Summary: A new study reveals taking a short daytime nap can help to consolidate learning and memory of new foreign words.
Source: University of Bern.
Sleeping time is sometimes considered unproductive time. This raises the question whether the time spent asleep could be used more productively – e.g. for learning a new language? To date sleep research focused on the stabilization and strengthening (consolidation) of memories that had been formed during preceding wakefulness. However, learning during sleep has rarely been examined. There is considerable evidence for wake-learned information undergoing a recapitulation by replay in the sleeping brain. The replay during sleep strengthens the still fragile memory traces und embeds the newly acquired information in the preexisting store of knowledge.
If re-play during sleep improves the storage of wake-learned information, then first-play – i.e., the initial processing of new information – should also be feasible during sleep, potentially carving out a memory trace that lasts into wakefulness. This was the research question of Katharina Henke, Marc Züst und Simon Ruch of the Institute of Psychology and of the Interfaculty Research Cooperation “Decoding Sleep” at the University of Bern, Switzerland. These investigators now showed for the first time that new foreign words and their translation words could be associated during a midday nap with associations stored into wakefulness. Following waking, participants could reactivate the sleep-formed associations to access word meanings when represented with the formerly sleep-played foreign words. The hippocampus, a brain structure essential for wake associative learning, also supported the retrieval of sleep-formed associations. The results of this experiment are published open access in the scientific journal Current Biology.
The brain cells’ active states are central for sleep-learning
The research group of Katharina Henke examined whether a sleeping person is able to form new semantic associations between played foreign words and translation words during the brain cells’ active states, the so-called “Up-states”. When we reach deep sleep stages, our brain cells progressively coordinate their activity. During deep sleep, the brain cells are commonly active for a brief period of time before they jointly enter into a state of brief inactivity. The active state is called “Up-state” and the inactive state “Down-state”. The two states alternate about every half-second.
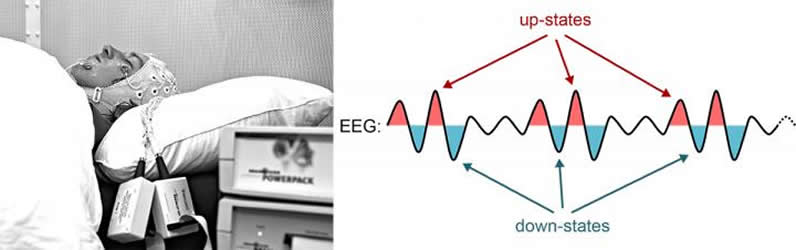
Semantic associations between sleep-played words of an artificial language and their German translations words were only encoded and stored, if the second word of a pair was repeatedly (2, 3 or 4 times) played during an Up-state. E.g., when a sleeping person heard the word pairs “tofer = key” and “guga = elephant”, then after waking they were able to categorize with a better-than-chance accuracy whether the sleep-played foreign words denominated something large (“Guga”) or small (“Tofer”). “It was interesting that language areas of the brain and the hippocampus – the brain’s essential memory hub – were activated during the wake retrieval of sleep-learned vocabulary because these brain structures normally mediate wake learning of new vocabulary”, says Marc Züst, co-first-author of this paper. “These brain structures appear to mediate memory formation independently of the prevailing state of consciousness – unconscious during deep sleep, conscious during wakefulness”.
Memory formation does not require consciousness
Besides its practical relevance, this new evidence for sleep-learning challenges current theories of sleep and theories of memory. The notion of sleep as an encapsulated mental state, in which we are detached from the physical environment is no longer tenable. “We could disprove that sophisticated learning be impossible during deep sleep”, says Simon Ruch, co-first-author. The current results underscore a new theoretical notion of the relationship between memory and consciousness that Katharina Henke published in 2010 (Nature Reviews Neuroscience). “In how far and with what consequences deep sleep can be utilized for the acquisition of new information will be a topic of research in upcoming years”, says Katharina Henke.
The research group of Katharina Henke is part of the Interfaculty Research Cooperation “Decoding Sleep: From Neurons to Health & Mind” (IRC). Decoding Sleep is a large, interdisciplinary research project that is financed by the University of Bern, Switzerland. Thirteen research groups in medicine, biology, psychology, and informatics are part of the IRC. The aim of these research groups is to gain a better understanding of the mechanisms involved in sleep, consciousness, and cognition.
The reported study was carried out in collaboration with Roland Wiest who is affiliated with the Support Center for Advanced Neuroimaging (SCAN) at the Institute of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology, Inselspital, University of Bern. Both research groups also belong to the BENESCO consortium, which consists of 22 interdisciplinary research groups specialized in sleep medicine, epilepsy and research on altered states of consciousness.
Source: Marc Zuest – University of Bern
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to Simon Ruch/Marc Züst, University of Bern.
Original Research: Open access research for “Implicit Vocabulary Learning during Sleep Is Bound to Slow-Wave Peaks” by Marc Alain Züst, Simon Ruch, Roland Wiest, and Katharina Henke in Current Biology. Published January 31 2019.
doi:10.1016/j.cub.2018.12.038
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]University of Bern”Learning New Vocabulary During Sleep.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 31 January 2019.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/sleep-vocabulary-learning-10667/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]University of Bern(2019, January 31). Learning New Vocabulary During Sleep. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved January 31, 2019 from https://neurosciencenews.com/sleep-vocabulary-learning-10667/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]University of Bern”Learning New Vocabulary During Sleep.” https://neurosciencenews.com/sleep-vocabulary-learning-10667/ (accessed January 31, 2019).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Implicit Vocabulary Learning during Sleep Is Bound to Slow-Wave Peaks
Learning while asleep is a dream of mankind, but is often deemed impossible because sleep lacks the conscious awareness and neurochemical milieu thought to be necessary for learning. Current evidence for sleep learning in humans is inconclusive. To explore conditions under which verbal learning might occur, we hypothesized that peaks of slow waves would be conducive to verbal learning because the peaks define periods of neural excitability. While in slow-wave sleep during a nap, a series of word pairs comprising pseudowords, e.g., “tofer,” and actual German words, e.g., “Haus” (house), were played to young German-speaking women and men. When the presentation of the second word of a pair (e.g., “Haus” of “tofer-house”) coincided with an ongoing slow-wave peak, the chances increased that a new semantic association between the pair had been formed and retained. Sleep-formed associations translated into awake ones, where they guided forced choices on an implicit memory test. Reactivations of sleep-formed associations were mirrored by brain activation increases measured with fMRI in cortical language areas and the hippocampus, a brain structure critical for relational binding. We infer that implicit relational binding had occurred during peaks of slow oscillations, recruiting a hippocampal-neocortical network comparable to vocabulary learning in the waking state.