Summary: A new neuroimaging study reveals how dogs process words they have been taught to associate with objects. Findings suggest dogs have a rudimentary neural representation of meaning for words they have been taught.
Source: Emory University.
When some dogs hear their owners say “squirrel,” they perk up, become agitated. They may even run to a window and look out of it. But what does the word mean to the dog? Does it mean, “Pay attention, something is happening?” Or does the dog actually picture a small, bushy-tailed rodent in its mind?
Frontiers in Neuroscience published one of the first studies using brain imaging to probe how our canine companions process words they have been taught to associate with objects, conducted by scientists at Emory University. The results suggest that dogs have at least a rudimentary neural representation of meaning for words they have been taught, differentiating words they have heard before from those they have not.
“Many dog owners think that their dogs know what some words mean, but there really isn’t much scientific evidence to support that,” says Ashley Prichard, a PhD candidate in Emory’s Department of Psychology and first author of the study. “We wanted to get data from the dogs themselves — not just owner reports.”
“We know that dogs have the capacity to process at least some aspects of human language since they can learn to follow verbal commands,” adds Emory neuroscientist Gregory Berns, senior author of the study. “Previous research, however, suggests dogs may rely on many other cues to follow a verbal command, such as gaze, gestures and even emotional expressions from their owners.”
The Emory researchers focused on questions surrounding the brain mechanisms dogs use to differentiate between words, or even what constitutes a word to a dog.
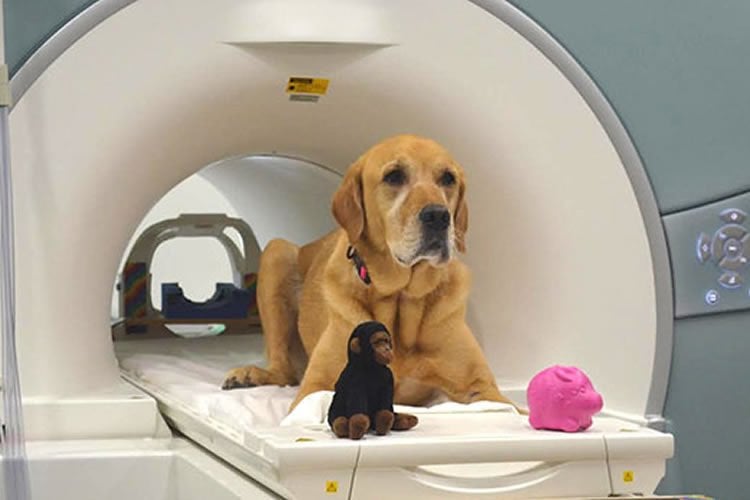
Berns is founder of the Dog Project, which is researching evolutionary questions surrounding man’s best, and oldest friend. The project was the first to train dogs to voluntarily enter a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scanner and remain motionless during scanning, without restraint or sedation. Studies by the Dog Project have furthered understanding of dogs’ neural response to expected reward, identified specialized areas in the dog brain for processing faces, demonstrated olfactory responses to human and dog odors, and linked prefrontal function to inhibitory control.
For the current study, 12 dogs of varying breeds were trained for months by their owners to retrieve two different objects, based on the objects’ names. Each dog’s pair of objects consisted of one with a soft texture, such as a stuffed animal, and another of a different texture, such as rubber, to facilitate discrimination. Training consisted of instructing the dogs to fetch one of the objects and then rewarding them with food or praise. Training was considered complete when a dog showed that it could discriminate between the two objects by consistently fetching the one requested by the owner when presented with both of the objects.
During one experiment, the trained dog lay in the fMRI scanner while the dog’s owner stood directly in front of the dog at the opening of the machine and said the names of the dog’s toys at set intervals, then showed the dog the corresponding toys.
Eddie, a golden retriever-Labrador mix, for instance, heard his owner say the words “Piggy” or “Monkey,” then his owner held up the matching toy. As a control, the owner then spoke gibberish words, such as “bobbu” and “bodmick,” then held up novel objects like a hat or a doll.
