Summary: Teens with schizophrenia symptoms and a genetic abnormality of chromosome 22 had significant brain atrophy in the hippocampus compared to those with the genetic variant and no psychiatric symptoms.
Source: University of Geneva
Schizophrenia causes hallucinations and memory or cognition problems inter alia. This psychiatric illness affects 0.5% of the general population, and it may be related to genetic abnormalities of chromosome 22, known as 22q11 deletion syndrome. However, not everyone who has the syndrome necessarily develops psychotic symptoms. So, what triggers the illness? Researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, have provided an initial answer after observing and analysing several years of patients with deletion syndrome. The scientists found that the size of the hippocampus, the area of the brain responsible for memory and emotions, was smaller than normal but followed the same developmental curve as in healthy subjects. Yet, when the first psychotic symptoms appear – generally in adolescence – the hippocampus atrophies dramatically.
The results, published in Molecular Psychiatry, open up new avenues for understanding the causes of schizophrenia.
22q11 deletion syndrome is a neurogenetic disorder that targets chromosome 22. Thirty percent of people affected by the syndrome end up developing psychotic symptoms specific to schizophrenia, such as auditory hallucinations, memory problems, disorders affecting their perception of reality, and difficulties in social interactions characterised by strong paranoia. “It’s now known that schizophrenia is linked to the hippocampus, a complex area of the brain that carries out a vast amount of processes simultaneously linked to memory, imagination and the emotions,” explains Stephan Eliez, professor in the Department of Psychiatry in UNIGE’s Faculty of Medicine. Recent studies have shown that also people suffering from deletion syndrome have a smaller than average hippocampus. “That’s why we studied the development of this structure in detail,” continues the UNIGE researcher, “so we could understand why some people affected by deletion syndrome eventually develop psychotic symptoms, while others don’t.”
18-year study investigating the development of the hippocampus
The Geneva team has been following 275 patients aged 6 to 35 years for 18 years: a control groups of 135 individuals – i.e. individuals without genetic problems – and 140 people with deletion syndrome, including 53 with moderate to severe psychotic symptoms. “They underwent an MRI every three years so that we could observe their brain development,” says Valentina Mancini, a researcher in UNIGE’s Department of Psychiatry. “This has helped us create a statistical model that measures and compares the development of the hippocampus in both groups of patients.” It was discovered that the hippocampus of the group affected by deletion syndrome, although smaller from the beginning, followed a growth curve identical to that of the control group. “This meant that we could hypothesise that the smaller size of the hippocampus originates in utero during its development in the womb.” The UNIGE scientists also observed the subfields of the hippocampus in detail, discovering that one of them – called CA3 – was not affected by the decrease in size. “This subfield plays a crucial role in the work of memorisation and seems stronger than the other sub-parts,” adds professor Eliez.
Adolescence: the period that counts the most
The researchers then compared the developmental curves of the hippocampus in people with deletion syndrome but no psychotic symptoms with those who developed psychotic symptoms. “There’s no doubt about our results: around the age of 17 or 18, people with schizophrenic symptoms experience a drastic atrophy in the size of their hippocampus, and especially in the CA3 area, despite CA3 had initially managed to develop normally, unlike the other subfields,” says Mancini. But why?
