Summary: Heart rate synchronization occurs, even when people listen to a story alone, when paying attention to certain points of a story.
Source: Cell Press
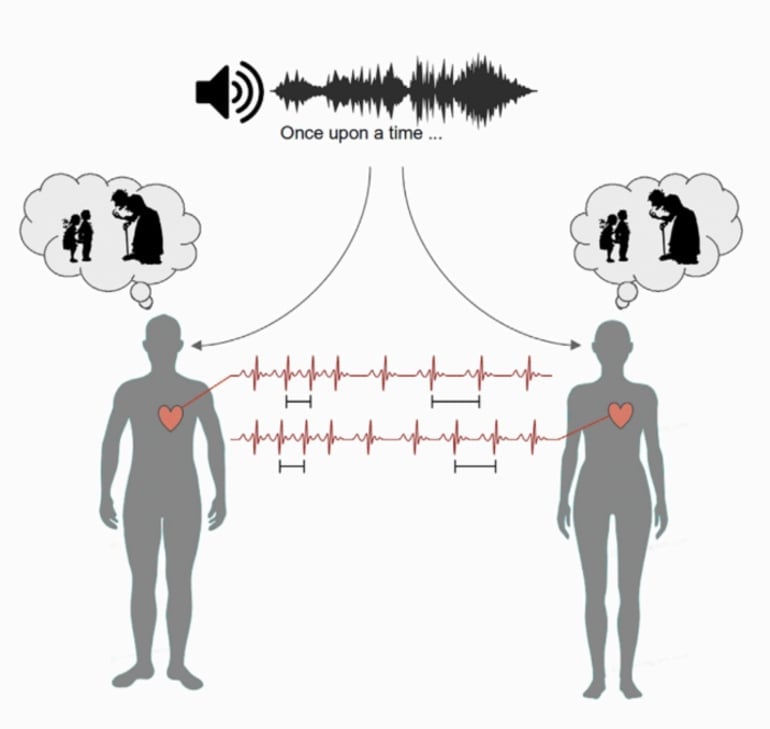
People often unconsciously synchronize bodily functions like heartbeat and breathing when they share an experience, such as a live performance or have a personal conversation. According to a new study, subjects’ heart rates synchronize even if they are just listening to a story by themselves, and this synchronization only occurs when the subjects are paying attention to the story.
The findings from the research are reported September 14 in the journal Cell Reports.
“There’s a lot of literature demonstrating that people synchronize their physiology with each other. But the premise is that somehow you’re interacting and physically present the same place,” says co-senior author Lucas Parra, a professor at City College of New York. “What we have found is that the phenomenon is much broader, and that simply following a story and processing stimulus will cause similar fluctuations in people’s heart rates. It’s the cognitive function that drives your heart rate up or down.”
“What’s important is that the listener is paying attention to the actions in the story,” adds co-senior author Jacobo Sitt, a researcher at the Paris Brain Institute and Inserm. “It’s not about emotions, but about being engaged and attentive, and thinking about what will happen next. Your heart responds to those signals from the brain.”
The investigators conducted a series of four experiments to explore the role of consciousness and attention in synchronizing participants’ heart rates. In the first, healthy volunteers listened to an audiobook of Jules Verne’s 20,000 Leagues Under the Sea.
As they listened, their heart rate changed based on what was happening in the story, as measured by electrocardiogram (EKG). The researchers found that the majority of subjects showed increases and decreases in their heart rate at the same points in the narrative.
In the second experiment, volunteers watched short instructional videos. Because the videos were educational with no underlying emotional variations, this experiment confirmed that emotional engagement in a story was not playing a part. The first time they watched the videos, heart rates across the subjects showed similar fluctuations.
The participants then watched the videos a second time while counting backwards in their heads. That time, the lack of attention resulted in a drop in the synchronization of heart rates across subjects, confirming that attention was important.
In the third experiment, the subjects listened to short children’s stories, some while attentive and others while being distracted, and then were asked to recall facts from the stories.
The researchers found that the fluctuations seen in the participants’ heart rates were predictive of how well they did at answering questions about the story—more synchronization predicted better test scores. This indicated that changes in heart rate were a signal of conscious processing of the narrative.
When the researchers looked at changes in breathing rates, they didn’t see the same synchronization among the subjects. This was surprising, since breathing is known to affect heart rate.
The fourth experiment was similar to the first, but it included both healthy volunteers and patients with disorders of consciousness—such as those in comas or persistent vegetative states. All subjects were presented with an audiobook of a children’s story. As expected, the patients had lower rates of heart synchronization than did healthy controls. When the patients were examined six months later, some of them with higher synchronization had regained some consciousness.
“This study is still very preliminary, but you can imagine this being an easy test that could be implemented to measure brain function,” Sitt says. “It doesn’t require a lot of equipment. It even could be performed in an ambulance on the way to the hospital.” He notes that much more validation is needed with larger numbers of patients as well as comparisons to accepted tests of brain function like EEGs and fMRIs. This is something his group is continuing to study.
Parra says such research is also important for understanding mindfulness and the brain-body connection. “Neuroscience is opening up in terms of thinking of the brain as part of an actual anatomical, physical body,” he says. “This research is a step in the direction of looking at the brain-body connection more broadly, in terms of how the brain affects the body.”
Funding: This work was supported by Paris Brain Institute (France) and the program “Investissements d’avenir,” a Sorbonne PhD grant, a CARNOT maturation grant; a Sorbonne Universités EMERGENCE grant, an EU-PerMed grant, a French embassy UK – Seeding Grant 2018, a Medical Research Council New Investigator Research Grant (UK), and the National Science Foundation.
Parra and Sitt both credit their trainees for conducting much of the work represented in the paper.
The co-first authors were Jens Madsen, a postdoctoral fellow in the Parra lab, and Pauline Pérez, a PhD student in the Sitt lab.
About this neuroscience research news
Author: Carly Britton
Source: Cell Press
Contact: Carly Britton – Cell Press
Image: The image is credited to Perez and Madsen et al./Cell Reports
Original Research: Open access.
“Conscious processing of narrative stimuli synchronizes heart rate between individuals” by Jacobo Sitt et al. Cell Reports
Abstract
Conscious processing of narrative stimuli synchronizes heart rate between individuals
Highlights
- Narrative stimuli can synchronize fluctuations of heart rate between individuals
- This interpersonal synchronization is modulated by attention and predicts memory
- These effects on heart rate cannot be explained by modulation of respiratory patterns
- Synchrony is lower in patients with disorders of consciousness
Summary
Heart rate has natural fluctuations that are typically ascribed to autonomic function. Recent evidence suggests that conscious processing can affect the timing of the heartbeat.
We hypothesized that heart rate is modulated by conscious processing and therefore dependent on attentional focus. To test this, we leverage the observation that neural processes synchronize between subjects by presenting an identical narrative stimulus.
As predicted, we find significant inter-subject correlation of heart rate (ISC-HR) when subjects are presented with an auditory or audiovisual narrative. Consistent with our hypothesis, we find that ISC-HR is reduced when subjects are distracted from the narrative, and higher ISC-HR predicts better recall of the narrative. Finally, patients with disorders of consciousness have lower ISC-HR, as compared to healthy individuals.
We conclude that heart rate fluctuations are partially driven by conscious processing, depend on attentional state, and may represent a simple metric to assess conscious state in unresponsive patients.






