Summary: Researchers have identified two alternative pathways for the development of amyloid pathologies in Alzheimer’s disease.
Source: Karolinska Institute
The two used methods for detecting amyloid pathology in Alzheimer’s disease give ambiguous results, with the risk of incorrect or delayed care interventions. Now, researchers at Karolinska Institutet have found genetic explanations for the differences. The study is published in Molecular Psychiatry and may be important for more individual diagnostics and the development of future drugs.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common dementia disease and leads to gradual memory loss and premature death. Approximately 120,000 people in Sweden have Alzheimer’s and there are approximately 50 million people worldwide. According to Hjärnfonden, the number will increase by 70 percent in 50 years, partly because we are living longer and longer.
One of the earliest signs of Alzheimer’s is a pathological accumulation of amyloid protein forming insoluble deposits in the brain, also called “plaques”. This process can last for many years without appreciably affecting the person’s cognitive ability.
Amyloid plaques are present in the brain from an early stage of Alzheimer’s disease, already before mild cognitive impairment. At the same time, an early diagnosis is important for care interventions that could dampen the course of the disease.
PET camera and CSF analysis
Today, brain imaging of amyloid plaques with a PET camera and analysis of cerebrospinal fluid, CSF, from the spinal cord are the accepted methods for detecting pathological accumulations of amyloid.
But in up to 20 percent of cases, especially at early stages of the disease, the methods show different results. These differences can have implications for the patient for early diagnosis and treatment.
Now, researchers at Karolinska Institutet and Vita-Salute San Raffaele University in Milano have identified two alternative pathways for the development of amyloid pathology in Alzheimer’s disease.
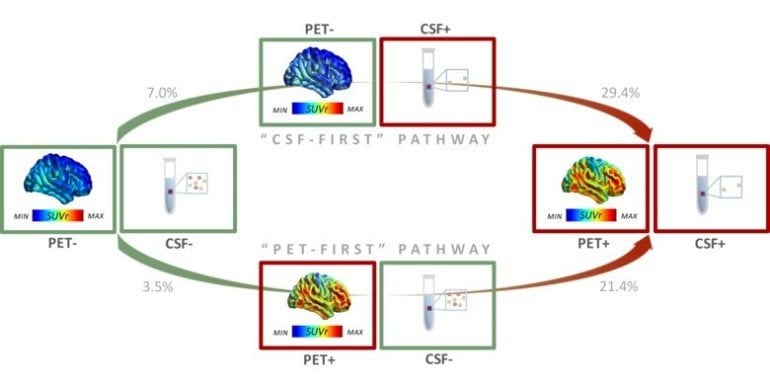
The results are based on PET imaging and CSF analyses in 867 participants, including patients with mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s dementia and healthy controls. For two years, the amyloid accumulation in a subset of nearly 300 participants had been documented with both a PET camera and CSF analysis.
The results show that pathological changes in some individuals are first detected in the brain with a PET camera, and in other individuals first with CSF analysis. In the latter group, the researchers also saw a higher incidence of Alzheimer’s genetic risk factor APOE-e4e4 and faster accumulation of amyloid plaques in the brain compared to the former group.
Complementary information about amyloid
According to the researchers, the results reveal two different groups of patients, with different genetics and speed of amyloid plaque accumulation in the brain.
“The results may be important as amyloid biomarkers play a significant role as early diagnostic markers for clinical diagnosis. Today, CSF and PET are considered equivalent to determine the degree of amyloid accumulation, but the study indicates that the two methods should rather be seen as complementary to each other,” says first author Arianna Sala, currently a post-doctoral fellow at the University of Liège, Belgium and Technical University of Munich, Germany.
“The differences in the results for biomarkers in the brain and CSF provide unique biological information and the opportunity for earlier and more individualized diagnosis and treatment for Alzheimer’s disease in the future. The results may also be important for the design of clinical trials of new drugs against amyloid accumulation in the brain,” says last author Elena Rodriguez-Vieitez, senior researcher at the Department of Neurobiology, Caring Sciences and Society, Karolinska Institutet.
Funding: The study was funded by the European Union Innovative Medicines Initiative AMYPAD, the Alzheimer’s Foundation, the Brain Foundation, the Dementia Foundation, the Foundation for Strategic Research (SSF), the Swedish Research Council, the Åke Wiberg Foundation and Region Stockholm. There are no reported conflicts of interest.
About this Alzheimer’s disease and genetics research news
Source: Karolinska Institute
Contact: Press Office – Karolinska Institute
Image: The image is credited to the researchers
Original Research: Open access.
“Longitudinal pathways of cerebrospinal fluid and positron emission tomography biomarkers of amyloid-β positivity‘ by Arianna Sala, Agneta Nordberg, Elena Rodriguez-Vieitez. Molecular Psychiatry
Abstract
Longitudinal pathways of cerebrospinal fluid and positron emission tomography biomarkers of amyloid-β positivity
Mismatch between CSF and PET amyloid-β biomarkers occurs in up to ≈20% of preclinical/prodromal Alzheimer’s disease individuals. Factors underlying mismatching results remain unclear. In this study we hypothesized that CSF/PET discordance provides unique biological/clinical information. To test this hypothesis, we investigated non-demented and demented participants with CSF amyloid-β42 and [18F]Florbetapir PET assessments at baseline (n = 867) and at 2-year follow-up (n = 289). Longitudinal trajectories of amyloid-β positivity were tracked simultaneously for CSF and PET biomarkers. In the longitudinal cohort (n = 289), we found that participants with normal CSF/PET amyloid-β biomarkers progressed more frequently toward CSF/PET discordance than to full CSF/PET positivity (χ2(1) = 5.40; p < 0.05). Progression to CSF+/PET+ status was ten times more frequent in cases with discordant biomarkers, as compared to csf−/pet− cases (χ2(1) = 18.86; p < 0.001). Compared to the CSF+/pet− group, the csf−/PET+ group had lower APOE-ε4ε4 prevalence (χ2(6) = 197; p < 0.001; n = 867) and slower rate of brain amyloid-β accumulation (F(3,600) = 12.76; p < 0.001; n = 608). These results demonstrate that biomarker discordance is a typical stage in the natural history of amyloid-β accumulation, with CSF or PET becoming abnormal first and not concurrently. Therefore, biomarker discordance allows for identification of individuals with elevated risk of progression toward fully abnormal amyloid-β biomarkers, with subsequent risk of neurodegeneration and cognitive decline. Our results also suggest that there are two alternative pathways (“CSF-first” vs. “PET-first”) toward established amyloid-β pathology, characterized by different genetic profiles and rates of amyloid-β accumulation. In conclusion, CSF and PET amyloid-β biomarkers provide distinct information, with potential implications for their use as biomarkers in clinical trials.







