Summary: A new study reveals the role the motor system plays in the perception of language.
Source: UC Merced.
Right now, while you are reading these typewritten words, your hand muscles are moving imperceptibly, but measurably. These movements would be even greater if the words were handwritten.
That’s because your motor system strongly contributes to your perception of language, in part by trying to simulate the movements that were necessary to craft the words you read on a page or screen.
That’s the point of a new paper in the journal Neuroscience Letters by UC Merced graduate student Chelsea Gordon and cognitive science professors Ramesh Balasubramaniam and Michael Spivey.
Their study enhances the campus’s cognitive science focus on embodied cognition, which says the brain guides the body, but the body also guides the brain.
“The conventional thinking was that the brain was modular,” Spivey said. “Each different section was responsible for specific major functions. More and more, though, we are realizing how interconnected the different areas of the brain are.”
Embodied cognition
Balasubramaniam suggests this is because the corticospinal (motor) system develops first in humans, and other functions develop on top of its foundation.
The researchers excited test subjects’ left primary motor cortices with transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) equipment, while showing each subject videos of typed and handwritten words and clusters of letters. The TMS-induced activity in the hand muscles allowed them to measure the motor system’s level of excitement for each different video.
Gordon said the results were somewhat surprising.
“We knew there would be movement, because there have been many studies showing that the tongue muscles are excited when a person hears someone else speaking to them,” she said. “But I thought there would be an equal amount of hand and arm excitement when people saw written and typed words.”
Why handwritten words provide a workout
While typed words did prompt some excitement in the hand muscles, handwritten words produced significantly more, Balasubramaniam said. The researchers believe this is because it takes more muscle work to handwrite words than it does to type them.
That might also be why, as studies have shown, students who take handwritten notes tend to do better in class than those who type notes.
“Handwriting notes means you have to quickly conceptualize, because no one can write as fast as other people speak or as fast as many people can type,” Gordon said.
Researchers also see more motor stimulation if what a person is looking at is something they know how to do, Spivey said.
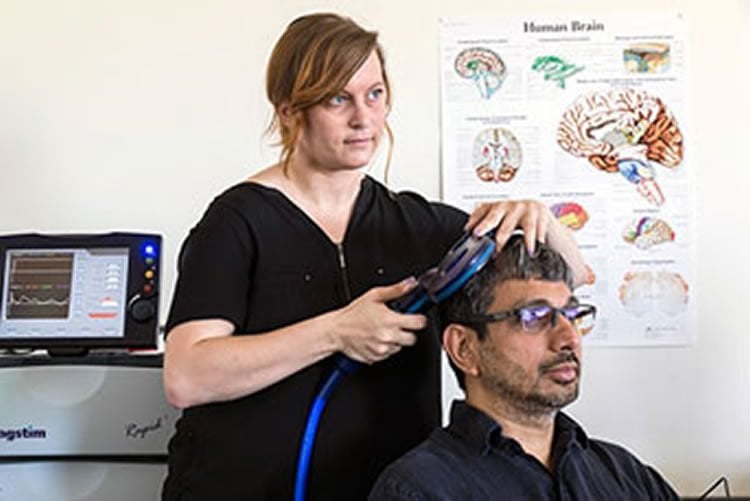
“This is part of how we visually recognize things,” he said. Our brains do this in fractions of seconds, thousands of times a day, without us consciously being aware of it.
How our motor systems affect how we learn
Gordon, a fourth-year Cognitive Science and Information Systems student originally from Rock, Mich., said she hopes to build on this experiment by trying to understand whether the motor system engages more with handwriting because the act of handwriting is a continuous, linear movement. She’s also interested in finding out what other perceptual tasks the motor system is integral to, such as understanding color.
These studies could someday have implications for people with disabilities, too.
“Damage to your motor system changes the way you think and see the world, and that damage can sometimes be serious enough to cause dementia-like symptoms,” Spivey said.
Balasubramaniam, Gordon’s advisor, said he’s also interested in seeing if there are differences among bilingual people when they are reading words in their native and second languages, and Spivey and one of his graduate students are pursuing several projects related to bilingualism.
They hope to better understand how people retain language and motor functions and contribute to the growing storehouse of knowledge about embodied cognition.
“Ultimately, your body is a big part of who you are,” Spivey said.
Source: Lorena Anderson – UC Merced
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to UC Merced.
Original Research: Abstract for “Corticospinal excitability during the processing of handwritten and typed words and non-words” by Chelsea L. Gordon, Michael J. Spivey, and Ramesh Balasubramaniam in Neuroscience Letters. Published online June 9 2017 doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2017.05.021
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]UC Merced “How Reading Makes Us Move.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 13 June 2017.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/reading-movement-6898/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]UC Merced (2017, June 13). How Reading Makes Us Move. NeuroscienceNew. Retrieved June 13, 2017 from https://neurosciencenews.com/reading-movement-6898/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]UC Merced “How Reading Makes Us Move.” https://neurosciencenews.com/reading-movement-6898/ (accessed June 13, 2017).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Corticospinal excitability during the processing of handwritten and typed words and non-words
A number of studies have suggested that perception of actions is accompanied by motor simulation of those actions. To further explore this proposal, we applied Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) to the left primary motor cortex during the observation of handwritten and typed language stimuli, including words and non-word consonant clusters. We recorded motor-evoked potentials (MEPs) from the right first dorsal interosseous (FDI) muscle to measure cortico-spinal excitability during written text perception. We observed a facilitation in MEPs for handwritten stimuli, regardless of whether the stimuli were words or non-words, suggesting potential motor simulation during observation. We did not observe a similar facilitation for the typed stimuli, suggesting that motor simulation was not occurring during observation of typed text. By demonstrating potential simulation of written language text during observation, these findings add to a growing literature suggesting that the motor system plays a strong role in the perception of written language.
“Corticospinal excitability during the processing of handwritten and typed words and non-words” by Chelsea L. Gordon, Michael J. Spivey, and Ramesh Balasubramaniam in Neuroscience Letters. Published online June 9 2017 doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2017.05.021