A new study from The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston fills an important gap in understanding the link between traumatic brain injury and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Previously, UTMB researchers found a toxic form of tau protein that increases after a traumatic brain injury that may contribute to development of chronic traumatic encephalopathy, a condition experienced by many professional athletes and military personnel. What remained a mystery was if this protein could cause dementia symptoms.
To test this hunch, the group isolated this protein from animals that had experienced a TBI and then injected it into another group of animals to see if they would develop impairments. The animals developed the same type of mental impairments caused by Alzheimer’s disease and these new findings can be found in the Journal of Neurotrauma.
“These findings provide direct evidence supporting our hypothesis that this form of toxic tau induces many of the symptoms of TBI and may be responsible for the increased risk for neurodegenerative disease and spread of impairments throughout the brain following TBI,” said Rakez Kayed, associate professor in the department of neurology and the Mitchell Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases. “Because this form of tau plays an important role in the toxicity underlying TBI, it may be a viable therapeutic target. Further study is needed to explore this possibility.”
A TBI can happen after a sudden blow or jolt to the head or body and each year there are about 1.5 million new cases in the United States.
In some cases, TBI not only induces immediate mental difficulties, but can also lead to increased risk of dementia and other neurological disorders later in life. There are no currently available treatments for the long-term effects of TBI.
Brain cells depend on tau protein to form highways for the cell to receive nutrients and get rid of waste. In some neurodegenerative diseases, the tau protein changes into a toxic form. When this happens, molecular nutrients can no longer move to where they are needed and the brain cells eventually die.
In the current study, the UTMB team led by Kayed and Bridget Hawkins, assistant professor in the department of anesthesiology, found toxic forms of tau in the brains of animals in two different models of TBI.
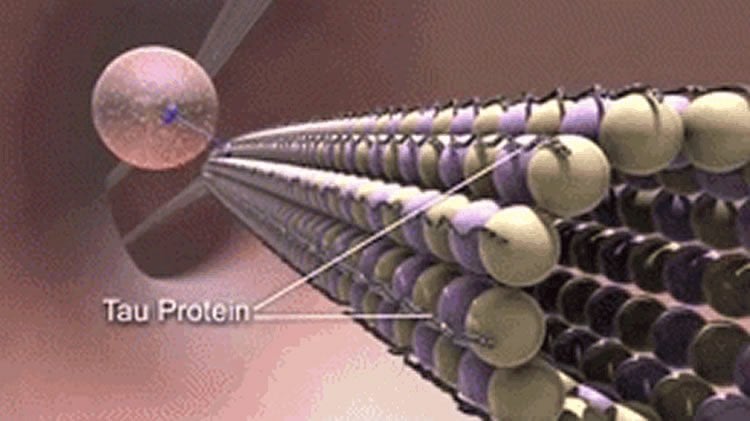
Using a separate group of mice, the team injected the toxic tau molecules into the hippocampus, a brain region critical to memory. These mice underwent behavioral tests to assess their memory and thinking abilities. The mice that received the toxic tau had difficulties with these tests compared with similar mice that didn’t receive the injections. In the mice with the toxic protein, levels increased in the injection sites and the cerebellum, a brain region involved in motor control. This was similar to a previous Alzheimer’s animal model study that found toxic tau molecules spread damage from the injection site to other brain regions.
Kayed said that their results suggest that TBI may share a common mechanism with neurodegenerative tau-mediated diseases. These data also suggest that the increased prevalence of acquiring CTE and Alzheimer’s disease many years after the occurrence of TBI may be due to the seeding and spread of toxic tau released following brain injury. This has important implications for both the treatment of TBI and for the prevention of neurodegeneration later in life.
Other authors include Julia Gerson, Diana L. Castillo-Carranza, Urmi Sengupta, Riddhi Bodani, Donald Prough and Douglas DeWitt.
Funding: This work was supported in part by the Darrell K. Royal Research Fund for Alzheimer’s Disease, the Mitchell Center for Neurodegenerative Disease and the Sealy Center for Vaccine Development. Additionally, these studies were completed as part of an interdisciplinary research team funded by The Moody Project for Translational Traumatic Brain Injury Research.
Source: Donna Ramirez – UTMB Galveston
Image Source: The image is in the public domain
Original Research: Abstract for “Tau oligomers derived from Traumatic Brain Injury cause cognitive impairment and accelerate onset of pathology in Htau mice” by Julia E Gerson, Dr. Diana L Castillo-Carranza, Urmi Sengupta, Riddhi Bodani, Dr. Donald S. Prough, Dr. Douglas DeWitt, Dr. Bridget E. Hawkins, and Dr. Rakez Kayed in Journal of Neurotrauma. Published online January 2016 doi:10.1089/neu.2015.4262
Abstract
Tau oligomers derived from Traumatic Brain Injury cause cognitive impairment and accelerate onset of pathology in Htau mice
Tau aggregation is a pathological feature of numerous neurodegenerative disorders and has also been shown to occur under certain conditions of traumatic brain injury (TBI). Currently, no effective treatments exist for the long-term effects of TBI. In some cases, TBI not only induces cognitive changes immediately following injury, but also leads to increased incidence of neurodegeneration later in life. Growing evidence from our lab and others suggests that the oligomeric forms of tau initiate the onset and spread of neurodegenerative tauopathies. Previously, we have shown increased levels of brain-derived tau oligomers in autopsy samples from patients diagnosed with Alzheimer’s Disease. We have also shown similar increases in tau oligomers in animal models of neurodegenerative diseases and TBI. In the current study, we evaluated the presence of tau oligomers in blast-induced TBI. To test the direct impact of TBI-derived tau oligomer toxicity, we isolated tau oligomers from the brains of rats that underwent either a blast-induced or a fluid percussion injury-induced TBI. Oligomers were characterized biochemically and morphologically and were then injected into the hippocampi of mice overexpressing human tau (Htau). Mice were cognitively evaluated and their brains were collected for immunological analysis following testing. We found that tau oligomers form as a result of brain injury in two different models of TBI. Additionally, these oligomers accelerated the onset of cognitive deficits when injected into the brains of Htau mice. Tau oligomer levels increased in the hippocampal injection sites and the cerebellum, suggesting that tau oligomers may be responsible for seeding the spread of pathology following TBI. Our results suggest that tau oligomers play an important role in the toxicity underlying TBI and may be a viable therapeutic target.
“Tau oligomers derived from Traumatic Brain Injury cause cognitive impairment and accelerate onset of pathology in Htau mice” by Julia E Gerson, Dr. Diana L Castillo-Carranza, Urmi Sengupta, Riddhi Bodani, Dr. Donald S. Prough, Dr. Douglas DeWitt, Dr. Bridget E. Hawkins, and Dr. Rakez Kayed in Journal of Neurotrauma. Published online January 2016 doi:10.1089/neu.2015.4262