Study is first time human amygdala has been stimulated, breathing loss recorded.
Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) is becoming increasingly recognized as a very real and devastating problem in which impaired breathing is thought to play a critical role. Researchers believe breathing may be impaired during and after seizures, without the patient’s knowledge.
By using electrical stimulation to activate the amygdala, a group of University of Iowa researchers has identified areas of the human brain in which breathing is controlled and, in some cases, impaired, providing an important insight into SUDEP.
Their study – which marks the first time researchers have stimulated the amygdala in humans and reported loss of breathing – is published in the July 15 issue of the Journal of Neuroscience.
Using a research participant with medically intractable epilepsy – epilepsy which can’t be well-controlled with two or more medications – whose brain was already being monitored to map the focus of seizures, researchers found that when seizures spread to the amygdala, the patient stopped breathing. That effect could be reproduced by electrically stimulating the amygdala. Strikingly, the patient wasn’t aware he wasn’t breathing even though he was wide awake at the time. This finding was reproduced in two other human subjects.
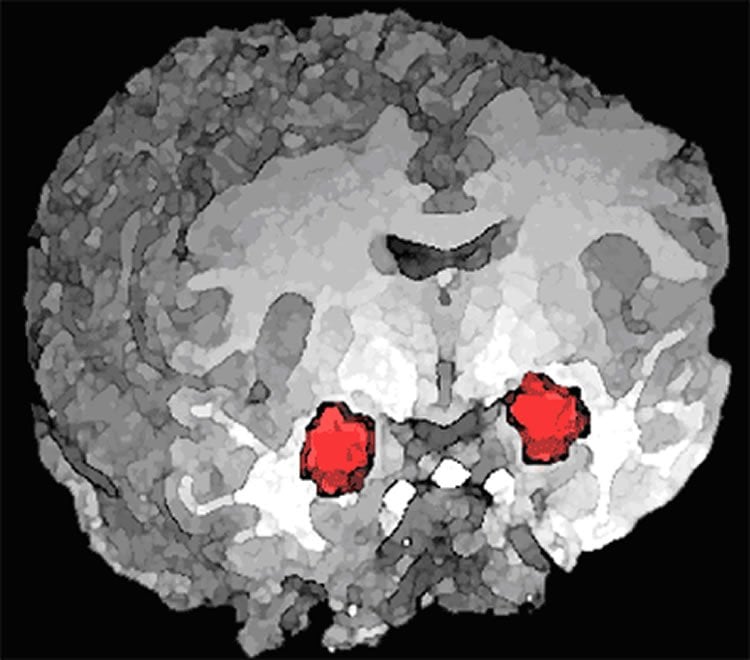
“Amazingly, the patient was completely unaware that he had stopped breathing,” says Brian Dlouhy, M.D., assistant professor of neurosurgery at UI Carver College of Medicine and lead author of the study. “It was remarkable to all of us that one of the essentials of life – breathing – could be inhibited and the patients themselves were completely unaware of this.”
“The patient just sat there, unconcerned that he was not breathing,” says John Wemmie, M.D., Ph.D., professor of psychiatry, molecular physiology and biophysics, and neurosurgery at the UI Carver College of medicine, and an author of the paper. “If we asked him to hold his breath for the same duration of time, it was difficult for him and he could barely do it. But when the amygdala was stimulated, he didn’t even notice that his breathing had stopped.”
Dr. George Richerson, M.D., Ph.D., professor and chairman of neurology, and professor of molecular physiology and biophysics, and neurosurgery at the UI Carver College of Medicine, also an author on the paper, says, “These findings provide an explanation for why SUDEP occurs after seizures, because patients would stop breathing but be completely unaware that their blood oxygen levels are progressively dropping to fatally low levels. The lack of awareness would prevent activation of the reflex that is needed to restore oxygen levels back to normal.”
The team’s findings may be key in helping to decrease instances of SUDEP, Dlouhy says.
“Identifying brain areas where seizure spread interferes with breathing may help identify patients at risk for SUDEP and lead to preventive strategies,” he says.
Funding: This work was supported by the US Department of Veterans Affairs, McKnight Neuroscience of Brain Disorders Award, NIH/National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, and Doris Duke Clinical Research Fellowship.
Source: Molly Rossiter – University of Iowa Health Care
Image Credit: The image is credited to the NIH and is in the public domain
Original Research: Abstract for “Breathing Inhibited When Seizures Spread to the Amygdala and upon Amygdala Stimulation” by Brian J. Dlouhy, Brian K. Gehlbach, Collin J. Kreple, Hiroto Kawasaki, Hiroyuki Oya, Colin Buzza, Mark A. Granner, Michael J. Welsh, Matthew A. Howard, John A. Wemmie, and George B. Richerson in Journal of Neuroscience. Published online July 15 2015 doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0888-15.2015
Abstract
Breathing Inhibited When Seizures Spread to the Amygdala and upon Amygdala Stimulation
Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) is increasingly recognized as a common and devastating problem. Because impaired breathing is thought to play a critical role in these deaths, we sought to identify forebrain sites underlying seizure-evoked hypoventilation in humans. We took advantage of an extraordinary clinical opportunity to study a research participant with medically intractable epilepsy who had extensive bilateral frontotemporal electrode coverage while breathing was monitored during seizures recorded by intracranial electrodes and mapped by high-resolution brain imaging. We found that central apnea and O2 desaturation occurred when seizures spread to the amygdala. In the same patient, localized electrical stimulation of the amygdala reproduced the apnea and O2 desaturation. Similar effects of amygdala stimulation were observed in two additional subjects, including one without a seizure disorder. The participants were completely unaware of the apnea evoked by stimulation and expressed no dyspnea, despite being awake and vigilant. In contrast, voluntary breath holding of similar duration caused severe dyspnea. These findings suggest a functional connection between the amygdala and medullary respiratory network in humans. Moreover, they suggest that seizure spread to the amygdala may cause loss of spontaneous breathing of which patients are unaware, and thus has potential to contribute to SUDEP.
SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) is the most common cause of death in patients with chronic refractory epilepsy. Impaired breathing during and after seizures is common and suspected to play a role in SUDEP. Understanding the cause of this peri-ictal hypoventilation may lead to preventative strategies. In epilepsy patients, we found that seizure invasion of the amygdala co-occurred with apnea and oxygen desaturation, and electrical stimulation of the amygdala reproduced these respiratory findings. Strikingly, the subjects were unaware of the apnea. These findings indicate a functional connection between the amygdala and brainstem respiratory network in humans and suggest that amygdala seizures may cause loss of spontaneous breathing of which patients are unaware—a combination that could be deadly.
“Breathing Inhibited When Seizures Spread to the Amygdala and upon Amygdala Stimulation” by Brian J. Dlouhy, Brian K. Gehlbach, Collin J. Kreple, Hiroto Kawasaki, Hiroyuki Oya, Colin Buzza, Mark A. Granner, Michael J. Welsh, Matthew A. Howard, John A. Wemmie, and George B. Richerson in Journal of Neuroscience. Published online July 15 2015 doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0888-15.2015