Summary: A new study reports researchers have discovered the mechanism behind the enzyme that controls our appetite in response to low glucose availability.
Source: DGIST.
Researchers from Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) in Korea have uncovered the mechanisms behind the enzyme that controls our appetite in response to low glucose availability in the brain.
Understanding how our appetite is controlled and influenced by our body and brain is important for countering the worldwide obesity epidemic. To maintain a healthy energy balance, our appetite needs to increase or decrease, depending on our caloric intake through food and energy use in our daily lives. Previous research has shown that a region of the brain, known as the hypothalamus, senses levels of sugar (e.g. glucose) and hormones (e.g. leptin) in the blood, and uses these signals to regulate food intake. However, many questions remain about the mechanisms by which the hypothalamus does this.
Now Professor Kim and her team have discovered that low glucose condition activates a hypothalamic enzyme called adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), which changes the properties of small protein-like molecules, called neuropeptides, that our brain uses to communicate. It does so by taking advantage of a natural “self-destruct” mechanism called autophagy. This process allows our body to recycle and degrade cellular materials. By way of analogy, imagine a movie where the hypothalamus is the director who sets the scene in motion by activating AMPK. Prof. Kim has discovered how the brain instructs its two key “actors” to do their job. The first “actor” is a neurohormone called neuropeptide Y (NPY), while the second is another neurohormone produced in the hypothalamus called pro-opiomelanocortin-alpha (POMC). The director activates AMPK, which sets increased autophagy in motion. This in turn influences how our actors, NPY and POMC, behave on a genetic level similar to a movie that tells a story of increased food intake and body weight.
The big challenge for researchers was to untangle the hundreds of possible pathways between the brain and body, in the form of hormones, enzymes and other chemical messengers that might be responsible. They conducted numerous experiments both in vitro, using cell lines, as well as in mice that were examined for changes in feeding behavior, body weight and brain structure. Using cell cultures, they were able to use pharmacological agents – i.e., substances that can change or stop the (genetic) expression of, for example, AMPK – to check whether its presence or absence is critical for autophagy to be induced under differing levels of energy (glucose) availability. By individually blocking off different pathways and activating or de-activating chemical messengers in turn, the researchers were able to determine the brain’s appetite control systems, much like how one might remove actors from a film and see what parts of the story are lost or no longer make sense in the script.
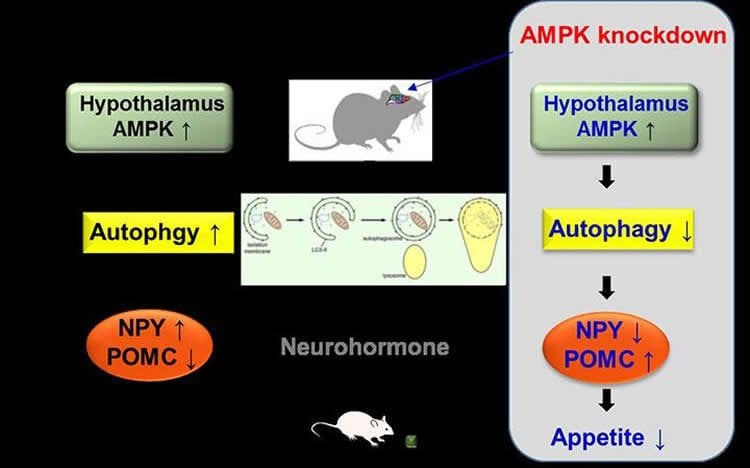
By injecting mice with lentiviruses — slow viruses that are used to introduce changes in the functioning of host genes — the researchers were able to “knock down” AMPK and prevent it from functioning. As a result, the obese mice ate considerably less food and subsequently showed reductions in bodyweight. Combining the results of the animal studies with the in vitro data confirmed that AMPK-knockdown changed the levels of NPY and POMC expression at a genetic level.
By demonstrating how AMPK-activated autophagy controls the expression of neurohormones in the brain’s hypothalamus, researchers are one step closer to understanding the dynamics of our eating behavior. The next step is to untangle how autophagy itself modulates (up or down) our brain’s neurohormones, such as NPY, to regulate our appetite.
Source: Eun-Kyoung Kim – DGIST
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to DGIST.
Original Research: Abstract for “Hypothalamic AMPK-induced autophagy increases food intake by regulating NPY and POMC expression” by Tae Seok Oh, Hanchae Cho, Jae Hyun Cho, Seong-Woon Yu and Eun-Kyoung Kim in Autophagy. Published online August 171 2016 doi:10.1080/15548627.2016.1215382
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]DGIST “How The Brain Controls Our Appetite.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 4 October 2016.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/appetite-glucose-neuroscience-5202/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]DGIST (2016, October 4). How The Brain Controls Our Appetite. NeuroscienceNew. Retrieved October 4, 2016 from https://neurosciencenews.com/appetite-glucose-neuroscience-5202/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]DGIST “How The Brain Controls Our Appetite.” https://neurosciencenews.com/appetite-glucose-neuroscience-5202/ (accessed October 4, 2016).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Hypothalamic AMPK-induced autophagy increases food intake by regulating NPY and POMC expression
Hypothalamic AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) plays important roles in the regulation of food intake by altering the expression of orexigenic or anorexigenic neuropeptides. However, little is known about the mechanisms of this regulation. Here, we report that hypothalamic AMPK modulates the expression of NPY (neuropeptide Y), an orexigenic neuropeptide, and POMC (pro-opiomelanocortin-α), an anorexigenic neuropeptide, by regulating autophagic activity in vitro and in vivo. In hypothalamic cell lines subjected to low glucose availability such as 2-deoxy-d-glucose (2DG)-induced glucoprivation or glucose deprivation, autophagy was induced via the activation of AMPK, which regulates ULK1 and MTOR complex 1 followed by increased Npy and decreased Pomc expression. Pharmacological or genetic inhibition of autophagy diminished the effect of AMPK on neuropeptide expression in hypothalamic cell lines. Moreover, AMPK knockdown in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus decreased autophagic activity and changed Npy and Pomc expression, leading to a reduction in food intake and body weight. AMPK knockdown abolished the orexigenic effects of intraperitoneal 2DG injection by decreasing autophagy and changing Npy and Pomc expression in mice fed a high-fat diet. We suggest that the induction of autophagy is a possible mechanism of AMPK-mediated regulation of neuropeptide expression and control of feeding in response to low glucose availability.
“Hypothalamic AMPK-induced autophagy increases food intake by regulating NPY and POMC expression” by Tae Seok Oh, Hanchae Cho, Jae Hyun Cho, Seong-Woon Yu and Eun-Kyoung Kim in Autophagy. Published online August 171 2016 doi:10.1080/15548627.2016.1215382