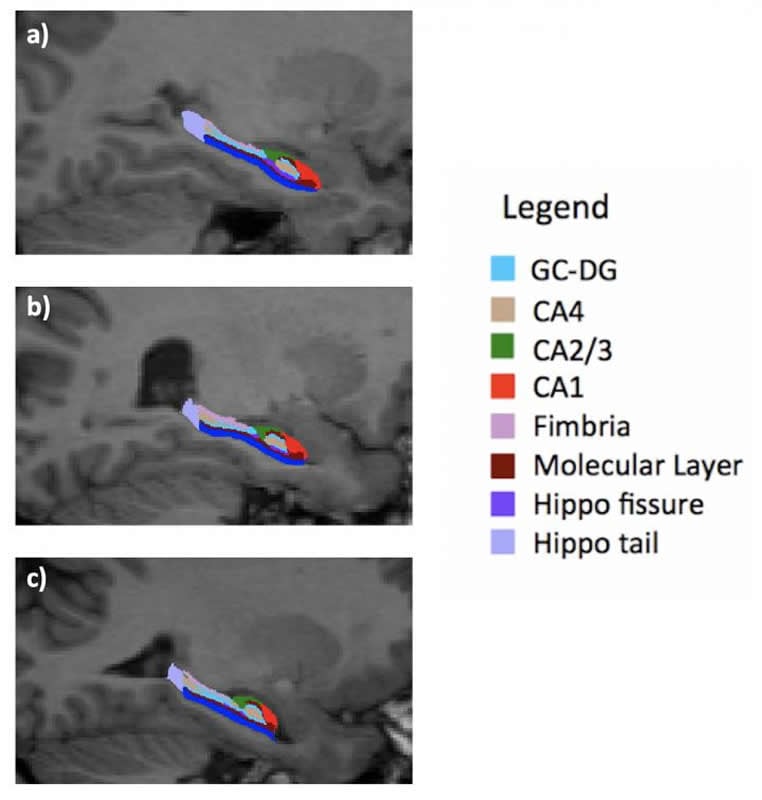
The researchers don’t have yet a precise answer that could explain the drastic drop in the development of this vital brain structure. But their hypotheses are geared towards environmental factors, such as stress or neuronal inflammation. “The hippocampus of individuals with deletion syndrome is smaller; this means it has to compensate for its size through hyperactivity. In the event of a huge stress factor, especially during the critical period of adolescence, this hyperactivity might lead to a significant rise in glutamate that ‘poisons’ the hippocampus and causes its atrophy,” explains Mancini. The psychotic symptoms may result from this hyper-compensation, which ends up destroying the hippocampus.
Act before the critical period
The study suggests the following hypothesis: the small size of the hippocampus in patients with 22q11 deletion syndrome is defined in the mother’s womb, probably due to poor vascularisation. However, a “second hit” later in development might determine the further hippocampal atrophy and the emergence of psychotic symptoms. As the critical period for schizophrenia is adolescence, the Genevan team is now working on the possibility of preventing the atrophy of the hippocampus in order to preserve its functions.
Source:
University of Geneva
Media Contacts:
Valentina Mancini – University of Geneva
Image Source:
The image is credited to UNIGE.
Original Research: Closed access
“Positive psychotic symptoms are associated with divergent developmental trajectories of hippocampal volume during late adolescence in patients with 22q11DS”.
Valentina Mancini, Corrado Sandini, Maria C. Padula, Daniela Zöller, Maude Schneider, Marie Schaer & Stephan Eliez.
Molecular Psychiatry. doi:10.1038/s41380-019-0443-z
Abstract
Positive psychotic symptoms are associated with divergent developmental trajectories of hippocampal volume during late adolescence in patients with 22q11DS
Low hippocampal volume is a consistent finding in schizophrenia and across the psychosis spectrum. However, there is a lack of studies investigating longitudinal hippocampal development and its relationship with psychotic symptoms. The 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (22q11DS) has proven to be a remarkable model for the prospective study of individuals at high risk of schizophrenia to unravel the pathophysiological processes predating the onset of psychosis. Repeated cerebral MRIs were acquired from 140 patients with 22q11DS (53 experiencing moderate-to-severe psychotic symptoms) and 135 healthy controls aged from 6 to 35 years and with up to 5 time points per participant. Hippocampal subfield analysis was conducted using FreeSurfer-v.6 and FIRST-FSL. Then, whole hippocampal and subfield volumes were compared across the groups. Relative to controls, patients with 22q11DS showed a remarkably lower volume of all subfields except for CA2/3. No divergent trajectories in hippocampal development were found. When comparing patients with 22q11DS exhibiting psychotic symptoms to those without psychosis, we detected a volume decrease during late adolescence, starting in CA1 and spreading to other subfields. Our findings suggested that hippocampal volume is consistently smaller in patients with 22q11DS. Moreover, we have demonstrated that patients with 22q11DS and psychotic symptoms undergo a further decrease in volume during adolescence, a vulnerable period for the emergence of psychosis. Interestingly, CA2/3, despite being affected in patients with psychotic symptoms, was the only area not reduced in patients with 22q11DS relative to controls, thus suggesting that its atrophy exclusively correlates with the presence of positive psychotic symptoms.







