In a double-blinded, randomized study, UNC researchers found that the IQ scores of people who underwent tDCS brain stimulation improved markedly less than did the IQ scores of people in the placebo group.
Using a weak electric current in an attempt to boost brainpower or treat conditions has become popular among scientists and do-it-yourselfers, but a new UNC School of Medicine study shows that using the most common form of electric brain stimulation had a statistically significant detrimental effect on IQ scores.
Published in the journal Behavioural Brain Research, the study adds to the increasing amount of literature showing that transcranial direct current stimulation – tDCS – has mixed results when it comes to cognitive enhancement.
“It would be wonderful if we could use tDCS to enhance cognition because then we could potentially use it to treat cognitive impairment in psychiatric illnesses,” said Flavio Frohlich, PhD, study senior author and assistant professor of psychiatry, cell biology and physiology, biomedical engineering, and neurology. “So, this study is bad news. Yet, the finding makes sense. It means that some of the most sophisticated things the brain can do, in terms of cognition, can’t necessarily be altered with just a constant electric current.”
Frohlich, though, said that using less common alternating current stimulation – so-called tACS – could be a better approach, one that he has been investigating. Earlier this year, Frohlich’s lab found that tACS significantly boosted creativity, likely because he used it to target the brain’s natural electrical alpha oscillations, which have been implicated in creative thought.
With tDCS, scientists don’t target these brain waves, which represent neuronal patterns of communication throughout regions of the brain. Instead, they use tDCS to target brain structures, such particular regions of the cortex.
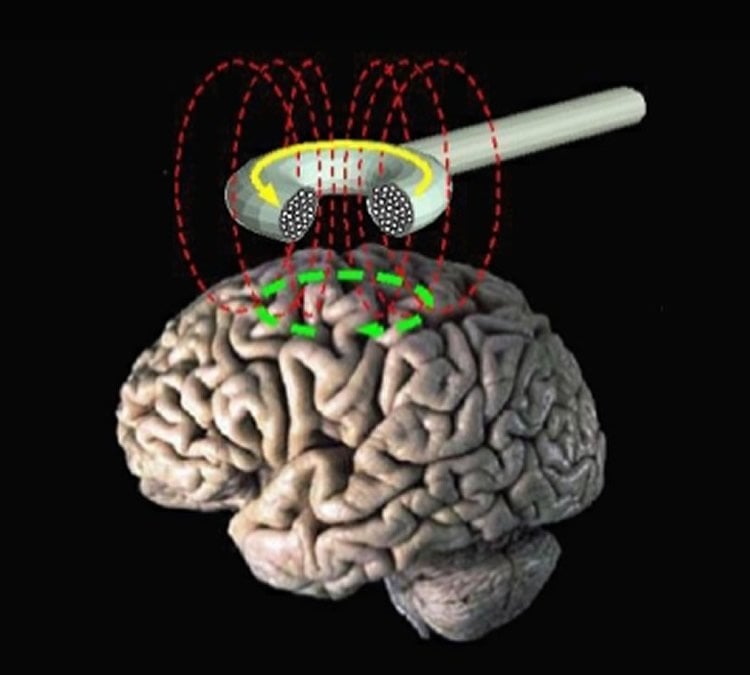
The tDCS boom started in 2000, when German scientists published a paper showing that tDCS could change the excitability of neurons in the motor cortex – the brain region that controls voluntary body movement. Since then, there’s been an explosion of tDCS studies to try to make neurons more active or less active and therefore change outcomes for a variety of brain functions, such as working memory and cognitive acuity, and for illnesses, such as depression and schizophrenia.
But Frohlich said that some of the studies that have made waves were poorly designed. Some studies were not properly double-blinded or properly placebo controlled. Other studies were very small – less than 10 people.
A recent meta-analysis of a large number of tDCS papers showed that tDCS is far from a magic pill for cognitive enhancement or brain-related health conditions.
“Aside from stimulating the motor cortex, which has very exciting implications for stroke rehabilitation, I think the jury is still out on tDCS,” said Frohlich, who is a member of the UNC Neuroscience Center.
In the Behavioural Brain Research study, Frohlich’s team – including graduate student Kristin Sellers, the paper’s first author – recruited 40 healthy adults, each of whom took the standard WAIS-IV intelligence test, which is the most common and well-validated test of IQ. It includes tests for verbal comprehension, perceptional reasoning, working memory, and processing speed.
A week later, Frohlich’s team divided the participants into two groups. Electrodes were placed on each side of each participant’s scalp, under which sat the frontal cortex. Duke University collaborator and co-author Angel Peterchev, PhD, created imaging simulations to ensure Frohlich’s team targeted the same parts of the cortex that previous tDCS studies had targeted.
