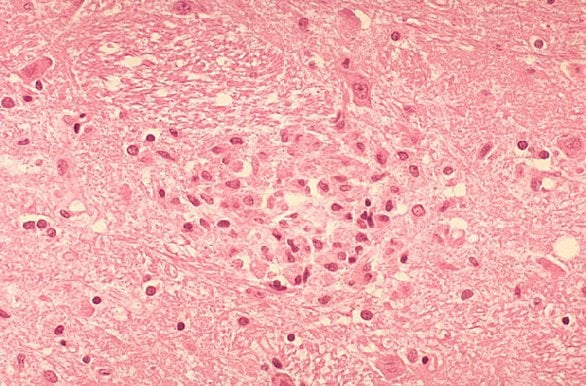
Even a mild injury to the brain can have long lasting consequences, including increased risk of cognitive impairment later in life. While it is not yet known how brain injury increases risk for dementia, there are indications that chronic, long-lasting, inflammation in the brain may be important. A new paper by researchers at the University of Kentucky Sanders-Brown Center on Aging (SBCoA), appearing in the Journal of Neuroscience, offers the latest information concerning a “switch” that turns “on” and “off” inflammation in the brain after trauma.
A team of researchers led by Linda Van Eldik, director of SBCoA, used a mouse model to study the role of p38a MAPK in trauma-induced injury responses in the microglia resident immune cell of the brain.
“The p38α MAPK protein is an important switch that drives abnormal inflammatory responses in peripheral tissue inflammatory disorders, including chronic debilitating diseases like rheumatoid arthritis,” said Van Eldik.
“However, less is known about the potential importance of p38α MAPK in controlling inflammatory responses in the brain. Our work supports p38α MAPK as a promising clinical target for the treatment of CNS disorders associated with uncontrolled brain inflammation, including trauma, and potentially others like Alzheimer’s disease. We are excited by our findings, and are actively working to develop drugs targeting p38a MAPK designed specifically for diseases of the brain.”

Lead author of the paper Adam D. Bachstetter said, “I was surprised when I looked under the microscope at the brain tissue of mice that had a diffuse brain injury. Microglia normally look like a small spider, but after suffering a brain injury the microglia become like angry spiders from a horror movie. In brain-injured mice that lack p38a MAPK there were no angry-looking microglia, only the normal small spider-like cells. When I started the study I never expected the results to be so clear and striking. I believe that the p38a MAPK is a promising clinical target for the treatment of CNS disorders with dysregulated inflammatory responses, but we are still a long way from development of CNS-active p38 inhibitor drugs. ”
Notes about this traumatic brain injury research
The paper, ” The p38a MAPK regulates microglial responsiveness to diffuse traumatic brain injury”, is from a team of researchers including Linda Van Eldik, as well as Adam Bachstetter, Machi Kaneko and Danielle Goulding of SBCoA; and Rachel K. Rowe and Jonathan Lifshitz, director of the Translational Neurotrauma Research Program Barrow Neurological Institute at Phoenix Children’s Hospital in Arizona.
Contact: Allison Elliott – University of Kentucky
Source: University of Kentucky press release
Image Source: The microglia brain slice image is available in the public domain.
Original Research: Abstract for “The p38α MAPK Regulates Microglial Responsiveness to Diffuse Traumatic Brain Injury” by Adam D. Bachstetter, Rachel K. Rowe, Machi Kaneko, Danielle Goulding, Jonathan Lifshitz, and Linda J. Van Eldik in Journal of Neuroscience. Published online April 3 2013 DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5399-12.2013