Neural dysfunction in cognitive control circuits during adolescence could be predictor of psychotic disorders.
Researchers led by Bradley S. Peterson, MD, director of the Institute for the Developing Mind at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, have shown that lower levels of conflict-related brain activity are associated with a higher risk for later psychosis. The study, in conjunction with colleagues at Columbia University, is available via PubMed in advance of publication by the journal Neuropsychopharmacology.
Adolescence is an important period for cognitive and emotional development, including the coordination of a vast array of cognitive functions that comprise cognitive control – the ability for the brain to negotiate competing demands in the service of attaining life goals. Many psychiatric disorders first manifest themselves during adolescence, and neurocognitive abnormalities, particularly in cognitive control, may be a core feature of such illness.
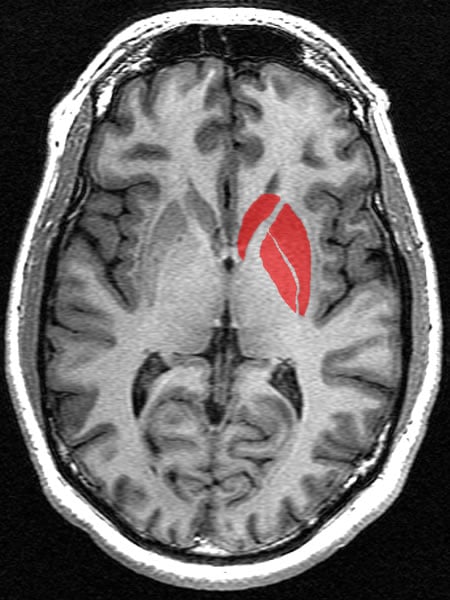
Little is known about the role in the development of psychosis played by functional brain circuits that support cognitive control. “The great strength of this and other studies that look at high-risk individuals is that we are able to disentangle what comes first – and is therefore a potential cause – and what comes second and more likely to be a consequence of the risk markers or indicators,” said Peterson, who is also director of the Division of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry at Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California (USC).
Using functional magnetic resonance imagining (fMRI) the scientists set out to determine the nature and extent of abnormalities in the neural system supporting cognitive control in adolescents and young adults at clinical high risk (CHR) for psychosis.
The team looked at 56 CHR individuals enrolled in the COPE (Center of Prevention and Evaluation) clinic at the New York Psychiatric Institute, and 49 healthy controls, all with a mean age of 21 and matched age, gender and minority status. During fMRI scanning to detect conflicting signals in the brain, study participants performed tests designed to measure cognitive flexibility, among other functions.
Comparing the two groups, the researchers detected reduced conflict-related functional activity in several cortical areas of the CHR group compared with healthy controls. These areas included the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex or DLPFC (a functional control region of the brain with a long period of maturation leading into adolescence) and the dorsal striatum (involved in reward and decision-making). Higher levels of conflict-related activation in these areas as shown by fMRI were associated with better social and role outcome. Furthermore, the study showed that conflict-related activations in the DLPFC of those CHR individuals who ultimately developed psychosis were smaller than in those who did not.
“We interpret these findings as evidence that conflict-related brain activation represents an adaptive process that is diminished in individuals at high risk for psychosis, though further study is needed,” Peterson concluded.
Additional contributors to the study include first author Tiziano Colibazzi, along with Guillermo Horga1, Zhishun Wang, Yuankai Huo, Cheryl Corcoran, Kristin Klahr, Gary Brucato, Ragy Girgis, Kelly Gill and Anissa Abi-Dargham, all of the Department of Psychiatry, New York State Psychiatric Institute and Columbia College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York.
Funding: This work was supported by NIMH grants 5T32MH15144, and K23 MH85063, K23 MH101637, UL1 RR024156, R21MH086125 and by funding from the National Alliance for Research on Schizophrenia and Depression (NARSAD), the Sackler Institute, the Herbert Irving Scholar Award, and the Bodini Fellowship at Columbia University.
Source: Children’s Hospital Los Angeles
Image Source: The image is credited to Lindsay Hanford, Geoff B Hall and is in the public domain
Original Research: Abstract for “Neural Dysfunction in Cognitive Control Circuits in Persons at Clinical High-Risk for Psychosis” by Tiziano Colibazzi, Guillermo Horga, Zhishun Wang, Yuankai Huo, Cheryl Corcoran, Kristin Klahr, Gary Brucato, Ragy Girgis, Kelly Gill, Anissa Abi-Dargham and Bradley S Peterson in Neuropsychopharmacology. Published online September 10 2015 doi:10.1038/npp.2015.273
Abstract
Neural Dysfunction in Cognitive Control Circuits in Persons at Clinical High-Risk for Psychosis
Cognitive control, a set of functions that develop throughout adolescence, is important in the pathogenesis of psychotic disorders. Whether cognitive control pays a role in conferring vulnerability for the development of psychotic illness is still unknown. The aim of this study was to investigate the neural systems supporting cognitive control in individuals deemed to be potentially prodromal for psychotic illness. We recruited 56 participants at clinical high-risk (CHR) for psychosis based on the Structured Interview for Psychosis-Risk Syndromes (SIPS) and 49 healthy controls. Twelve of the CHR participants eventually developed psychosis. We compared functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) BOLD signal during the performance of the Simon task. We tested for differences between CHR individuals and controls in conflict-related functional activity. In the CHR group when compared to controls, we detected smaller conflict-related activations in several cortical areas, including the Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex (DLPFC). Furthermore, conflict-related activations in the DLPFC of those CHR individuals who ultimately developed psychosis (CHR converters) were smaller than in non-converters (CHR-non converters). Higher levels of conflict-related activation were associated with better social and role outcome. Risk for psychosis was associated at the neural level with reduced conflict-related brain activity. This neural phenotype appears correlated within the DLPFC with the development of psychosis and functional outcome.
“Neural Dysfunction in Cognitive Control Circuits in Persons at Clinical High-Risk for Psychosis” by Tiziano Colibazzi, Guillermo Horga, Zhishun Wang, Yuankai Huo, Cheryl Corcoran, Kristin Klahr, Gary Brucato, Ragy Girgis, Kelly Gill, Anissa Abi-Dargham and Bradley S Peterson in Neuropsychopharmacology. Published online September 10 2015 doi:10.1038/npp.2015.273