Recent scientific advances have meant that eyesight can be partially restored to those who previously would have been blind for life. However, scientists at the University of Montreal and the University of Trento have discovered that the rewiring of the senses that occurs in the brains of the long-term blind means that visual restoration may never be complete. “We had the opportunity to study the rare case of a woman with very low vision since birth and whose vision was suddenly restored in adulthood following the implantation of a Boston Keratoprosthesis in her right eye,” explained Giulia Dormal, who led the study. “On one hand, our findings reveal that the visual cortex maintains a certain degree of plasticity – that is the capacity to change as a function of experience – in an adult person with low vision since early life. On the other, we discovered that several months after the surgery, the visual cortex had not regained full normal functioning.” The visual cortex is the part of the brain that processes information from our eyes.
Scientists know that in cases of untreatable blindness, the occipital cortex – that is the posterior part of the brain that is normally devoted to vision – becomes responsive to sound and touch in order to compensate for the loss of vision. “This important brain reorganization represents a challenge for people encountering eye surgery to recover vision, because the deprived and reorganized occipital cortex may not be capable of seeing anymore after having spent years in the dark,” Dormal said.
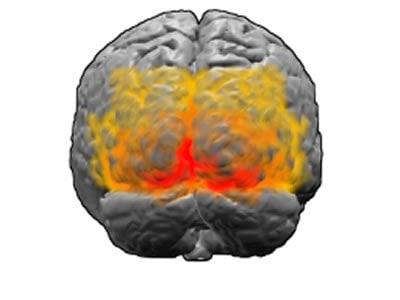
In order to ascertain how much of a challenge this may be, the researchers worked with the patient, a 50 year old Quebec woman. They conducted behavioral and neurophysiological measurements before and after surgery to track changes in her sight and brain anatomy, and in the way her brain responded to sights and sounds. This involved taking MRI images as she completed various visual and auditory tasks and comparing her scans with scans that had been taken from people with normal eyesight and people with untreatable blindness who had performed the same tasks. “We show that structural and functional reorganization of occipital regions were present in this patient before surgery as a result of longstanding visual impairment, and that some reorganizations can be partially reversed by visual restoration in adulthood,” said Oliver Collignon, who supervised the research. “Because of important advances in visual restoration techniques, such findings have important clinical implications for the predictive outcome of blind individuals who are candidate to such interventions.”
The study suggests that eye surgery can lead to a positive outcome even when performed in adulthood after a life-time of profound blindness. There is however an important caveat. “The recovery observed in the visual cortex, that is highlighted by a decrease in auditory-driven responses and by an increase in both visually-driven responses and grey matter density with time, is not total,” Dormal explained. “Indeed, auditory-driven responses were still evidenced in certain regions of the visual cortex even 7 months after surgery, and these responses overlapped with visually-driven responses. This overlap may be the reason some aspects of vision, despite having improved with time, still remained below normal range 7 months after surgery.”
The clinical implications of the research are two-fold. “Our findings open the door to the use of functional magnetic resonance imaging before surgery as a prognostic tool for visual outcome and pave the way for the development of adapted rehabilitation programs following visual restoration,” Collignon said.
The research received funding from the Canada Research Chair Program, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Saint-Justine Foundation, the European Research Council (starting grant MADVIS, ERC-StG 337573, the Veronneau Troutman Foundation, the Fonds de recherche en ophtalmologie de l’Université de Montréal, PAI/UIAP grant PAI/33, and the Belgian National Fund for Scientific Research. The University of Montreal is officially known as Université de Montréal.
Contact: William Raillant-Clark – University of Montreal
Source: University of Montreal press release
Image Source: The image is credited to Washington irving and is licensed Creative Commons Attribution Share Alike 3.0 Unported
Original Research: Abstract for “Tracking the evolution of crossmodal plasticity and visual functions before and after sight-restoration” by Giulia Dormal, Franco Lepore, Mona Harissi-Dagher, Geneviève Albouy, Armando Bertone, Bruno Rossion, and Olivier Collignon in Journal of Neurophysiology. Published online December 17 2014 doi:10.1152/jn.00420.2014