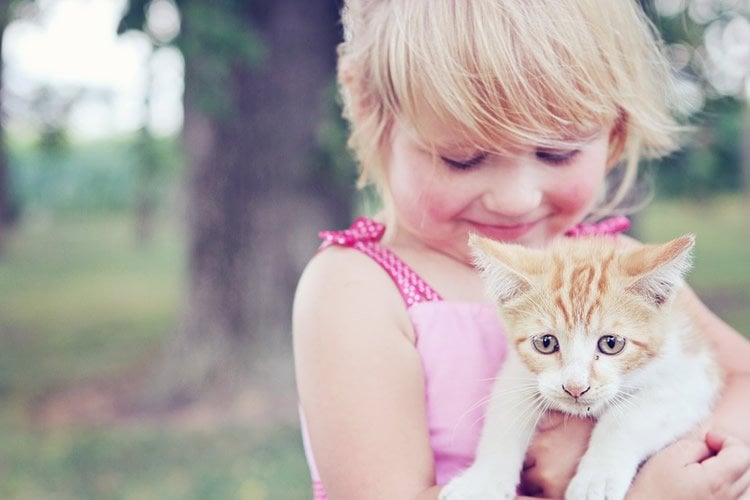
Summary: According to a new study, children report strong relationships with their pets relative to their siblings.
Source: University of Cambridge.
Children get more satisfaction from relationships with their pets than with their brothers or sisters, according to new research from the University of Cambridge. Children also appear to get on even better with their animal companions than with siblings.
The research adds to increasing evidence that household pets may have a major influence on child development, and could have a positive impact on children’s social skills and emotional well-being.
Pets are almost as common as siblings in western households, although there are relatively few studies on the importance of child-pet relationships.
‘‘Anyone who has loved a childhood pet knows that we turn to them for companionship and disclosure, just like relationships between people,” says Matt Cassells, a Gates Cambridge Scholar at the Department of Psychiatry, who led the study. “We wanted to know how strong these relationships are with pets relative to other close family ties. Ultimately this may enable us to understand how animals contribute to healthy child development”
This study, published in the Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, was conducted in collaboration with the WALTHAM Centre for Pet Nutrition, part of Mars Petcare and co-funded by the Economic and Social Research Council as part of a larger study, led by Prof Claire Hughes at the University of Cambridge Centre for Family Research. Researchers surveyed 12 year old children from 77 families with one or more pets of any type and more than one child at home. Children reported strong relationships with their pets relative to their siblings, with lower levels of conflict and greater satisfaction in owners of dogs than other kinds of pets.

‘‘Even though pets may not fully understand or respond verbally, the level of disclosure to pets was no less than to siblings,” says Cassels. “The fact that pets cannot understand or talk back may even be a benefit as it means they are completely non-judgmental.
“While previous research has often found that boys report stronger relationships with their pets than girls do, we actually found the opposite. While boys and girls were equally satisfied with their pets, girls reported more disclosure, companionship, and conflict with their pet than did boys, perhaps indicating that girls may interact with their pets in more nuanced ways.’’
“Evidence continues to grow showing that pets have positive benefits on human health and community cohesion,” says Dr Nancy Gee, Human-Animal Interaction Research Manager at WALTHAM and a co-author of the study. “The social support that adolescents receive from pets may well support psychological well-being later in life but there is still more to learn about the long term impact of pets on children’s development.”
Source: Craig Brierley – University of Cambridge
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is in the public domain.
Original Research: Abstract for “One of the family? Measuring early adolescents’ relationships with pets and siblings” by Matthew T Cassels, Naomi White, Nancy Gee, and Claire Hughes in Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology. Published online January 20 2017 doi:10.1016/j.appdev.2017.01.003
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]University of Cambridge “Pets, Not Siblings, Are A Child’s Best Friend.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 27 January 2017.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/sibling-pet-relationships-6019/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]University of Cambridge (2017, January 27). Pets, Not Siblings, Are A Child’s Best Friend. NeuroscienceNew. Retrieved January 27, 2017 from https://neurosciencenews.com/sibling-pet-relationships-6019/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]University of Cambridge “Pets, Not Siblings, Are A Child’s Best Friend.” https://neurosciencenews.com/sibling-pet-relationships-6019/ (accessed January 27, 2017).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
One of the family? Measuring early adolescents’ relationships with pets and siblings
Pets are common but their importance to children and early adolescents has received scant empirical attention. This is partly due to a lack of tools for measuring child-pet relationships. The first aim of the present study (involving 77 12-year-olds) was to evaluate a pet adaptation of an established measure of human relationship quality, the Network of Relationships Inventory (NRI). Next, we applied the NRI to examine how pet relationship quality varies with pet type and participant’s gender, and to compare participants’ relationships with pets and with siblings. Results showed that girls reported more disclosure, companionship, and conflict with their pet than did boys, while dog owners reported greater satisfaction and companionship with their pet than did owners of other pets. Highlighting the importance of early adolescents’ pet relationships, participants derived more satisfaction and engaged in less conflict with their pets than with their siblings.
“One of the family? Measuring early adolescents’ relationships with pets and siblings” by Matthew T Cassels, Naomi White, Nancy Gee, and Claire Hughes in Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology. Published online January 20 2017 doi:10.1016/j.appdev.2017.01.003