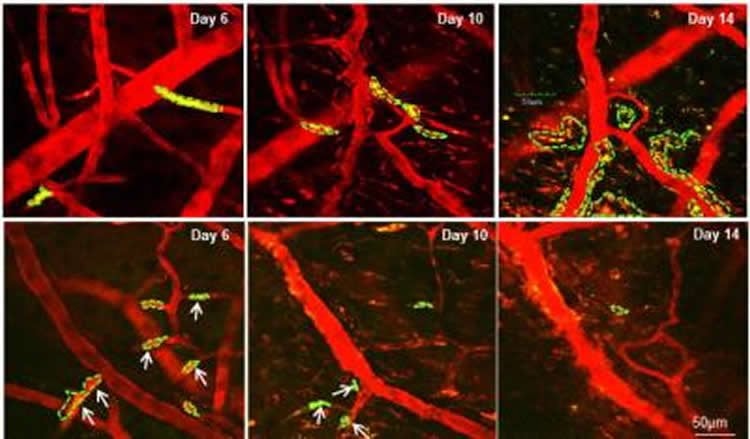
In the March 22 online issue of Cancer Research, scientists explained how they injected triple negative breast cancer stem cells from patients into mice. After treating them with this compound, the cancer stem cells did not grow once they metastasized to the brain.
“This compound stopped the cancer cells from communicating with brain cells as they traveled from the breast to the brain. Repurposing a drug compound to prevent the spread of cancer could be a game-changer in the prevention and treatment of metastatic brain disease,” said Stephen T. Wong, Ph.D., P.E., chair of the systems medicine and bioengineering at Houston Methodist Research Institute and one of the corresponding authors.
Triple negative patients usually have shorter survival time after diagnosis of brain metastasis, suggesting that these tumor cells adapt much more readily once they’ve moved to the brain. Triple negative remains the most challenging type of breast cancer to treat, and tends to show more traits possessed by cancer stem cells than other breast cancer subtypes.
“Viable treatment options for brain metastases are still an unmet need,” said Hong Zhao, M.D., Ph.D., assistant professor of systems medicine and bioengineering at Houston Methodist Research Institute and co-corresponding author. “Since edelfosine is already FDA-approved, we want to try and move this compound into a phase II clinical study for metastatic brain cancer in the next few years.”
Bringing a new drug to market can cost billions of dollars and take up to 17 years. This isn’t the first time Wong and his lab have explored repurposed drugs for breast cancer. In 2011, they applied big data mathematical and bioinformatics models to screen for existing FDA-approved medications that might be effective against cancer stem cells. In collaborating with the Houston Methodist Cancer Center, they identified the anti-malarial drug chloroquine as a potential cancer stem cell killer. A few years ago, the group discovered another existing compound that improved blood flow in damaged hearts, also proved to be effective in treating locally advanced or metastatic triple negative when combined with chemotherapy. Both drugs are currently in clinical trials.
Wong and his lab want to see if edelfosine could be incorporated into future clinical research focused on other tumor sites such as lung, ovarian and pancreatic cancers.
Funding: This research was funded by National Institutes of Health (U54 CA149196, R01 CA121225), and the John S. Dunn Research Foundation.
Source: Gale Smith – Houston Methodist
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to Houston Methodist.
Original Research: Abstract in Cancer Research.
doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2994
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]Houston Methodist “Compound that Prevents Breast Cancer Cells From Activating in the Brain Identified.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 22 March 2018.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/breast-brain-cancer-compound-8671/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]Houston Methodist (2018, March 22). Compound that Prevents Breast Cancer Cells From Activating in the Brain Identified. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved March 22, 2018 from https://neurosciencenews.com/breast-brain-cancer-compound-8671/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]Houston Methodist “Compound that Prevents Breast Cancer Cells From Activating in the Brain Identified.” https://neurosciencenews.com/breast-brain-cancer-compound-8671/ (accessed March 22, 2018).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Targeting Brain-Adaptive Cancer Stem Cells Prohibits Brain Metastatic Colonization of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) exhibits more traits possessed by cancer stem cells (CSC) than other breast cancer subtypes and is more likely to develop brain metastases. TNBC patients usually have shorter survival time after diagnosis of brain metastasis, suggesting an innate ability of TNBC tumor cells in adapting to the brain. In this study, we establish novel animal models to investigate early tumor adaptation in brain metastases by introducing both patient-derived and cell line–derived CSC-enriched brain metastasis tumorsphere cells into mice. We discovered astrocyte-involved tumor activation of protocadherin 7 (PCDH7)-PLCβ-Ca2+-CaMKII/S100A4 signaling as a mediator of brain metastatic tumor outgrowth. We further identified and evaluated the efficacy of a known drug, the selective PLC inhibitor edelfosine, in suppressing the PCDH7 signaling pathway to prohibit brain metastases in the animal models. The results of this study reveal a novel signaling pathway for brain metastases in TNBC and indicate a promising strategy of metastatic breast cancer prevention and treatment by targeting organ-adaptive cancer stem cells.