Then the placebo group received sham stimulation – a brief electrical current, which led participants to think they had been receiving the full tDCS. The other participants received the standard tDCS for twenty minutes – a weak electrical current of 2 millioamperes.
All participants then retook the IQ tests. Frohlich expected that most, if not all, IQ scores would improve because of the practice effect, but that tDCS would not markedly improve scores.
Frohlich’s team did find that all scores improved. Surprisingly, though, the participants who did not receive tDCS saw their IQ scores increase by ten points, whereas participants who received tDCS saw their IQ scores increase by just shy of six points, on average.
When Frohlich and colleagues analyzed the test scores, they saw that the scores for three of the four main kinds of cognitive tests were very similar between the two groups of participants. But the scores for perceptual reasoning were much lower among people who underwent tDCS.
Perceptual reasoning tests fluid intelligence, which is defined as the ability to think logically and apply innovative problem solving to new problems.
Within the category of perceptual reasoning, the researchers saw the biggest differences in the subcategory of matrix reasoning – when participants viewed two groups of symbols and had to find the one symbol missing from the other group.
Frohlich emphasized, “Our findings do not preclude the possibility that other tDCS paradigms may be less harmful or even beneficial. However, it is time to make sure that everybody uses gold standard, placebo-controlled, double-blind study designs. Also, our study demonstrates the importance of more research on how stimulation interacts with brain activity.”
Frohlich stressed that the scientific community should be careful not to create simplistic storylines about tDCS being a ‘magic pill’ for many brain-related conditions. “There could be dangerous consequences, especially if tDCS is used daily,” he said. “Ours was an acute study. We don’t know what the long-term effects are. There is so much more we need to understand before tDCS is ready for home use without medical supervision.”
Frohlich added, “I think our study demonstrates that we need to think of smarter ways to engage the brain to really target the specific brain dynamics involved in what we want to improve, such as cognition for people with depression or schizophrenia. I think tACS is an option, as well as more sophisticated modalities we’ve yet to develop.”
Funding: The National Institutes of Health funded this study.
Additional Information: The research paper “Quantitative Review Finds No Evidence of Cognitive Effects in Healthy Populations From Single-session Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS)” by Jared Cooney Horvathc, Jason D. Forte, and Olivia Carter is also mentioned in this article.
Source: Mark Derewicz – UNC Health Care
Image Source: The image is credited to Eric Wassermann, M.D/NIH and is in the public domain
Original Research: Abstract for “Transcranial direct current stimulation of frontal cortex decreases performance on the WAIS-IV intelligence test” by Kristin K. Sellers, Juliann M. Mellin, Caroline M. Lustenberger, Michael R. Boyle, Won Hee Lee, Angel V. Peterchev, Flavio Frohlich in Behavioural Brain Research. Published online April 28 2015 doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2015.04.031
Abstract
Transcranial direct current stimulation of frontal cortex decreases performance on the WAIS-IV intelligence test
ranscranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) modulates excitability of motor cortex. However, there is conflicting evidence about the efficacy of this non-invasive brain stimulation modality to modulate performance on cognitive tasks. Previous work has tested the effect of tDCS on specific facets of cognition and executive processing. However, no randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled study has looked at the effects of tDCS on a comprehensive battery of cognitive processes. The objective of this study was to test if tDCS had an effect on performance on a comprehensive assay of cognitive processes, a standardized intelligence quotient (IQ) test. The study consisted of two substudies and followed a double-blind, between-subjects, sham-controlled design. In total, 41 healthy adult participants completed the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, Fourth Edition (WAIS-IV) as a baseline measure. At least one week later, participants in substudy 1 received either bilateral tDCS (anodes over both F4 and F3, cathode over Cz, 2 mA at each anode for 20 min) or active sham tDCS (2 mA for 40 s), and participants in substudy 2 received either right or left tDCS (anode over either F4 or F3, cathode over Cz, 2 mA for 20 min). In both studies, the WAIS-IV was immediately administered following stimulation to assess for performance differences induced by bilateral and unilateral tDCS. Compared to sham stimulation, right, left, and bilateral tDCS reduced improvement between sessions on Full Scale IQ and the Perceptual Reasoning Index. This demonstration that frontal tDCS selectively degraded improvement on specific metrics of the WAIS-IV raises important questions about the often proposed role of tDCS in cognitive enhancement.
“Transcranial direct current stimulation of frontal cortex decreases performance on the WAIS-IV intelligence test” by Kristin K. Sellers, Juliann M. Mellin, Caroline M. Lustenberger, Michael R. Boyle, Won Hee Lee, Angel V. Peterchev, Flavio Frohlich in Behavioural Brain Research. Published online April 28 2015 doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2015.04.031