Old world monkey had tiny yet complex brain.
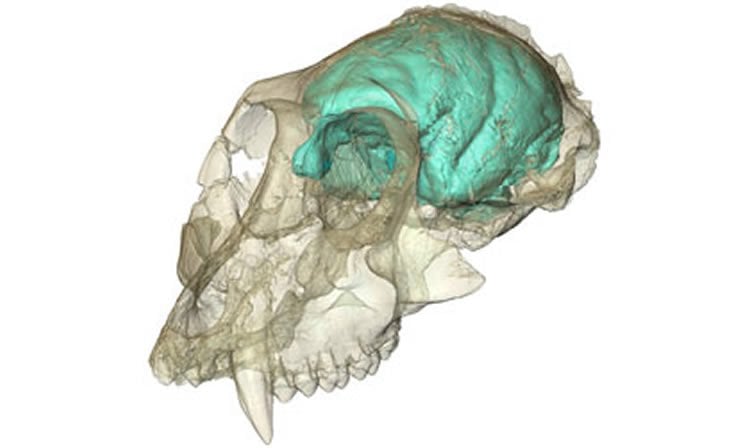
The brain hidden inside the oldest known Old World monkey skull has been visualized for the first time. The creature’s tiny but remarkably wrinkled brain supports the idea that brain complexity can evolve before brain size in the primate family tree.
The ancient monkey, known scientifically as Victoriapithecus, first made headlines in 1997 when its fossilized skull was discovered on an island in Kenya’s Lake Victoria, where it lived 15 million years ago.
Now, thanks to high-resolution X-ray imaging, researchers have peered inside its cranial cavity and created a three-dimensional computer model of what the animal’s brain likely looked like.
Micro-CT scans of the creature’s skull show that Victoriapithecus had a tiny brain relative to its body.
Co-authors Fred Spoor of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology and Lauren Gonzales of Duke University calculated its brain volume to be about 36 cubic centimeters, which is less than half the volume of monkeys of the same body size living today.
If similar-sized monkeys have brains the size of oranges, the brain of this particular male was more akin to a plum.
“When Lauren finished analyzing the scans she called me and said, ‘You won’t believe what the brain looks like,’” said co-author Brenda Benefit of New Mexico State University, who first discovered the skull with NMSU co-author Monte McCrossin.
Despite its puny proportions, the animal’s brain was surprisingly complex.
The CT scans revealed numerous distinctive wrinkles and folds, and the olfactory bulb — the part of the brain used to perceive and analyze smells — was three times larger than expected.
“It probably had a better sense of smell than many monkeys and apes living today,” Gonzales said. “In living higher primates you find the opposite: the brain is very big, and the olfactory bulb is very small, presumably because as their vision got better their sense of smell got worse.”
“But instead of a tradeoff between smell and sight, Victoriapithecus might have retained both capabilities,” Gonzales said.
The findings, published in the July 3 issue of Nature Communications, are important because they offer new clues to how primate brains changed over time, and during a period from which there are very few fossils.
“This is the oldest skull researchers have found for Old World monkeys, so it’s one of the only clues we have to their early brain evolution,” Benefit said.
In the absence of fossil evidence, previous researchers have disagreed over whether primate brains got bigger first, and then more folded and complex, or vice versa.
“In the part of the primate family tree that includes apes and humans, the thinking is that brains got bigger and then they get more folded and complex,” Gonzales said. “But this study is some of the hardest proof that in monkeys, the order of events was reversed — complexity came first and bigger brains came later.”
The brain hidden inside the oldest known Old World monkey skull has been visualized for the first time. The ancient monkey, known as Victoriapithecus, first made headlines in 1997 when its 15 million-year-old skull was discovered on an island in Kenya’s Lake Victoria. Now, thanks to high-resolution X-ray imaging, researchers have peered inside its cranial cavity and created a three-dimensional computer model of what the animal’s brain likely looked like. The tiny but remarkably wrinkled brain supports the idea that brain complexity can evolve before brain size in the primate family tree.
The findings also lend support to claims that the small brain of the human ancestor Homo floresiensis, whose 18,000-year-old skull was discovered on a remote Indonesian island in 2003, isn’t as remarkable as it might seem. In spite of their pint-sized brains, Homo floresiensis were able to make fire and use stone tools to kill and butcher large animals.
“Brain size and brain complexity can evolve independently; they don’t have to evolve together at the same time,” Benefit said.
Funding: The work was funded by the Max Planck Society and University College London. The skull was originally discovered with support from the National Science foundation (9505778).
Source: Robin Ann Smith – Duke University
Image Credit: Image is credited to Fred Spoor of the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology
Video Source: The video is available at the Duke University YouTube page
Original Research: Full open access research for for “Cerebral complexity preceded enlarged brain size and reduced olfactory bulbs in Old World monkeys” by Lauren A. Gonzales, Brenda R. Benefit, Monte L. McCrossin and Fred Spoor in Nature Communications. Published online July 3 2015 doi:10.1093/chemse/bjv030
Abstract
Cerebral complexity preceded enlarged brain size and reduced olfactory bulbs in Old World monkeys
Analysis of the only complete early cercopithecoid (Old World monkey) endocast currently known, that of 15-million-year (Myr)-old Victoriapithecus, reveals an unexpectedly small endocranial volume (ECV) relative to body size and a large olfactory bulb volume relative to ECV, similar to extant lemurs and Oligocene anthropoids. However, the Victoriapithecus brain has principal and arcuate sulci of the frontal lobe not seen in the stem catarrhine Aegyptopithecus, as well as a distinctive cercopithecoid pattern of gyrification, indicating that cerebral complexity preceded encephalization in cercopithecoids. Since larger ECVs, expanded frontal lobes, and reduced olfactory bulbs are already present in the 17- to 18-Myr-old ape Proconsul these features evolved independently in hominoids (apes) and cercopithecoids and much earlier in the former. Moreover, the order of encephalization and brain reorganization was apparently different in hominoids and cercopithecoids, showing that brain size and cerebral organization evolve independently.
“Cerebral complexity preceded enlarged brain size and reduced olfactory bulbs in Old World monkeys” by Lauren A. Gonzales, Brenda R. Benefit, Monte L. McCrossin and Fred Spoor in Nature Communications. Published online July 3 2015 doi:10.1093/chemse/bjv030






