Summary: Polydactyly, a condition where one is born with an extra finger, has significant benefits when it comes to motor skill and control. fMRI neuroimaging reveals those with extra fingers are able to move the digits independently of other fingers. The findings could help with the development of new prosthetics that extend motor abilities.
Source: University of Freiburg
Polydactyly is the extraordinary condition of someone being born with more than five fingers or toes. In a case study published in Nature Communications, researchers from the University of Freiburg, Imperial College London, the University Hospital of Lausanne, and EPFL have for the first time examined the motor skills and sensorimotor brain areas in people with polydactyly. The results show that an extra finger can significantly extend the manipulation abilities and skill. It enables people with six fingers to perform movements with one hand where people with only five fingers would need two hands. The augmented motor abilities observed in the polydactyly subjects are made possible by dedicated areas in the sensorimotor brain areas. These findings may serve as blueprint for the development of additional artificial limbs extending motor abilities.
The case study of the researchers from Freiburg, London and Lausanne investigates for the first time the movement abilities of people with six fingers per hand. In the case of the two examined subjects, an additional finger between thumb and forefinger is fully formed on each hand. “We wanted to know if the subjects have motor skills that go beyond people with five fingers and how the brain is able to control the additional degrees of freedom,” explains Prof. Dr. Carsten Mehring from the University of Freiburg and the Bernstein Center Freiburg.
To find out the extent of their abilities, the researchers had the subjects perform several behavioural experiments, and their brain activity was monitored using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). The results show that the subjects’ extra fingers are moved by own muscles. This allows the subjects to move their extra fingers as far as possible independently of all other fingers. “Our subjects can use their extra fingers independently, similar to an additional thumb, either alone or together with the other five fingers, which makes manipulation extraordinary versatile and skilful. For instance, in our experiments subjects can carry out a task with one hand, for which we normally need two hands,” summarises Professor Mehring. “Despite the extra finger increasing the number of degrees of freedom that the brain has to control, we found no disadvantages relative to five-finger people. In a nutshell, it is amazing that the brain has enough capacity to do it without sacrificing elsewhere. That’s exactly what our subjects do,” says Prof. Dr. Etienne Burdet of Imperial College London.
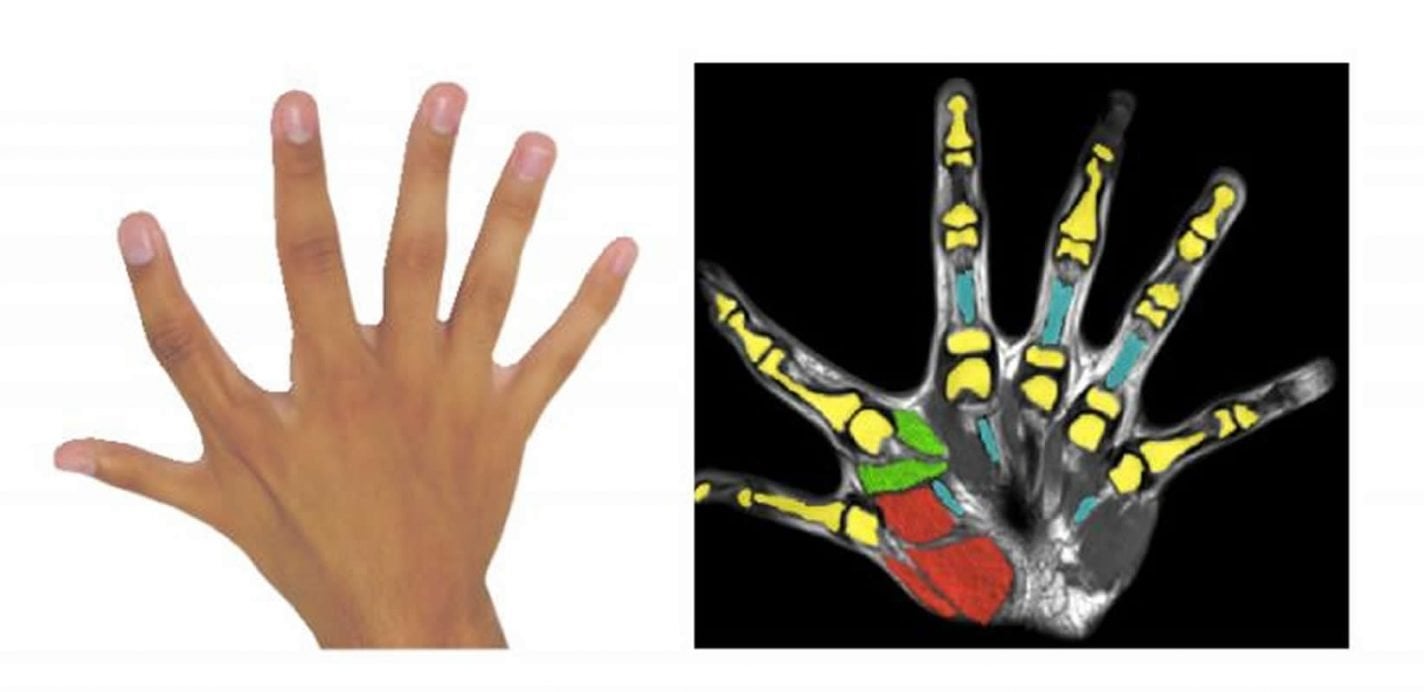
To understand how the brain of polydactyly subjects controls the additional fingers, the scientist used high-resolution functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). “We found dedicated neural resources that control the sixth finger, and the somatosensory and motor cortex are organized exactly to allow for the additional motor skills observed,” comment Prof. Dr. Andrea Serino and Dr. Michael Akselrod, who carried out the neuroimaging studies at EPFL and Lausanne University Hospital.
The study of these polydactyly hands could advance the development of additional artificial limbs to expand people’s motor skills. For example, an extra arm to help working alone in a narrow environment, or to enable a surgeon carrying out operations without an assistant. However, the scientists note, “The additional extremities have been trained in the subjects since birth. This does not necessarily mean that similar functionality can be achieved when artificial limbs are supplemented later in life. Yet, people with polydactyly provide a unique opportunity to analyse the neuronal control of extra limbs and the possibilities of sensorimotor skills.”
Source:
University of Freiburg
Media Contacts:
Carsten Mehring – University of Freiburg
Image Source:
The image is adapted from the University of Freiburg news release.
Original Research: Open access
“Augmented manipulation ability in humans with six fingered hands”. C. Mehring, M. Akselrod, L. Bashford, M. Mace, H. Choi, M. Blu?her, A-S. Buschhoff, T. Pistohl, R. Salomon, A. Cheah, O. Blanke, A. Serino and E. Burdet.
Nature Communications. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-10306-w9
Abstract
Augmented manipulation ability in humans with six fingered hands
Neurotechnology attempts to develop supernumerary limbs, but can the human brain deal with the complexity to control an extra limb and yield advantages from it? Here, we analyzed the neuromechanics and manipulation abilities of two polydactyly subjects who each possess six fingers on their hands. Anatomical MRI of the supernumerary finger (SF) revealed that it is actuated by extra muscles and nerves, and fMRI identified a distinct cortical representation of the SF. In both subjects, the SF was able to move independently from the other fingers. Polydactyly subjects were able to coordinate the SF with their other fingers for more complex movements than five fingered subjects, and so carry out with only one hand tasks normally requiring two hands. These results demonstrate that a body with significantly more degrees-of-freedom can be controlled by the human nervous system without causing motor deficits or impairments and can instead provide superior manipulation abilities.