Summary: A new study refutes popular assumption that hormone levels in women alter perceptions of male attractiveness. The study reveals hormone levels do not influence the type of men women find attractive.
Source: APS.
Data from almost 600 participants show that women’s perceptions of male attractiveness do not vary according to their hormone levels, in contrast with some previous research. The study findings are published in Psychological Science.
“We found no evidence that changes in hormone levels influence the type of men women find attractive,” say lead researcher Benedict C. Jones of the University of Glasgow.
“This study is noteworthy for its scale and scope — previous studies typically examined small samples of women using limited measures,” Jones explains. “With much larger sample sizes and direct measures of hormonal status, we weren’t able to replicate effects of hormones on women’s preferences for masculine faces.”
To address the limitations of previous studies, Jones and coauthors recruited 584 heterosexual women to participate in a series of weekly test sessions. In each session, the participants reported whether they were currently in a romantic relationship and whether they were currently using hormonal contraceptives. They provided a saliva sample for hormone analyses and completed a task that measured their preferences for different types of male faces.
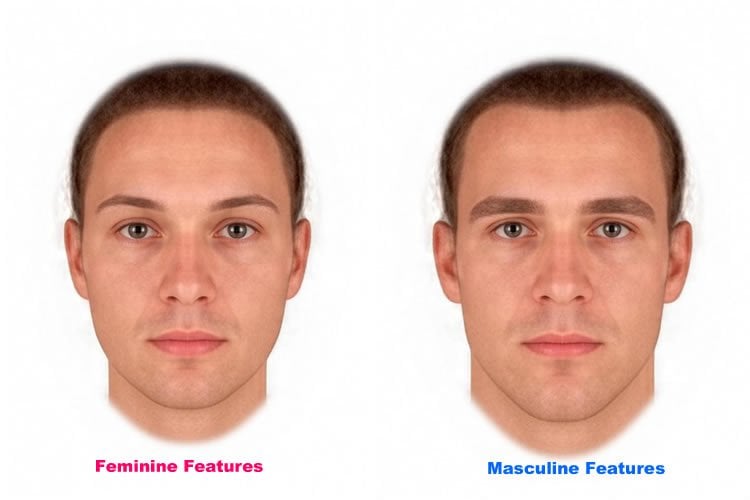
In each face-preference task, the participants saw 10 pairs of male faces and selected the face in each pair that they found more attractive, rating how strong their preference was. The two faces in each pair were digitally altered versions of the same photo – one face was altered to have somewhat feminized features and the other was altered to have somewhat masculinized features. To obscure the specific objective of the study, the researchers interspersed these attractiveness judgments among other filler questions.
As expected, women generally rated the masculinized faces as more attractive than the feminized faces. Preference for the more masculinized faces was also slightly stronger when women judged attractiveness in the context of a short-term relationship as opposed to a long-term relationship.
However, there was no evidence that women’s preferences varied according to levels of fertility-related hormones, such as estradiol and progesterone. There was also no association between attractiveness judgments and levels of other potentially influential hormones, such as testosterone and cortisol.

These findings run counter to the hypothesis that sexual selection pressures lead women to prefer more masculine mates, who supposedly have greater genetic “fitness,” when they are most fertile and most likely to conceive.
The data also showed that oral contraceptive use did not dampen women’s preference for masculine faces, as has been shown previously.
“There has been increasing concern that the birth control pill might disrupt romantic relationships by altering women’s mate preferences, but our findings do not provide evidence of this,” says Jones.
In light of these findings, Jones and coauthors are continuing to investigate whether other fertility-related differences hold up in larger, more robust studies.
Funding: This research was supported by European Research Council grants awarded to B. C. Jones (OCMATE) and L. M. DeBruine (KINSHIP).
Source: Anna Mikulak – APS
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to Jones et al.
Original Research: Open access research for “No Compelling Evidence That Preferences for Facial Masculinity Track Changes in Women’s Hormonal Status” by Benedict C. Jones, Amanda C. Hahn, Claire I. Fisher, Hongyi Wang, Michal Kandrik, Chengyang Han, Vanessa Fasolt, Danielle Morrison, Anthony J. Lee, Iris J. Holzleitner, Kieran J. O’Shea, S. Craig Roberts, Anthony C. Little, and Lisa M. DeBruine in Psychological Science. Published April 30 2018.
doi:10.1177/0956797618760197
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]APS “Women’s Preference for Masculine Faces Not Linked to Hormones.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 7 May 2018.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/masculine-face-women-8977/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]APS (2018, May 7). Women’s Preference for Masculine Faces Not Linked to Hormones. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved May 7, 2018 from https://neurosciencenews.com/masculine-face-women-8977/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]APS “Women’s Preference for Masculine Faces Not Linked to Hormones.” https://neurosciencenews.com/masculine-face-women-8977/ (accessed May 7, 2018).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
No Compelling Evidence That Preferences for Facial Masculinity Track Changes in Women’s Hormonal Status
Although widely cited as strong evidence that sexual selection has shaped human facial-attractiveness judgments, findings suggesting that women’s preferences for masculine characteristics in men’s faces are related to women’s hormonal status are equivocal and controversial. Consequently, we conducted the largest-ever longitudinal study of the hormonal correlates of women’s preferences for facial masculinity (N = 584). Analyses showed no compelling evidence that preferences for facial masculinity were related to changes in women’s salivary steroid hormone levels. Furthermore, both within-subjects and between-subjects comparisons showed no evidence that oral contraceptive use decreased masculinity preferences. However, women generally preferred masculinized over feminized versions of men’s faces, particularly when assessing men’s attractiveness for short-term, rather than long-term, relationships. Our results do not support the hypothesized link between women’s preferences for facial masculinity and their hormonal status.