Identifying bipolarity through MRI’s proves successful in initial results.
What are some of the most troubling numbers in mental health? Six to 10 — the number of years it can take to properly diagnose a mental health condition. Dr. Elizabeth Osuch, a Researcher at Lawson Health Research Institute and a Psychiatrist at London Health Sciences Centre and the Department of Psychiatry at Western University, is helping to end misdiagnosis by looking for a ‘biomarker’ in the brain that will help diagnose and treat two commonly misdiagnosed disorders.
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD), otherwise known as Unipolar Disorder, and Bipolar Disorder (BD) are two common disorders. Currently, diagnosis is made by patient observation and verbal history. Mistakes are not uncommon, and patients can find themselves going from doctor to doctor receiving improper diagnoses and prescribed medications to little effect.

Dr. Osuch looked to identify a ‘biomarker’ in the brain which could help optimize the diagnostic process. She examined youth who were diagnosed with either MDD or BD (15 patients in each group) and imaged their brains with an MRI to see if there was a region of the brain which corresponded with the bipolarity index (BI). The BI is a diagnostic tool which encompasses varying degrees of bipolar disorder, identifying symptoms and behavior in order to place a patient on the spectrum.
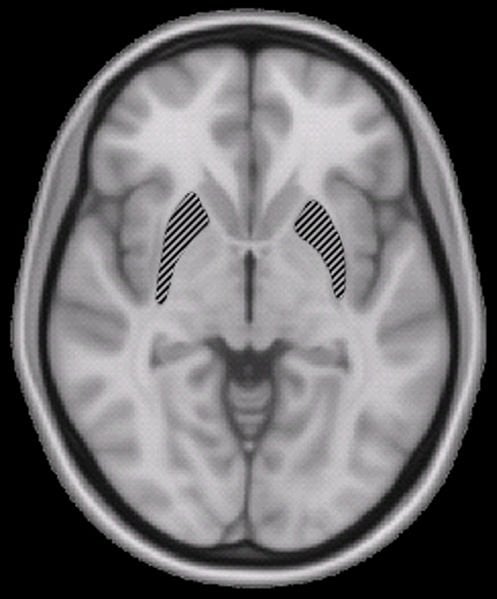
What she found was the activation of the putamen correlated positively with BD. This is the region of the brain that controls motor skills, and has a strong link to reinforcement and reward. This speaks directly to the symptoms of bipolar disorder. “The identification of the putamen in our positive correlation may indicate a potential trait marker for the symptoms of mania in bipolar disorder,” states Dr. Osuch.
In order to reach this conclusion, the study approached mental health research from a different angle. “The unique aspect of this research is that, instead of dividing the patients by psychiatric diagnoses of bipolar disorder and unipolar depression, we correlated their functional brain images with a measure of bipolarity which spans across a spectrum of diagnoses.” Dr. Osuch explains, “This approach can help to uncover a ‘biomarker’ for bipolarity, independent of the current mood symptoms or mood state of the patient.”
Moving forward Dr. Osuch will repeat the study with more patients, seeking to prove that the activation of the putamen is the start of a trend in large numbers of patients. The hope is that one day there could be a definitive biological marker which could help differentiate the two disorders, leading to a faster diagnosis and optimal care.
In using a co-relative approach, a novel method in the field, Dr. Osuch uncovered results in patients that extend beyond verbal history and observation. These results may go on to change the way mental health is diagnosed, and subsequently treated, worldwide.
Notes about this neuroimaging and mental health research
Contact: Maximilian Specht – Lawson Health Research Institute
Source: Lawson Health Research Institute press release
Image Source: The putamen brain scan image is credited to Woutergroen and is in the public domain.
Original Research: The research will appear in the Journal of Affective Disorders. We will provide a link to the research when available.