Summary: Researchers have identified a pre-programmed neural circuit in the basolateral amygdala of mice that processes both positive and negative stimuli.
Source: CSHL
Are we born to fear punishment or crave rewards? Or do those capacities evolve with experience?
Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor Bo Li and his lab found that mice have pre-programmed circuits that process “positive” and “negative” stimuli. These neurons are found in the mouse’s amygdala, a section of the brain that deals with learning rewards and punishments. The researchers’ findings may be useful for studying neurological and psychiatric disorders in humans.
Previously, Li and his colleagues discovered that the amygdala is the hub for both fear- and reward-based learning. Xian Zhang, a postdoc in Li’s lab, wanted to find out the exact circuitry that takes in positive or negative stimuli that trigger either pleasure or fear.
In an experiment similar to how Pavlov’s dog was taught to associate a bell sound with food, Li and Zhang trained mice to connect certain sounds with either a reward (a refreshing drink of water) or a punishment (an annoying puff of air to the whiskers). Then, in collaboration with CSHL Adjunct Professor Z. Josh Huang, they developed a method to mark and observe different neurons in the mouse amygdala.
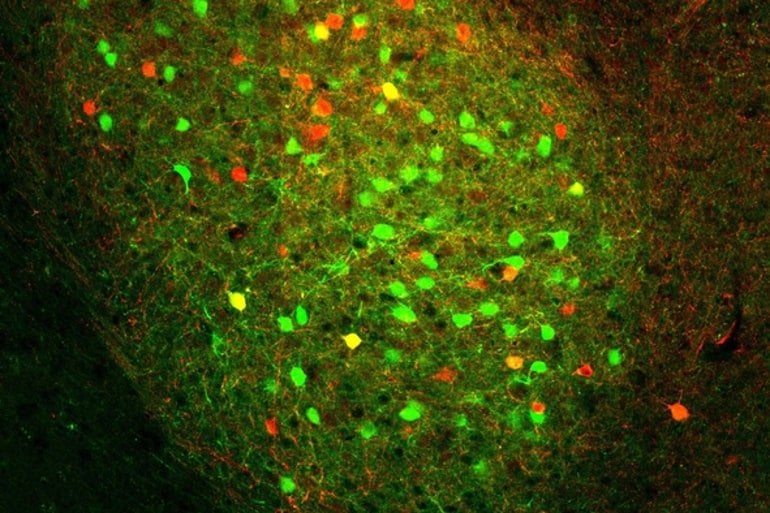
They discovered two distinct types of neurons: one that was activated when the mouse heard the reward sound, and one that was activated when it heard the punishment sound. Both neuron populations exist throughout the entire amygdala. Li explains:
“They’re spatially intermingled. When you start to image them, you know that some of the neurons respond only to good things, some of the neurons respond only to bad things, just like the pepper and the salt mixed together, and they do different jobs.”
The researchers were surprised to discover that some amygdala cells are hardwired to process motivation stimuli, even without training. A puff of air or sip of water triggered the same neurons in both untrained and trained mice.
Zhang thinks their findings may be relevant to human psychiatric disorders like depression. He says:
“If you have an imbalanced bit in different neural circuits, you probably have a deficit of your motivation, like you lost your interest in pursuing rewards, or you lost your interest in avoiding punishment. I think this finding is important to know for the future, to help people with depression or other mental disorders.”
In mouse models of depression, animals lack the motivation to seek rewards or avoid punishments. Li and Zhang hope that this study, published in Nature Neuroscience, will help researchers understand how motivation works or goes wrong in mammalian brains.
About this neuroscience research news
Author: Sara Roncero-Menendez
Source: CSHL
Contact: Sara Roncero-Menendez – CSHL
Image: The image is credited to Xian Zhang/Li lab/CSHL, 2021
Original Research: Closed access.
“Genetically identified amygdala-striatal circuits for valence-specific behaviors” by Xian Zhang, Wuqiang Guan, Tao Yang, Alessandro Furlan, Xiong Xiao, Kai Yu, Xu An, William Galbavy, Charu Ramakrishnan, Karl Deisseroth, Kimberly Ritola, Adam Hantman, Miao He, Z. Josh Huang & Bo Li. Nature Neuroscience
Abstract
Genetically identified amygdala-striatal circuits for valence-specific behaviors
The basolateral amygdala (BLA) plays essential roles in behaviors motivated by stimuli with either positive or negative valence, but how it processes motivationally opposing information and participates in establishing valence-specific behaviors remains unclear.
Here, by targeting Fezf2-expressing neurons in the BLA, we identify and characterize two functionally distinct classes in behaving mice, the negative-valence neurons and positive-valence neurons, which innately represent aversive and rewarding stimuli, respectively, and through learning acquire predictive responses that are essential for punishment avoidance or reward seeking.
Notably, these two classes of neurons receive inputs from separate sets of sensory and limbic areas, and convey punishment and reward information through projections to the nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle, respectively, to drive negative and positive reinforcement.
Thus, valence-specific BLA neurons are wired with distinctive input–output structures, forming a circuit framework that supports the roles of the BLA in encoding, learning and executing valence-specific motivated behaviors.