The results showed greater activation in auditory regions of the brain to the novel pseudowords relative to the trained words.
“We expected to see that dogs neurally discriminate between words that they know and words that they don’t,” Prichard says. “What’s surprising is that the result is opposite to that of research on humans — people typically show greater neural activation for known words than novel words.”
The researchers hypothesize that the dogs may show greater neural activation to a novel word because they sense their owners want them to understand what they are saying, and they are trying to do so. “Dogs ultimately want to please their owners, and perhaps also receive praise or food,” Berns says.
Half of the dogs in the experiment showed the increased activation for the novel words in their parietotemporal cortex, an area of the brain that the researchers believe may be analogous to the angular gyrus in humans, where lexical differences are processed.
The other half of the dogs, however, showed heightened activity to novel words in other brain regions, including the other parts of the left temporal cortex and amygdala, caudate nucleus, and the thalamus.
These differences may be related to a limitation of the study — the varying range in breeds and sizes of the dogs, as well as possible variations in their cognitive abilities. A major challenge in mapping the cognitive processes of the canine brain, the researchers acknowledge, is the variety of shapes and sizes of dogs’ brains across breeds.
“Dogs may have varying capacity and motivation for learning and understanding human words,” Berns says, “but they appear to have a neural representation for the meaning of words they have been taught, beyond just a low-level Pavlovian response.”
This conclusion does not mean that spoken words are the most effective way for an owner to communicate with a dog. In fact, other research also led by Prichard and Berns and recently published in Scientific Reports, showed that the neural reward system of dogs is more attuned to visual and to scent cues than to verbal ones.
“When people want to teach their dog a trick, they often use a verbal command because that’s what we humans prefer,” Prichard says. “From the dog’s perspective, however, a visual command might be more effective, helping the dog learn the trick faster.”
Co-authors of the Frontiers in Neuroscience study include Peter Cook (a neuroscientist at the New College of Florida), Mark Spivak (owner of Comprehensive Pet Therapy) and Raveena Chhibber (an information specialist in Emory’s Department of Psychology).
Co-authors of the Science Reports paper also include Spivak and Chhibber, along with Kate Athanassiades (from Emory’s School of Nursing).
Source: Carol Clark – Emory University
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is credited to Gregory Berns.
Original Research: Open access research for “Awake fMRI Reveals Brain Regions for Novel Word Detection in Dogs” by Ashley Prichard, Peter F. Cook, Mark Spivak, Raveena Chhibber and Gregory S. Berns in Frontiers in Neuroscience. Published October 15 2018.
doi:10.3389/fnins.2018.00737
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]Emory University”How Dogs Process Words.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 16 October 2018.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/dog-word-processing-10031/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]Emory University(2018, October 16). How Dogs Process Words. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved October 16, 2018 from https://neurosciencenews.com/dog-word-processing-10031/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]Emory University”How Dogs Process Words.” https://neurosciencenews.com/dog-word-processing-10031/ (accessed October 16, 2018).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Awake fMRI Reveals Brain Regions for Novel Word Detection in Dogs
How do dogs understand human words? At a basic level, understanding would require the discrimination of words from non-words. To determine the mechanisms of such a discrimination, we trained 12 dogs to retrieve two objects based on object names, then probed the neural basis for these auditory discriminations using awake-fMRI. We compared the neural response to these trained words relative to “oddball” pseudowords the dogs had not heard before. Consistent with novelty detection, we found greater activation for pseudowords relative to trained words bilaterally in the parietotemporal cortex. To probe the neural basis for representations of trained words, searchlight multivoxel pattern analysis (MVPA) revealed that a subset of dogs had clusters of informative voxels that discriminated between the two trained words. These clusters included the left temporal cortex and amygdala, left caudate nucleus, and thalamus. These results demonstrate that dogs’ processing of human words utilizes basic processes like novelty detection, and for some dogs, may also include auditory and hedonic representations.