Summary: Researchers report the impairment of the right thalamic and caudate prefrontal pathways appear to be associated with attention deficits in patients following a stroke.
Source: RSNA.
Damage to some of the pathways that carry information throughout the brain may be responsible for attention deficit in patients who have had a subcortical stroke in the brain’s right hemisphere, according to a study published online in the journal Radiology. Researchers hope the findings may provide a measure for selecting suitable patients for early interventions aimed at reducing cognitive decline following stroke.
A stroke may affect cortical regions of the cerebral cortex, which includes the gray matter that lines the surface of the brain, or it may affect brain regions below the cortex, including white matter tracts connecting different regions of the brain. A stroke affecting brain structures below the cortex is known as a subcortical stroke.
More than one-third of patients experience cognitive decline after a stroke, including attention deficit, which can affect and impair the patient’s ability to carry out routine activities of daily living.
“Impairment of attention has been observed in patients with both cortical and subcortical stroke,” said senior study author Chunshui Yu, M.D., from the Department of Radiology at Tianjin Medical University General Hospital in Tianjin, China. “In cortical stroke, the direct involvement of cortical regions associated with attention may account for the deficit. However, the parts of the nervous and brain systems underlying attention deficit in subcortical stroke remain largely unknown.”
To investigate the mechanisms underlying attention deficit in chronic subcortical stroke, Dr. Yu and colleagues combined voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping (VLSM) and diffusion tensor tractography (DTT) in 49 patients (32 men and 17 women between the ages of 40 and 71) after subcortical stroke and 52 control patients (30 men and 22 women, age 40-68). VLSM is a method of analyzing relationships between tissue damage and behavioral deficits, and DTT is an MRI technique that allows for 3-D visualization of specific white matter tracts in the brain.
A modified version of the attention network test was used to assess visual attention function. VLSM was used to identify lesion locations related to attention deficit in the stroke patients. Then DTT was used to determine the responsible impaired brain connections at the chronic stage (> 6 months post-stroke).
The results showed that compared to the controls, patients with chronic stroke exhibited prolonged reaction time during the attention task. VLSM revealed that having an acute stroke lesion in the right caudate nucleus and nearby white matter was correlated to the prolonged reaction time. DTT showed that the responsible lesion was located in the right thalamic- and caudate-prefrontal pathways in controls.
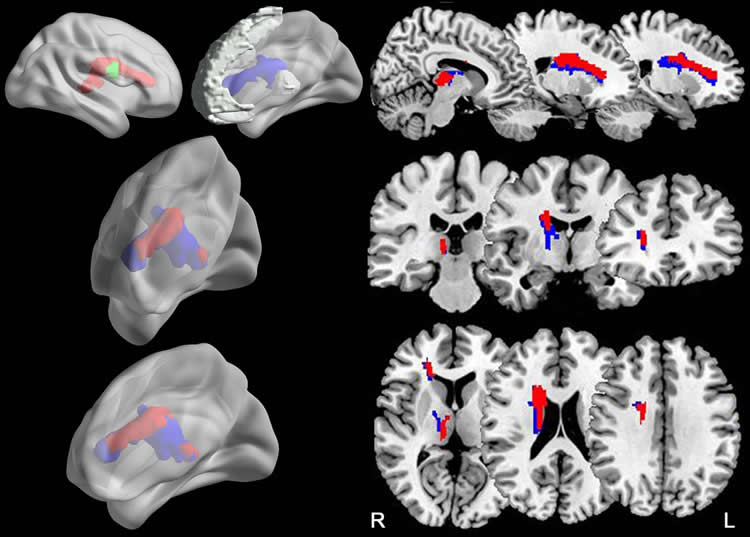
The right brain damage subgroup had significantly decreased fractional anisotropy (FA) in these pathways, which were correlated with the prolonged reaction time. FA provides a way to measure diffusion occurring within a region of the brain. FA is typically higher in brain regions of high organization. Reductions in FA have been previously associated with advancing age and in cases of cognitive impairment.
“The impairment of the right thalamic- and caudate-prefrontal pathways was consistently associated with attention deficit in patients with right subcortical stroke,” Dr. Yu said. “Based on this association, one can estimate which patients with stroke would be more likely to develop into long-term persisting attention deficit by evaluating the lesion-induced damage to these pathways.”
Funding: Funding provided by Natural Science Foundation of China, Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin, Tianjin Medical University General Hospital.
Source: Linda Brooks – RSNA
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to RSNA.
Original Research: Abstract for “Connection Disruption Underlying Attention Deficit in Subcortical Stroke” by Jingchun Liu, Caihong Wang, Qingqing Diao, Wen Qin, Jingliang Cheng, and Chunshui Yu in Radiology. Published May 8 2018.
doi:10.1148/radiol.2018171730
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]RSNA “Impaired Brain Pathways May Cause Attention Problems Following Stroke.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 8 May 2018.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/stroke-attention-9001/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]RSNA (2018, May 8). Impaired Brain Pathways May Cause Attention Problems Following Stroke. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved May 8, 2018 from https://neurosciencenews.com/stroke-attention-9001/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]RSNA “Impaired Brain Pathways May Cause Attention Problems Following Stroke.” https://neurosciencenews.com/stroke-attention-9001/ (accessed May 8, 2018).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Connection Disruption Underlying Attention Deficit in Subcortical Stroke
Purpose
To investigate neural substrates underlying attention deficit in patients with chronic subcortical stroke by combining voxel-based lesion-symptom mapping (VLSM) and diffusion-tensor (DT) tractography.
Materials and Methods
Institutional review board approval and written informed consent were obtained. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging data were prospectively acquired from August 1, 2014, to March 30, 2015, in 49 patients (32 men, 17 women; mean age, 55.7 years ± 8.0; age range, 40–71 years) with subcortical infarctions in the basal ganglia and neighboring regions and 52 control subjects (30 men, 22 women; mean age, 54.4 years ± 7.5; age range, 40–68 years). A modified version of the attention network test was used to assess visual attention function. On the basis of the lesion map at the acute stage, VLSM was used to identify lesion locations related to attention deficit in patients with stroke. DT tractography then was used to determine the responsible impaired connections by using diffusion data at the chronic stage (>6 months after stroke).
Results
When compared with control subjects, patients with chronic stroke exhibited prolonged reaction time (RT) of correct responses (P = .009). VLSM revealed that acute stroke lesion in the right caudate nucleus and nearby white matter (found in seven patients) was correlated with the prolonged RT (P < .05). DTT showed that the responsible lesion was located in the right thalamic- and caudate-prefrontal pathways in control subjects. The subgroup with right-sided brain damage had significantly decreased fractional anisotropy in these pathways (P < .001), which were correlated with the prolonged RT (P = .009 for the thalamic-prefrontal pathway, P < .001 for the caudate-prefrontal pathway).
Conclusion
Thalamic-prefrontal and caudate-prefrontal pathways impaired by stroke lesions appear to underlie attention deficit in patients with subcortical stroke in the right hemisphere.