Summary: UCLA researchers reveal the mechanism behind how estrogen can protect central nervous system damage in people with MS. The researchers report estrogen treatments have positive effects on immune cells in the brain and oligodendrocytes.
Source: UCLA.
A study by UCLA researchers reveals the cellular basis for how the hormone estrogen protects against damage to the central nervous system in people with multiple sclerosis (MS). The researchers found that estrogen treatment exerts positive effects on two types of cells during disease –immune cells in the brain and also cells called oligodendrocytes. Complementary actions on these two types provide protection from disease.
Multiple sclerosis is a chronic autoimmune, neurodegenerative disease marked by visual impairment, weakness and sensory loss, as well as cognitive decline. These symptoms emerge when inflammatory immune cells destroy the myelin sheath that surrounds nerve processes called axons. Loss of that protective insulation disrupts electrical communication between nerve cells.
The third trimester of pregnancy has been previously shown to reduce relapse rates by approximately 70 percent as compared to before pregnancy, and other studies have shown benefit over the long term due to multiple pregnancies. An estrogen unique to pregnancy that is made by the fetus and placenta has been proposed by Dr. Rhonda Voskuhl and colleagues to mediate this pregnancy protection in both the MS mouse model as well as in two successfully completed clinical trials of estriol treatment in MS patients.
How that happens has remained a critical question. Voskuhl, who led the latest study, reported mouse studies showing that estrogen protected the brain from damage by activating a protein called estrogen receptor beta (ERb). Her new research identifies which cells within the brain are mediating this protective effect.
METHOD
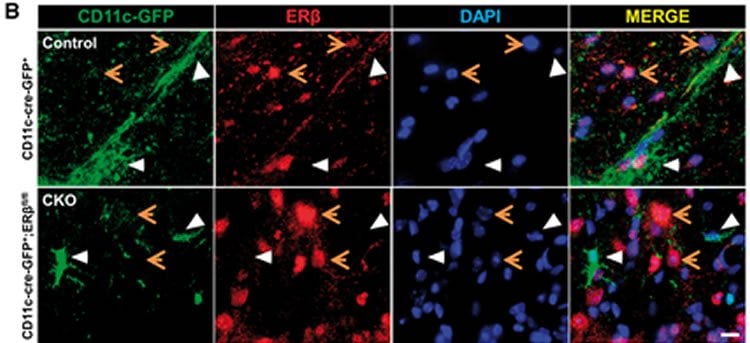
The researchers first genetically eliminated ERb in either immune cells of the brain or in oligodendrocytes, the cells that make the myelin sheath, as a way of making cells unresponsive to estrogen during the MS like disease in mice. They then treated mice without or with ERb in these cells to ask if disease protection was lost or not. Loss of protection during treatment meant that the treatment was acting on the cell that had the receptor removed. Results showed that the estrogen-like treatment was acting on both immune cells of the brain as well as on oligodendrocytes, together resulting in repair of myelin and less disability.
IMPACT
Drug developers often optimize therapies by targeting only one single cell type. By contrast, this study confirms that this estrogen-like compound can combat MS via complementary effects on two distinct cell types. Voskuhl and other UCLA researchers are in fact now developing a next-generation estrogen-like compound with robust biochemical effects on oligodendrocytes and immune cells in the brain.
Voskuhl, who is a professor of neurology and directs UCLA’s Multiple Sclerosis Program, is the study’s senior author. Others include first author Roy Y. Kim, a graduate student in Voskuhl’s lab; Darian Mangu, Alexandria S. Hoffman, Rojan Kovash, and Eunice Jung–all UCLA undergraduates; and Noriko Itoh, all of the Department of Neurology at UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine.
Funding: Funding was provided by the National Institutes of Health and by grants from the Conrad Hilton Foundation, the California Community Foundation, and the Tom Sherak MS Hope Foundation.
Source: Tami Dennis – UCLA
Publisher: Organized by NeuroscienceNews.com.
Image Source: NeuroscienceNews.com image is Kim et al./Brain.
Original Research: Full open access research for “Oestrogen receptor β ligand acts on CD11c + cells to mediate protection in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis” by Roy Y Kim, Darian Mangu, Alexandria S Hoffman, Rojan Kovash, Eunice Jung, Noriko Itoh, and Rhonda Voskuhl in Brain. Published online December 8 2017 doi:10.1093/brain/awx315
[cbtabs][cbtab title=”MLA”]UCLA “Songbirds May Hold the Secret toHow Babies Learn to Speak.” NeuroscienceNews. NeuroscienceNews, 29 December 2017.
<https://neurosciencenews.com/estrogen-multiple-sclerosis-8243/>.[/cbtab][cbtab title=”APA”]UCLA (2017, December 29). Songbirds May Hold the Secret toHow Babies Learn to Speak. NeuroscienceNews. Retrieved December 29, 2017 from https://neurosciencenews.com/estrogen-multiple-sclerosis-8243/[/cbtab][cbtab title=”Chicago”]UCLA “Songbirds May Hold the Secret toHow Babies Learn to Speak.” https://neurosciencenews.com/estrogen-multiple-sclerosis-8243/ (accessed December 29, 2017).[/cbtab][/cbtabs]
Abstract
Oestrogen receptor β ligand acts on CD11c + cells to mediate protection in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Oestrogen treatments are neuroprotective in a variety of neurodegenerative disease models. Selective oestrogen receptor modifiers are needed to optimize beneficial effects while minimizing adverse effects to achieve neuroprotection in chronic diseases. Oestrogen receptor beta (ERβ) ligands are potential candidates. In the multiple sclerosis model chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis, ERβ-ligand treatment is neuroprotective, but mechanisms underlying this neuroprotection remain unclear. Specifically, whether there are direct effects of ERβ-ligand on CD11c+ microglia, myeloid dendritic cells or macrophages in vivo during disease is unknown. Here, we generated mice with ERβ deleted from CD11c+ cells to show direct effects of ERβ-ligand treatment in vivo on these cells to mediate neuroprotection during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Further, we use bone marrow chimeras to show that ERβ in peripherally derived myeloid cells, not resident microglia, are the CD11c+ cells mediating this protection. CD11c+ dendritic cell and macrophages isolated from the central nervous system of wild-type experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice treated with ERβ-ligand expressed less iNOS and T-bet, but more IL-10, and this treatment effect was lost in mice with specific deletion of ERβ in CD11c+ cells. Also, we extend previous reports of ERβ-ligand’s ability to enhance remyelination through a direct effect on oligodendrocytes by showing that the immunomodulatory effect of ERβ-ligand acting on CD11c+ cells is necessary to permit the maturation of oligodendrocytes. Together these results demonstrate that targeting ERβ signalling pathways in CD11c+ myeloid cells is a novel strategy for regulation of the innate immune system in neurodegenerative diseases. To our knowledge, this is the first report showing how direct effects of a candidate neuroprotective treatment on two distinct cell lineages (bone marrow derived myeloid cells and oligodendrocytes) can have complementary neuroprotective effects in vivo.
“Oestrogen receptor β ligand acts on CD11c + cells to mediate protection in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis” by Roy Y Kim, Darian Mangu, Alexandria S Hoffman, Rojan Kovash, Eunice Jung, Noriko Itoh, and Rhonda Voskuhl in Brain. Published online December 8 2017 doi:10.1093/brain/awx315







